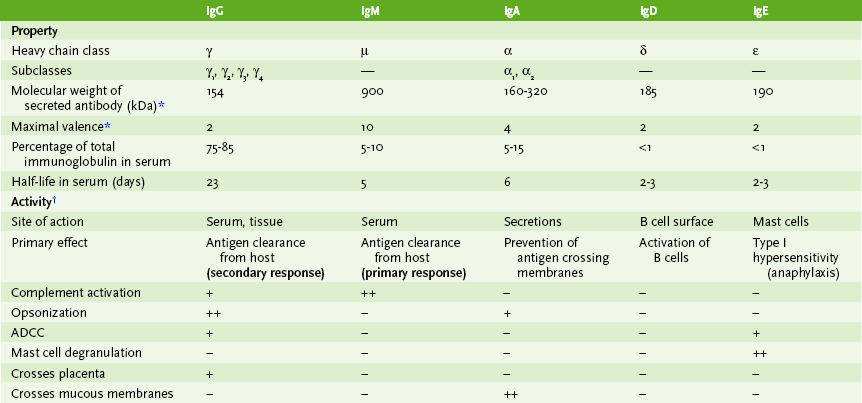
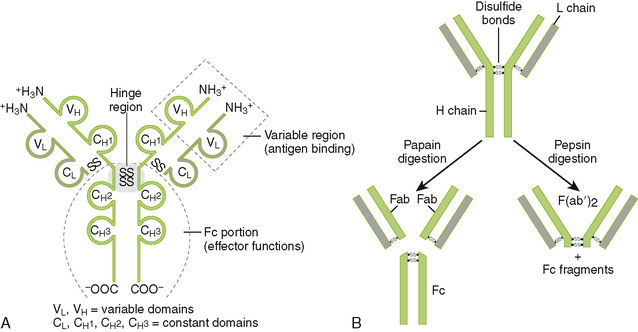
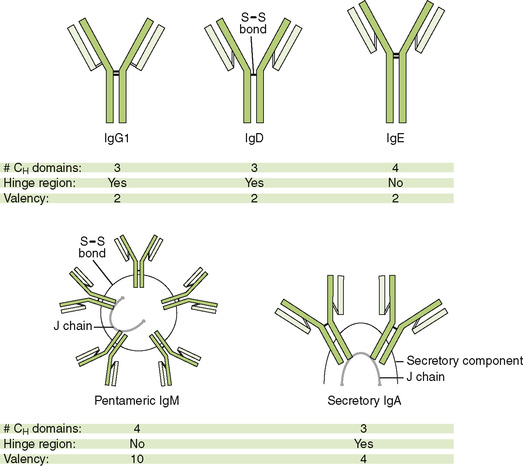
Chapter 3 I Immunoglobulin Structure and Functions • Immunoglobulins, synthesized by B cells, are antigen-binding glycoproteins (antibodies) that function in the recognition of and defense against antigens (Table 3-1). TABLE 3-1 Antigen and Antibody Terminology A Chain structure of immunoglobulins (Fig. 3-1A) 1. Each monomeric antibody molecule comprises two identical heavy (H) chains and two identical light (L) chains (κ or λ). 2. Antigenic specificity is determined by the amino acid sequence of the variable domains near the amino-terminal end of each chain. • Light chains contain one variable domain (VL) and one constant domain (CL). • Heavy chains contain one variable domain (VH) and three or four constant domains (CH1, CH2, etc.). B Functional regions of antibody molecules 1. Papain digestion cleaves the antibody molecule into two Fab fragments and one Fc fragment (Fig. 3-1B). 2. The Fab portion contains variable region (VL/VH) domains, which bind antigen. 3. The Fc portion mediates antigen clearance by binding to complement and to Fc receptors on immune system cells (Table 3-2). TABLE 3-2 Functions Mediated by Interactions with Antibody Fc Region ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; NK, natural killer. 4. Membrane-spanning region is a heavy-chain carboxyl-terminal domain present only in immunoglobulins expressed on the surface of B cells. C Properties of immunoglobulin isotypes • The five major immunoglobulin classes, or isotypes, exhibit different functions and roles in immunity (Table 3-3; Fig. 3-2). TABLE 3-3 ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. *IgG, IgD, and IgE always exist as monomers. IgM always exists as a pentamer. IgA exists as a monomer (160 kDa) or dimer.
Immunoglobulins and Their Production by B Cells
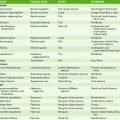
Term
Definition
Adjuvant
Substance that enhances immune response to an antigen when administered with it; used to improve response to vaccines
Affinity
Binding strength of a single variable region of an antibody for a corresponding epitope on the larger antigen structure
Antigen
Substance that binds to antibodies and T cell receptors. Although most antigens are also immunogens, some small molecules are antigenic but not immunogenic.
Avidity
Combined binding strength of the multiple interactions between a multivalent antibody molecule and all the corresponding epitopes on an antigen
Epitope (antigenic determinant)
Region on an antigen molecule to which a single antibody molecule or T cell receptor binds. An antigen usually has multiple epitopes and thus can react with antibodies of different specificities.
Fab fragment
Portion of antibody molecule, produced by papain digestion, that contains a single antigen-binding site. All antibodies have two or more Fab regions and thus are bivalent or multivalent.
Fc fragment
Portion of antibody molecule, produced by papain digestion, that fixes complement and binds to Fc receptors; varies among immunoglobulin isotypes
Hinge region
Flexible portion of antibody heavy chains located between the Fab and Fc regions and containing intrachain disulfide bonds; present in IgG, IgA, and IgD
Immunogen
Substance capable of eliciting a specific immune response
Monoclonal antibody
Homogeneous antibody that recognizes only one epitope; produced by a single clone of plasma cells
Polyclonal antibody
Mixture of antibodies that recognize different epitopes on an antigen; produced by multiple clones of plasma cells in response to an antigen containing different epitopes. Natural antiserum to a microbial antigen is polyclonal.
Thymus-dependent antigens
Antigens that require helper T cells to induce antibody production (humoral response); most protein antigens
Thymus-independent antigens
Antigens possessing many repetitive structures (e.g., flagellin, polysaccharide, and LPS) that can induce antibody production (humoral response) without helper T cells
Function
Fc Region Interacts with
Opsonization
Fc receptors on macrophages and neutrophils
Killing by means of ADCC
Fc receptors on neutrophils, macrophages, NK cells, eosinophils
Degranulation leading to allergic and antiparasitic responses
Fc receptors for IgE on mast cells
Activation of cells
Fc receptors on lymphocytes
Transmucosal movement
Fc receptors for dimeric IgA on epithelial cells
Activation of classical complement pathway leading to cell lysis (especially of bacteria), opsonization, and inflammatory response
Initial component of pathway (C1)