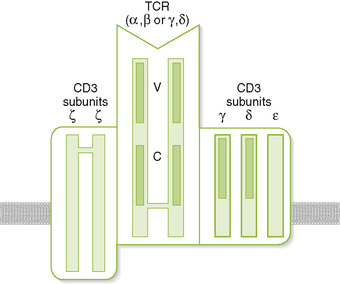
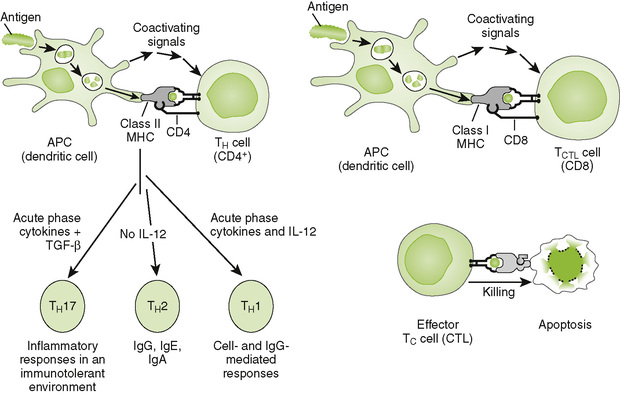
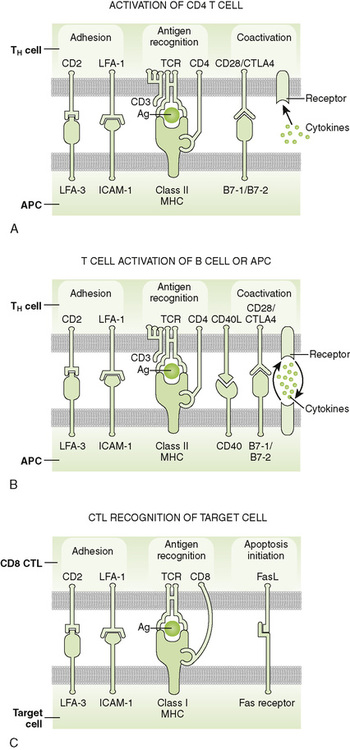
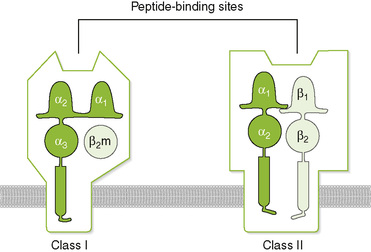
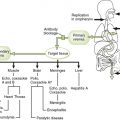
Chapter 2 A T cell receptor (TCR) complex • Comprises an antigen-recognizing heterodimer associated with a multimeric activation unit (CD3) (Box 2-1; Fig. 2-1) 1. All TCRs expressed by a single T cell are specific for the same antigen. 2. TCRs only recognize antigenic peptides bound to class I or II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. 1. CD4 and CD8 coreceptors define two main functional subtypes of T cells. • CD4, present on helper T (TH) cells, binds to class II MHC molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). • CD8, present on cytolytic T (TC) and suppressor T (TS) cells, binds to class I MHC molecules on the surface of all nucleated cells. 2. Adhesion molecules (e.g., CD2, LFA-1) help bind T cells to APCs and target cells or direct T cells to sites of inflammation and lymph nodes. 3. Coreceptor activating molecules (e.g., CD28 and CTLA-4) transduce signals important in regulating functional responses of T cells. II Development and Activation of T Cells A Antigen-independent maturation 1. Begins in bone marrow and is completed in the thymus, generates immunocompetent, MHC-restricted, naive T cells 2. Diversity of antigenic specificity of TCRs results from rearrangement of V, D, and J gene segments during maturation (similar to rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes). • Each T cell possesses only one functional TCR gene and thus recognizes a single antigen (or a small number of related cross-reacting antigens). 3. Thymic selection eliminates developing thymocytes that react with self-antigens (including self MHC molecules). B Antigen-dependent activation 1. Leads to proliferation and differentiation of naive T cells (clonal expansion) into effector cells and memory T cells (Fig. 2-2) 2. Effective stimulation requires primary and coactivating signals (fail-safe mechanism) that trigger intracellular signal transduction cascades, ultimately resulting in new gene expression (Fig. 2-3). • Signal 1 (primary): specificity—dependent on antigen and MHC a. Antigen-specific binding of TCR to antigenic peptide:MHC molecule on APC or target cell b. Binding of CD4 or CD8 coreceptor to MHC molecule on APC or target cell • Signal 2 (coactivating): permission—independent of antigen and MHC 3. Signal 3 (determines nature of response): direction—cytokine from dendritic cell (DC) or APC • Determines the cytokine response and function of the T cell (TH1, TH2, TH17, regulatory T [Treg] cell) 4. Adhesion molecules: selectin (E-, L-, P-), ICAM (-1, -2, -3, LFA-3 CD2), and integrin (VLA, LFA-1, CR3) • Strengthens cell-cell interactions; binds cells to epithelium in immune organs or facilitates migration and homing of cells. C Antigen processing and presentation by class I and II MHC molecules (Fig. 2-4)
Role of T Cells in Immune Responses