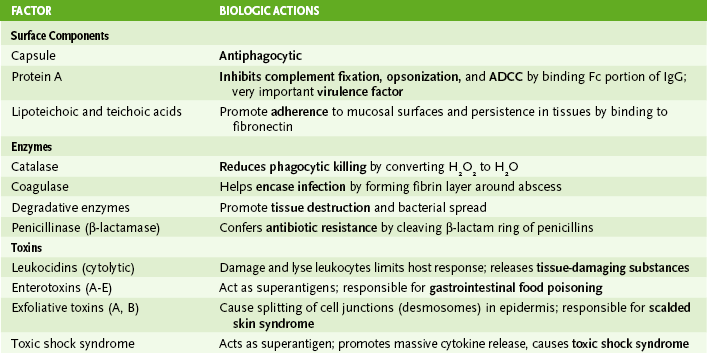
Chapter 9 • Three staphylococcal species commonly cause human disease: S. aureus (most virulent), S. epidermidis, and S. saprophyticus. A Shared staphylococcal properties 1. Gram-positive cocci in grape-like clusters 2. Catalase positive; growth in 7.5% salt 3. Ubiquitous distribution; part of normal flora; responsible for many nosocomial infections B Coagulase-positive staphylococci (S. aureus) • S. aureus is normal flora of skin and the anterior nares. 2. Diseases caused by S. aureus (Box 9-1) • Community-acquired methicillin resistant S. aureus (CA-MRSA) carries resistance plasmids that also have the Panton valentine leukocidin gene and may be more virulent. • Inflammatory diseases mediated by pyogenic and necrotic activities of S. aureus • Person-to-person contact and via fomites • Endogenous spread via blood or aspiration of nasal secretions • Ingestion of preformed enterotoxins in food • Most staphylococci produce penicillinase (a β-lactamase) and are commonly treated with a penicillinase-resistant β-lactam penicillin derivative, such as nafcillin, oxacillin, or methicillin. • MRSA strains (hospital acquired) are treated with vancomycin, linezolid, daptomycin, tigecycline, trimethoprim sulfa, or clindamycin. • CA-MRSAs are becoming more common. • Methicillin- and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus was acquired from an Enterococcus plasmid. C Coagulase-negative staphylococci (S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus) 1. These bacteria are normally benign colonizers of the skin. 2. They are less virulent than S. aureus, although their virulence factors are similar (except for lack of coagulase). 3. S. epidermidis can adhere to artificial heart valves, vascular catheters, shunts, and prosthetic joints, colonizing the implant area and causing tissue destruction mediated by degradative enzymes. 4. S. saprophyticus is a frequent cause of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in sexually active young women. • Most common streptococcal pathogens in humans are S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, viridans group, and S. pneumoniae. A Shared streptococcal properties 1. Gram-positive spherical or football-shaped cocci in pairs or chains 3. Species-dependent hemolysis in blood agar (Table 9-2) TABLE 9-2
Gram-Positive Cocci
Hemolytic reaction
Organism
Differentiating property
α (Incomplete) hemolysis
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access