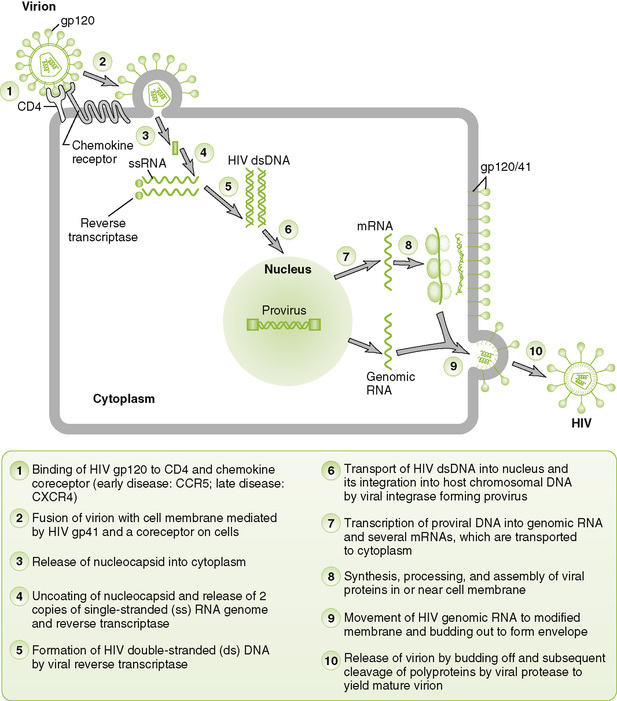
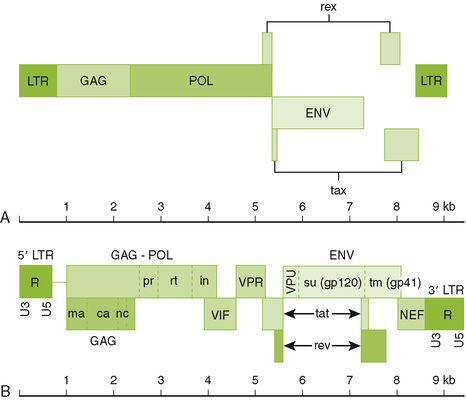
Chapter 26 I Retroviridae: General Features • Midsized viruses with an enveloped capsid containing two copies of a single-stranded (+) RNA genome, transfer RNA (tRNA), reverse transcriptase, integrase, and protease. • Two human pathogens—human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and human T lymphotropic virus (HTLV)—are retroviruses. 1. All retroviral genomes contain three genes—gag, pol, and env—and are flanked by long-terminal repeats (Table 26-1). TABLE 26-1 Retrovirus Genes and Their Function From Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Pfaller MA: Medical Microbiology, 6th ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2009, Table 64-2. 2. Complex retroviruses, such as HIV, have several other genes encoding auxiliary and regulatory proteins (e.g., nef, tat, and rev) B Key HIV proteins (Fig. 26-1) 26-1 Genome structure of human retroviruses: (A) HTLV-1 and (B) HIV. The basic retrovirus genome consists of the long terminal repeat (ltr) group–specific antigen (capsid proteins)(gag)-enzymes(polymerase, integrase, protease)(env) and the glycoproteins (env). Complex retroviruses, such as HIV have additional proteins that enhance their virulence. These are described in Table 26-1. (Redrawn from Belshe RB: Textbook of Human Virology, 2nd ed. St Louis, Mosby, 1991. In Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Pfaller MA: Medical Microbiology, 6th ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2009, Fig. 64-4.) 1. Major envelope glycoprotein consists of two associated proteins: an attachment protein (HIV gp120) and transmembrane fusion protein (HIV gp41) both cleaved from gp160 precursor. 2. Three enzymes are carried within the nucleocapsid: reverse transcriptase, integrase, and protease. 3. Matrix protein (HIV p17) forms a layer underlying the envelope. 4. Nucleocapsid protein (HIV p24) forms the outer layer of the virion core, and detection in blood indicates infection. • Binding of viral gp120/gp41 to CD4 and a chemokine coreceptor is required for HIV infection of cells. • Reverse transcriptase carried in the virion synthesizes a complementary DNA (cDNA) from viral genome, forming an RNA-DNA hybrid. The same enzyme then degrades the RNA strand and synthesizes a complementary DNA strand, forming double-stranded viral DNA. • Viral integrase catalyzes integration of viral DNA into host nuclear DNA, forming provirus. 3. Viral messenger RNA (mRNA) and genome replication • Host DNA-dependent RNA polymerase transcribes a full-length (+) RNA copy of the integrated genome and several shorter mRNA copies for individual proteins and polyproteins. • After synthesis of viral proteins, nucleocapsids containing two copies of genome associate with glycoprotein modified plasma membrane and bud off. • After budding, protease cleaves gag-pol polyprotein to produce mature (cone-shaped) nucleocapsid and functional integrase and reverse transcriptase enzymes.
Retroviruses
Gene
Virus
Function
gag
All
Group-specific antigen: core and capsid proteins
int
All
Integrase
pol
All
Polymerase: reverse transcriptase, protease, integrase
pro
All
Protease
env
All
Envelope: glycoproteins
tax
HTLV
Transactivation of viral and cellular genes
tat
HIV-1
Transactivation of viral and cellular genes
rex
HTLV
Regulation of RNA splicing and promotion of export to cytoplasm
rev
HIV-1
Regulation of RNA splicing and promotion of export to cytoplasm
nef
HIV-1
Alteration of cell activation signals; progression to AIDS (essential)
vif
HIV-1
Virus infectivity, promotion of assembly, blocks a cellular antiviral protein
vpu
HIV-1
Facilitates virion assembly and release, decrease of cell surface CD4
vpr (vpx*)
HIV-1
Transport of complementary DNA to nucleus, arresting of cell growth
LTR
All
Promoter, enhancer elements
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Retroviruses