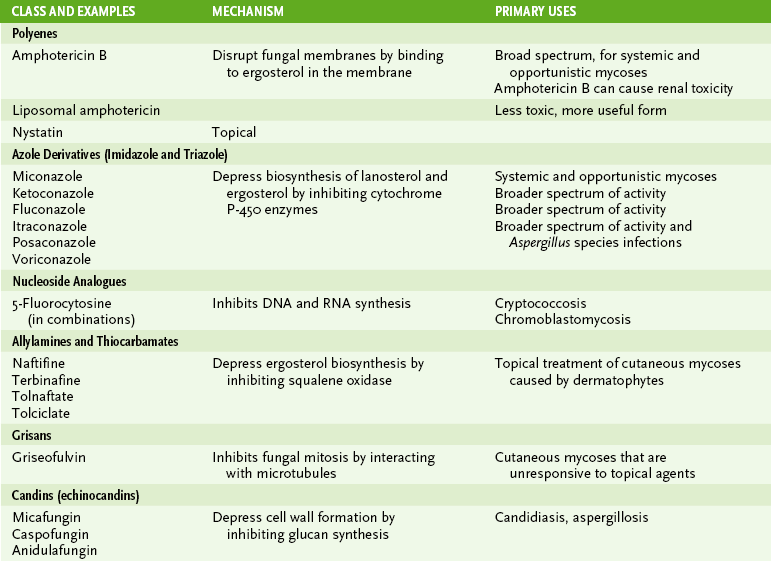
Chapter 28 1. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms. 2. Fungal membranes contain ergosterol rather than cholesterol found in other eukaryotic membranes. 3. The cell wall surrounding fungal cells, which differs in composition from bacterial cell walls, contains chitin, glucans, and protein. 1. Molds, or filamentous fungi, are composed of a mass of branching, thread-like tubular filaments (hyphae) that elongate at their tips. • Septate hyphae are divided into individual walled-off cells, each containing a nucleus. • Aseptate (coenocytic) hyphae are hollow and multinucleate. 2. Yeasts are unicellular, usually round fungi. 3. Dimorphic fungi exist as molds or yeasts depending on temperature or other environmental factors. 4. Dematiaceous fungi are dark colored and usually from soil. 1. All fungi can reproduce asexually, and asexually reproducing forms are most commonly encountered in clinical situations. 2. Some fungi can also reproduce sexually. • Aerial hyphae release spores, which germinate on suitable substrates, leading to growth of new hyphae. D Conditions conducive to fungal infections • Although fungi are ubiquitous in the environment, they generally colonize tissues and cause infection only when the body’s normal defenses or the normal flora are disrupted. 1. Disruption of the body’s physical, chemical, or physiologic barriers • Intact skin, pH, fatty acids in the skin, normal bacterial flora, and various humoral factors normally prevent fungal infection. 2. Immunosuppression, particularly loss of CD4 TH1 responses • Opportunistic infections by normal flora (e.g., Candida albicans) or increased susceptibility to environmental fungi (e.g., Aspergillus species) may result. 3. Disruption of normal bacterial flora E Types of fungal infections (mycoses) • Fungal infections and the agents causing them are commonly classified based on the site of disease or the immune status of the host. 1. Superficial mycoses involve the keratinized outermost layers of skin, hair, and nails. 2. Cutaneous mycoses involve the keratin-containing epidermis and deeper layers of the hair, skin, and nails. 3. Subcutaneous mycoses involve the dermis, subcutaneous tissues, muscles, and fascia. 4. Systemic mycoses often originate in the lungs but disseminate to other organs (especially in immunocompromised individuals). 5. Opportunistic mycoses generally occur only in patients with compromised immune systems (e.g., cancer patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy and human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]-infected individuals). F Diagnosis of fungal infections • Fungal infections mimic other diseases and therefore must be distinguished through careful differential diagnosis (Table 28-1). TABLE 28-1 Differential Diagnosis of Fungal Infections 1. Culture and microscopic examination • Isolation of fungi from specimens may require culturing for up to 30 days at 25°C and 35°C on appropriate media. a. Sabouraud agar, Mycosel agar b. Antibacterial antibiotics are often included in the medium to inhibit bacterial overgrowth. • Specific histologic stains can be used for direct visualization of fungi in tissue specimens. • Sugar utilization tests (similar to the fermentation tests for Enterobacteriaceae) are useful in identifying yeasts. 2. Detection of fungal antigens in blood or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by Ouchterlony (double-immunodiffusion) test or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay II Superficial and Cutaneous Mycoses
Fungi
Infection
Etiologic agent
Other conditions to exclude
Aspergillosis
Aspergillus species
Zygomycoses and other mold infections
Blastomycosis
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Bacterial and viral pneumonia, atypical mycobacterial infection, other systemic mycoses, bacterial or mycobacterial skin infections
Candidiasis
Candida albicans
Bacterial and other fungal infections
Chromoblastomycosis
Dematiaceous soil fungi
Sporotrichosis, tularemia, plague, gangrene, actinomycosis, atypical mycobacterial infection
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioides immitis
Bacterial and viral pneumonia; skin infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or other fungi
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcus neoformans
Meningitis caused by bacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and viruses, lung cancer, other systemic mycoses (especially histoplasmosis)
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasma capsulatum
Other systemic mycoses, bacterial and viral pneumonia, tuberculosis
Mycetoma, eumycotic
Dematiaceous soil
Mycetoma caused by soil bacteria fungi
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
Bacterial and viral pneumonia; skin infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or other fungi
Ringworm (tinea)
Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton species
Candidal infections; bacterial and viral skin infections
Sporotrichosis
Sporothrix schenckii
Tularemia, plague, gangrene, nocardiosis, chronic staphylococcal skin infections, atypical mycobacterial infection, other mycoses
Zygomycosis
Rhizopus and Mucor species
Aspergillosis and other mold infections
Fungi