Heritable Disorder |
Chromosomal Assignment |
Heritability |
Cause of Iron Loading |
References |
HFE Hemochromatosis |
6p21.3 |
Autosomal recessive |
Mutations of HFE |
36 |
Juvenile Hemochromatosis |
|
HJV Hemochromatosis |
1q21 |
Autosomal recessive |
Mutations of hemojuvelin |
1, 12, 98, 99, 100, 101 |
|
HAMP Hemochromatosis |
19q13 |
Autosomal recessive |
Hepcidin antimicrobial peptide gene mutations |
13, 72, 73, 74 |
TFR2 Hemochromatosis |
7q22 |
Autosomal recessive |
Inactivation of transferrin receptor 2 |
20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26, 102 |
SLC40A1 Hemochromatosis |
2q32 |
Autosomal dominant |
Ferroportin gene mutations |
27, 101, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107 |
H-Ferritin Hemochromatosis |
11q 12-q13 |
Autosomal dominant |
H-ferritin gene mutations |
108 |
Porphyria cutanea tarda |
1p34 |
Autosomal dominant or sporadic |
Heterogeneous |
109, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 128, 129 |
African iron overload |
Unknown |
Autosomal dominant |
Unknown |
130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137 |
Neonatal iron overload |
Unknown |
Heterogeneous |
In utero iron transfer |
138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144 |
Atransferrinemia |
3q21 |
Autosomal recessive |
Transferrin gene mutations and red cell transfusions |
145, 146 |
Aceruloplasminemia |
3q23-q24 |
Autosomal recessive |
Ceruloplasmin gene mutations |
147, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 154 |
Hereditary hyperferritinemia and cataract syndrome |
19q13.1-q13.3.3 |
Autosomal dominant |
L-Ferritin gene mutations |
155, 156, 157, 158, 159, 160, 161, 162, 163, 164, 165 |
Friedreich ataxia |
9p23-p11,9q13 |
Autosomal recessive |
Frataxin gene mutations |
166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, 173 |
Panthothenase kinase-associated neurodegeneration |
20p13-p12.3 |
Autosomal recessive |
Pantothenase kinase gene mutations |
174, 175 |
β-Thalassemia major |
11p15.5 |
Autosomal recessive |
β-Globin gene mutations, chronic hemolysis, red cell transfusions |
— |
Other chronic hemolytic anemias |
Hereditary X-linked sideroblastic anemia |
Xp11.21 |
X-Linked |
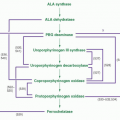
δ-Aminolevulinic acid synthase gene mutations |
176, 177, 178 |
X-Linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia |
Xq13.1-q13.3 |
X-Linked |
ABCB7 mutationsa |
179, 180, 181, 182 |
MLASA syndromeb |
12q24.33 |
Autosomal recessive |
Pseudouridine synthase-1 mutations |
183, 184 |
GLRX5 sideroblastic anemia |
14q32.13 |
Autosomal recessive |
Glutaredoxin 5 mutations |
185, 186 |
DMT1 iron overloadc |
12q13 |
Autosomal recessive |
SLC11A2 mutationsd |
187, 188 |
Pyruvate kinase deficiency |
1q21 |
Autosomal recessive |
Pyruvate kinase gene mutations |
189, 190, 191 |
G6PD deficiencye |
Xq28 |
X-Linked |
G6PD gene mutations |
192, 193 |
Congenital dyserythropoietic anemias |
Type I 15q15.1-q15.3 |
Autosomal recessive |
Ineffective erythropoiesis |
194, 195 |
|
Type II 20q11.2 |
Autosomal recessive |
Ineffective erythropoiesis |
196, 197, 198 |
|
Type III 15q21 |
Autosomal dominant |
Ineffective erythropoiesis |
199, 200 |
Acquired Disorder |
Cause of Iron Loading |
Transfusions |
Red cell iron infusion |
Medicinal iron |
Excessive iron ingestion |
Iron injections |
Parenteral injection |
Myelodysplasia with ring sid-eroblasts |
Excessive iron absorption; transfusion |
Portacaval shunt |
Excessive iron absorption |
Hemodialysis |
Iron infusion |
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
Excessive iron absorption |
a ABCB7, ATP-binding cassette, subfamily B, member 7.
b MLASA, myopathy with lactic acidosis and sideroblastic anemia.
c DMT1, divalent metal transporter-1.
d SLC11A2, solute carrier family 11, member 2.
e G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. |
|