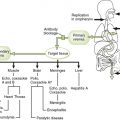
Chapter 19 I Factors Affecting Viral Virulence 1. Species that can be infected by a virus 2. Cells must express surface molecules recognized by a viral attachment protein or other structure. 3. Cells must provide compatible biochemical machinery to replicate virus. B Routes of viral entry into host cells • Initial viral replication generally occurs at the site of entry, but some viruses spread to target tissues where major pathologic effects occur. C Tissue specificity (tropism) • Consequences of viral infection depend on target organs involved and extent of the damage to these tissues. 1. Local infection without spread (e.g., rhinovirus, other common cold viruses) • Viruses that manifest symptoms at the initial site of entry cause diseases with short incubation periods and early prodromes. 2. Viremic spread from viral point of entry (e.g., measles, mumps, and chickenpox viruses) results in diseases with longer incubation periods. • Example: varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is acquired by respiratory route and initiates infection in the lungs. Infection spreads through blood to liver and other organs, initiates a secondary viremia, and then reach the skin to cause classic symptoms of chickenpox. Incubation period is 10 to 30 days. • Attenuated virus strain that cannot reach or infect its disease-related target organ may lose its virulence (e.g., attenuated live polio vaccine, cannot infect the brain to cause major disease). • Virus-specific antibodies can block viremic spread to target tissue. D Support of viral replication by host cells 1. Permissive cells possess all the biochemical machinery needed by a virus to enter the cell and replicate, yielding a productive infection. 2. Nonpermissive cells do not support replication, but they may be transformed by DNA tumor viruses (e.g., Epstein-Barr virus and HPV). 3. Semipermissive cells allow some viral functions to occur or support low levels of replication. 1. Major viral mechanisms for disrupting the structure and functioning of infected cells are summarized in Table 19-1. TABLE 19-1 HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HSV, herpes simplex virus. 2. Appearance of characteristic inclusion bodies in infected cells facilitates laboratory diagnosis of infection by some viruses (e.g., rabies, HSV, and cytomegalovirus).
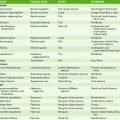
Viral Pathogenesis
Mechanism
Representative Viruses
Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis
Polioviruses, HSV, togaviruses
Inhibition of cellular DNA synthesis; degradation of DNA
Herpesviruses
Alteration of cell membranes
Glycoprotein insertion
All enveloped viruses
Syncytia (giant cell) formation
HSV, varicella-zoster virus, paramyxoviruses, HIV
Permeability changes
Togaviruses, herpesviruses
Disruption of cytoskeleton
Naked capsid viruses, HSV
Formation of inclusion bodies
Negri bodies (cytoplasmic)
Rabies
Basophilic (owl’s eye) nuclear bodies
Cytomegalovirus
Cowdry type A nuclear bodies
HSV
Nuclear basophilic bodies
Adenoviruses
Acidophilic perinuclear bodies
Reoviruses
Toxicity of virion components
Adenovirus fibers
Immunosuppression
HIV, cytomegalovirus, measles virus, influenza virus