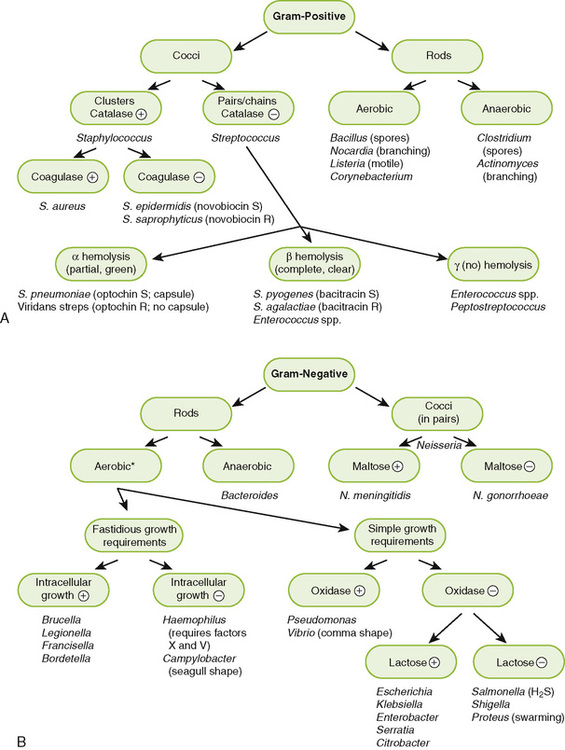
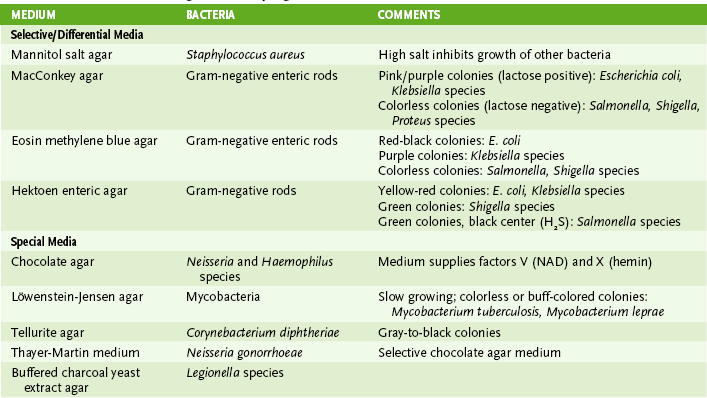
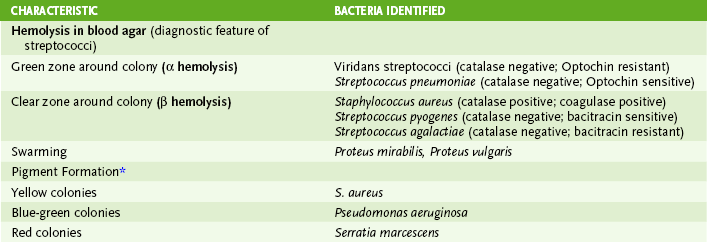
Chapter 8 I Laboratory Identification of Bacteria • Most medically important bacteria can be classified as gram-positive or gram-negative and further identified based on their shape and various metabolic properties as summarized in Figure 8-1. • Step 1: treat smear with crystal violet primary stain. • Step 2: add iodine solution, which precipitates primary stain within the peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall. • Step 3: rinse with solvent that dissolves the outer membrane and washes out the crystal violet from the thin peptidoglycan layer of gram-negative bacteria but not from the thick peptidoglycan layer of gram-positive bacteria. • Step 4: counterstain with red safranin, which is taken up by gram-negative organisms, allowing them to be visualized. • Purple (positive reaction): organisms with thick peptidoglycan cell wall • Red (negative reaction): organisms with thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane • Gram-variable or gram-resistant: modified cell wall old cultures or cells treated with β-lactam antibiotics in which the peptidoglycan is weakened—therefore, poor or no color retention; modified cell wall (Box 8-1) B Growth and isolation of bacteria • Most bacteria will grow on blood agar or other nonselective media. • Selective medium inhibits growth of some bacteria (e.g., EMB agar inhibits gram-positive bacteria). • Differential medium incorporates an identifying test. a. MacConkey agar is both selective (inhibits gram-positive bacteria) and differential (tests for lactose use). • Special medium incorporates particular metabolites or provides specific culture conditions required by certain bacteria. 2. Colony characteristics (Table 8-2) 1. Metabolic tests for fermentation of various sugars and production of byproducts (e.g., acid or gases) • Lactose fermentation differentiates the more and less pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae. a. Lactose fermenting includes more benign Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species. b. Nonlactose fermenting includes more pathogenic Shigella and Salmonella species. • Glucose and maltose fermentation differentiate Neisseria species.
Diagnosis, Therapy, and Prevention of Bacterial Diseases
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Diagnosis, Therapy, and Prevention of Bacterial Diseases