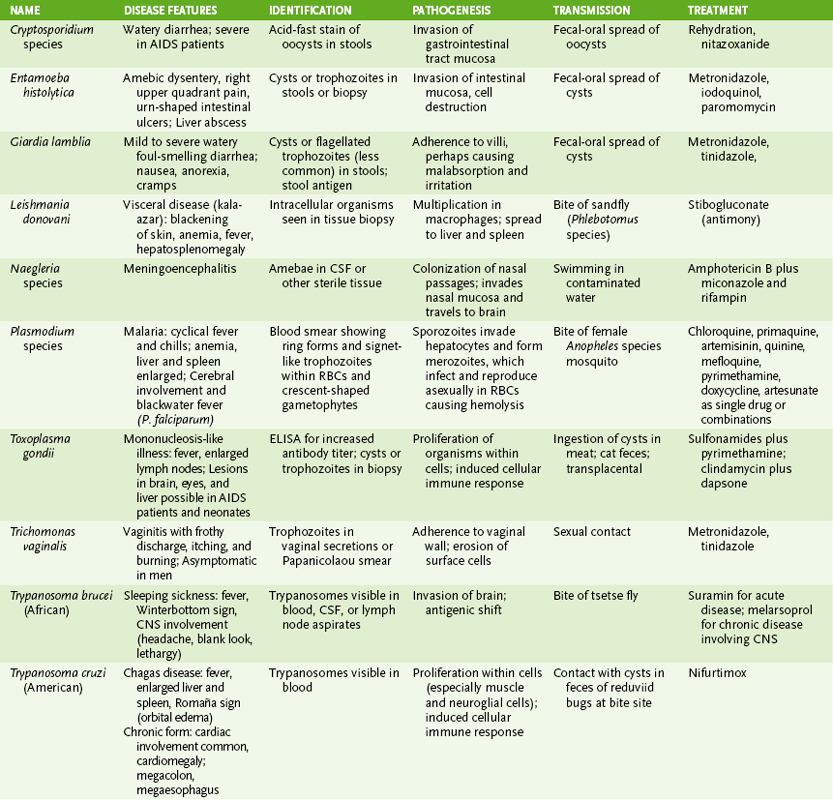
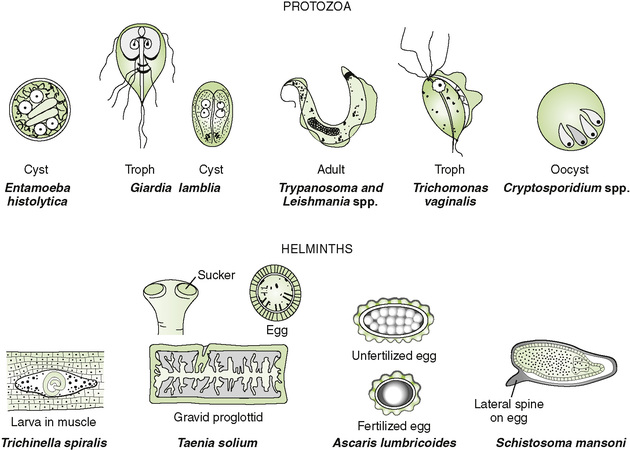
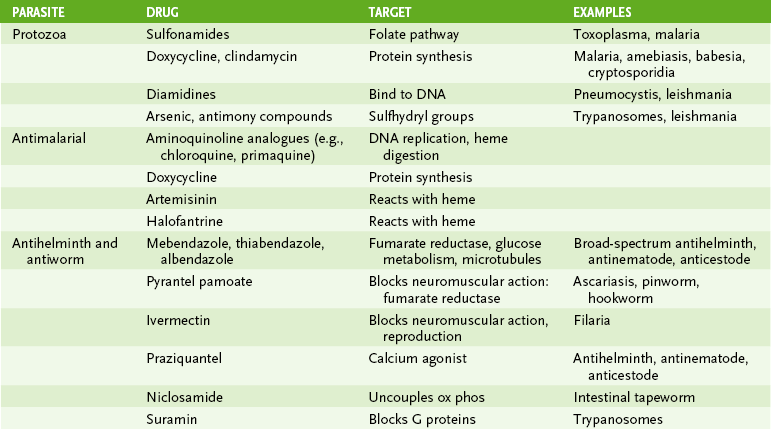
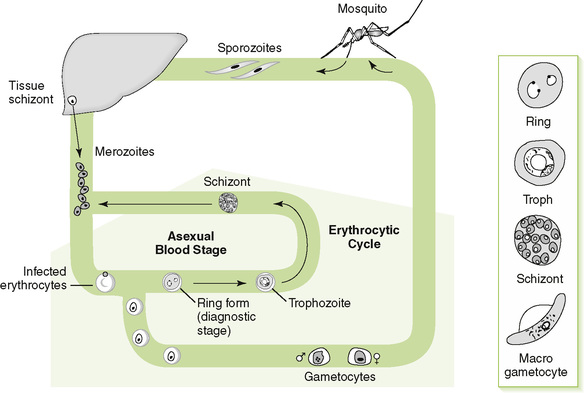
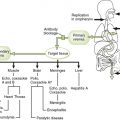
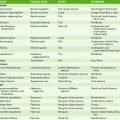
Chapter 29 I Introduction to Parasitology 1. Two groups of parasitic organisms cause human disease: the single-celled protozoa and the multicellular helminths (worms). 2. Like fungi, parasites are eukaryotes, but they lack the plant-like cell wall present in fungi. 1. Entry of organisms occurs primarily by ingestion or direct penetration of the skin (sometimes by bite of insect vector). 2. Replication of parasites takes place in specific cell types or organs. • A characteristic route of entry leads to infection. • Site and route of entry and release are determined by the life cycle of the organism. • Life cycle may differ in different hosts, for example, human versus snail or mosquito. 3. Cell and tissue damage result from four general mechanisms. • Toxic substances produced by parasites • Mechanical damage due to the size and movement of parasites • Cell-mediated immune response elicited in the host 1. Disease determined by affected tissue and nature of disruption 2. Periodicity of symptoms due to life cycle of parasite 1. Definitive diagnosis of most parasitic diseases depends on microscopic identification of parasitic forms (e.g., larvae, eggs, and adults) in clinical specimens (Fig. 29-1). 2. Serologic testing is useful in diagnosis of Entamoeba and Strongyloides species infection. 1. Effective sanitation for organisms spread by fecal-oral route 2. Thorough cooking for organisms transmitted in meat or fish 3. Elimination of vectors and protection from their bites for organisms transmitted by insects II Protozoan Parasites (Table 29-2) TABLE 29-2 A Intestinal and urogenital protozoa • Self-limited watery diarrhea and flu-like symptoms in normal individuals • Severe, prolonged diarrhea in AIDS patients • Watery, foul-smelling diarrhea with malabsorption, flatulence, and cramps • Often acquired from drinking contaminated creek water (campers, hikers) • Common in immunodeficiency conditions with absent immunoglobulin A (IgA) • Endemic to tropical and subtropical regions • Transmitted by sandfly (Phlebotomus species) • Infection of macrophages leading to cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral disease a. Characterized by episodic paroxysms of high fever and severe chills followed by sweats b. Life cycle of plasmodia within humans includes an exoerythrocytic phase within hepatocytes and a series of erythrocytic cycles within red blood cells (RBCs) (Fig. 29-2).
Parasites