Because of its rarity and high curability, progress in advancing therapeutics in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) has been difficult. Over recent years, several new mutations that cooperate with MYC have been identified, and this has paved the way for testing novel agents in the disease. One of the challenges of most standard approaches typically used is severe treatment-related toxicity that often leads to discontinuation of therapy. To that point, there has been recent success developing intermediate intensity approaches that are well tolerated in all patient groups and maintain high cure rates in a multicenter setting.
Key points
- •
While Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is highly curable with short duration, intensive therapies in children these are poorly tolerated in middle-aged and older adults and immunosuppressed patients.
- •
Some novel less intensive approaches that maintain high cure rates while significantly decreasing treatment-related toxicity compared with traditional strategies are promising.
- •
There have been great strides in the molecular elucidation of BL that have provided several new targets for novel drug development in the disease.
Introduction
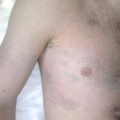
Burkitt lymphoma (BL), first described by Denis Burkitt in African children over 50 years ago, is a rare and highly aggressive B-cell lymphoma. In Burkitt’s initial paper, he reported unusual jaw tumors associated with a specific distribution pattern of anatomic sites in a group of 38 Ugandan children. This endemic variant, which was the first to be described, occurs in equatorial Africa and some other specific regions of the world, peaks in incidence in 4- to 7-year–old children, and has a predilection for males ( Table 1 ). Two other epidemiologic variants are recognized. Sporadic BL typically affects children and young adults, presents worldwide, and is the most common variant in the Western world. Immunodeficiency-associated BL occurs in association with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and is approximately 1000 times more common in HIV-infected individuals compared with HIV-negative counterparts. Over recent years, the understanding of the biology of BL has advanced significantly with the identification of novel mutations that cooperate with MYC , and there has also been therapeutic progress with the development of less toxic strategies that maintain the high cure rates of historical high-dose, intensive strategies.