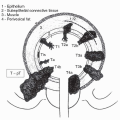
risk of TGCT to the contralateral testis (pooled RR = 1.74, 95% CI 1.01, 2.98) (11). The strong risk for ipsilateral disease supports the concept that the physical location of the UDT mediates risk of disease and that UDT is an intermediate on the causal pathway for TGCT; however, the notion of a common factor mediating risk in both testes, possibly from prenatal exposures, is supported—perhaps only weakly—by the increased risk of contralateral disease.
TABLE 29.1 SUMMARY OF FAMILIAL RISKS OF TGCT AMONG BROTHERS, FATHERS, AND SONS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
and perinatal clinical risk factors that were possibly linked to maternal estrogen levels (e.g., nausea, preterm delivery, birth weight) demonstrated that extreme nausea during the first trimester was associated with an increased TGCT risk (OR = 2.0, 95% CI 1.0, 3.9) (44). A recent nested case-referent study of Finnish, Swedish, and Icelandic mothers evaluated early pregnancy endogeneous steroid levels (dehydroepiandrostene sulfate [DHEA], androstenedione, testosterone, estradiol, estrone, and sex hormone binding globulin) and TGCT risk. Offspring of mothers with a high DHEA level had a significantly decreased risk of TGCT. However, offspring of mothers with high androstenedione and estradiol levels did demonstrate an increased risk of TGCT (45). In sum, studies are inconclusive concerning the role of maternal endogeneous estrogen in TGCT etiology. Additional study of this question is needed.
Norway did not demonstrate an association between physical activity and TGCT risk (82). A more recent Canadian study suggested that the extent of moderate or strenuous physical activity in adolescence increased the risk of TGCT (83).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree