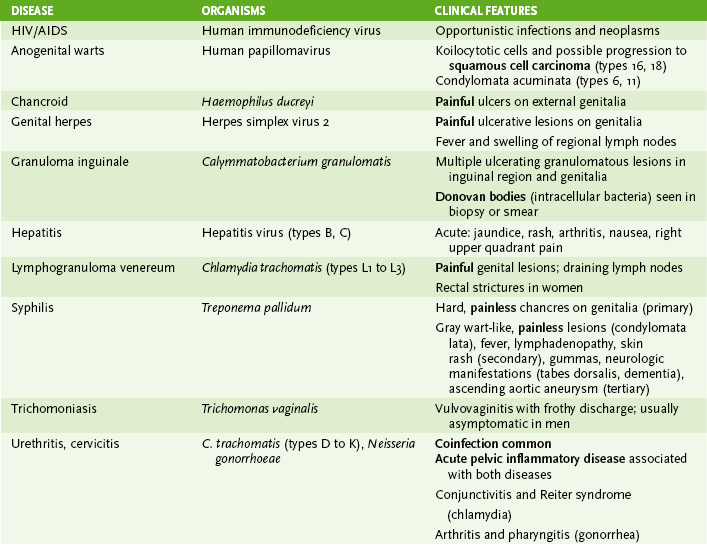
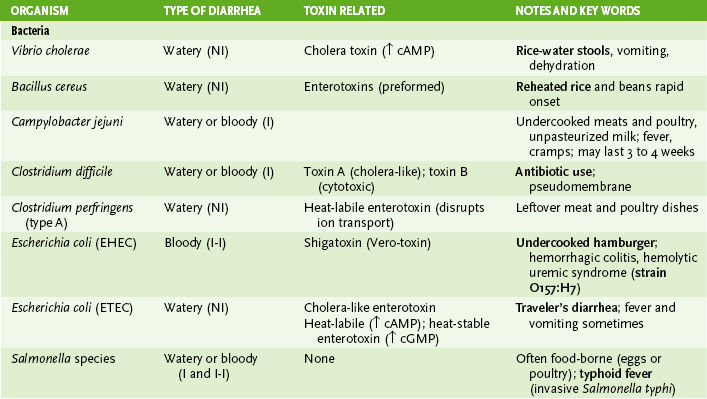
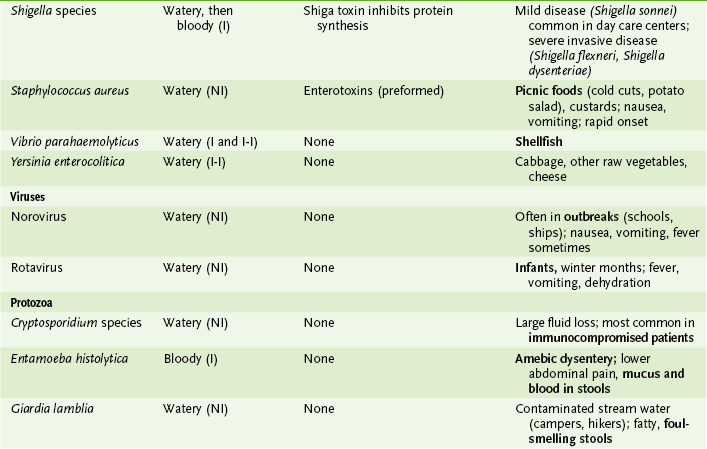
Chapter 30 I Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) 1. Usually spread during asymptomatic period when partners are unaware of problem 2. Chlamydia trachomatis and human papillomavirus (HPV) infections are the most common STDs worldwide. B Table 30-1 summarizes diseases spread primarily by sexual contact. II Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) (Table 30-2) TABLE 30-2 Bacteria Causing Urinary Tract Infections • Most common causes of nosocomial UTIs are Escherichia coli, Enterococcus species, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 1. Most commonly caused by E. coli. 3. Dysuria, frequency, urgency, suprapubic pain 4. Not accompanied by bacteremia B Pyelonephritis (upper UTI): flank pain, fever, chills, dysuria C Genitourinary tract pathogens that are not sexually transmitted III Infectious Diarrheas (Tables 30-3 and 30-4) TABLE 30-4 Food Sources of Bacterial Infections
Infectious Diseases
Clinical Correlations
Organism
Distinguishing Features
Notes
Escherichia coli
Gram negative, no capsule, red-black colonies on EMB agar
Most common cause of UTIs (50% to 80%)
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Gram positive, coagulase negative, resistant to novobiocin
Second most common cause of UTIs in young women (10% to 30%)
Proteus mirabilis
Gram negative, urease positive, swarming growth on agar
Associated with struvite urinary stones
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Gram negative, nonmotile, prominent capsule, large mucoid colonies
Usually in catheterized patients
Enterobacter species
Gram negative, motile, capsule, moist colonies, often drug resistant
Usually in immunocompromised patients
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Gram negative, oxidase positive, fruity odor, blue-green pigment
Usually in patients with kidney stones, chronic prostatitis, or a catheter
Enterococcus faecalis
Gram positive, variable hemolysis, salt tolerant (6.5% NaCl)
Usually in immunocompromised or catheterized patients
Food
Bacteria
Poultry
Salmonella enteritidis, Campylobacter species
Raw eggs
Salmonella enteritidis
Dairy products
Listeria monocytogenes, Brucella species, Mycobacterium bovis
Shellfish
Vibrio species
Reheated rice
Bacillus cereus
Undercooked beef
Escherichia coli O157:H7, B. cereus, Brucella species, C. perfringens
Picnic foods (mayonnaise, custard, salted meats)
S. aureus toxin mediated
Infectious Diseases: Clinical Correlations