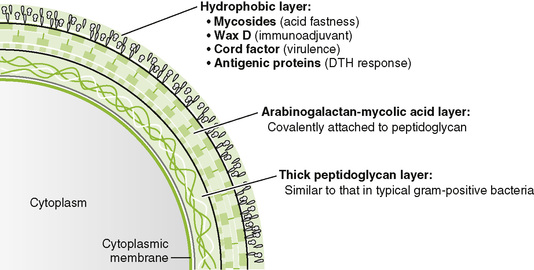
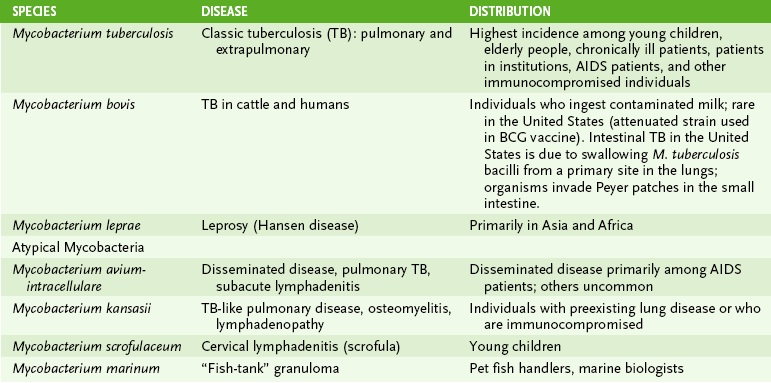
Chapter 16 I Shared Mycobacterial Properties • Mycobacteria are slow-growing, aerobic, facultative intracellular rods with a lipid-rich cell wall that makes them acid fast. B Mycobacterial diseases (Table 16-1) 1. Microscopic detection of acid-fast rods in sputum or biopsy specimen 2. Isolation by culturing on egg-based Löwenstein-Jensen medium or on special broth media 3. Serologic tests and DNA probes • Intradermal injection of purified protein derivative (PPD) from cell wall induces a delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) response in those who have been previously exposed to M. tuberculosis or vaccinated. • Positive reaction is indicated by an area of induration (>15 mm for healthy adults) 48 to 72 hours after PPD injection. a. Tuberculin skin test is a classic example of a type IV hypersensitivity reaction (DTH). b. Skin test reactivity usually develops 3 to 4 weeks after infection. c. False-negative results may occur in those with very recent infection, anergic individuals (especially human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]-infected patients), and older people in whom the DTH response has waned. d. False-positive results occur in individuals vaccinated with bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG), the antituberculosis vaccine used in Europe and other countries. 1. Humans are the only natural reservoir of M. tuberculosis 2. Spread of tubercle bacilli through respiratory droplets is promoted by crowded conditions and coughing. 3. Young children, elderly people, and immunocompromised individuals have the highest risk for developing active tuberculosis (TB). • Infection with M. tuberculosis may involve any organ, but the lungs are the initial and most common sites affected. 1. Inhaled mycobacteria are engulfed by alveolar macrophages and replicate freely in these cells. • Cell wall components prevent bacterial destruction in macrophage lysosomes. • Intracellular growth protects mycobacteria from antibody-mediated elimination. • Other macrophages are attracted to the site and destroy the infected cells, releasing mycobacteria that can spread through the bloodstream. 2. Sequence of formation of a tuberculous granuloma (type IV hypersensitivity reaction)
Mycobacteria