Coagulation Studies
Because the recognition and management of coagulopathy is of the utmost importance in treating patients with APL, the initial laboratory evaluation may include a platelet count, prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (PTT), D-dimer or fibrin split products, and fibrinogen.
22 This disease-related coagulopathy, typically bleeding diathesis, represents a major source of morbidity, and despite the effective antileukemia therapy presently available, it remains the leading cause of peri-induction mortality,
23, 24 and 25 with early hemorrhagic death rates generally ranging from 5% to 11%.
23,25, 26 and 27 Although less common than hemorrhage, thrombotic complications have been reported in up to 10% of patients at the time of diagnosis.
28 The mechanism underlying the coagulopathy is complex and has been the subject of intensive investigation. Historically, the coagulopathy had been ascribed to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), which resulted as the abnormal promyelocytes lysed and liberated the procoagulant contents of their granules.
29 Evidence for DIC as the underlying mechanism has been provided by finding that APL cells release increased levels of tissue factor.
30,
31 Tissue factor may serve to promote interaction between factor VII and other circulating procoagulants resulting in a widespread generation of thrombin. The coagulopathy can occur in the absence of chemotherapy as the neoplastic cells undergo autolysis, and it is found in approximately 80% of APL patients at the time of diagnosis. The coagulopathy may be exacerbated by the institution of chemotherapy, which results in the massive lysis of abnormal promyelocytes amplifying the already existing activation of the coagulation pathway. Both the PT and PTT are abnormally elevated, and the fibrinogen is low, reflecting an ongoing consumption. In addition, a number of other coagulation parameters such as the thrombin time and the level of fibrin split products are elevated, reflecting widespread disruption of the normal coagulation cascade. It is important to note that a fibrinogen in the low range of normal is still cause for concern given that it is an acute-phase reactant and ordinarily would be elevated in an ill patient. Serial measurements (approximately 6 to 12 hours apart) often reveal the developing hypofibrinogenemia indicative of consumption and help guide replacement therapy with blood products.
More recently, other explanations for the bleeding diathesis have attributed important roles for hyperfibrinolysis as well as nonspecific proteolysis.
32 An ongoing unchecked fibrinolytic process will also result in a low fibrinogen producing a clinical picture where hemorrhage is the primary sequela. Evidence for this hypothesis has been provided by the finding that low plasma levels of plasminogen,
α2-plasmin inhibitor, and plasminogenactivator inhibitor 1 are found in fibrinolytic states and are also found in APL. In addition, annexin II, a cell-surface receptor for plasminogen and tissue plasminogen activator, is expressed at abnormally high levels on APL cells but not on blasts from other forms of acute leukemia.
33,34 The increased expression of annexin II may lead to overproduction of plasmin, which results in dysregulated fibrinolysis. The potential for hemorrhage is further amplified by the depletion of the main inhibitor of plasmin,
α2-plasmin inhibitor, which is consumed in an effort to counter the increased production of plasmin. The clinical manifestations of the coagulopathy are controlled and some of the coagulation parameters progressively improve within days following the institution of therapy with either ATRA or ATO.
24,33
Morphology, Cytochemistry, and Immunophenotype
Examination of the bone marrow aspirate and biopsy are the standard tests by which the diagnosis of acute leukemia is made. The morphologic features of the cells in the blood and the bone marrow may be different, underscoring the importance of sampling the bone marrow. The various morphologic subtypes of APL and their defining features are summarized in
Table 78.1.
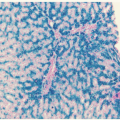
14,16,17,35,36 Characteristic examples of the morphology are provided in
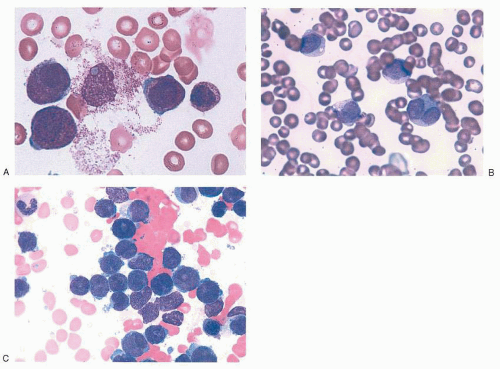
Figure 78.2. In the classic hypergranular variety of APL, the bone marrow aspirate is generally hypercellular and the abnormal promyelocytes constitute the predominant population. Blasts may be increased, but their number alone may not meet the minimal criteria by which classification systems
such as the French-American-British (FAB) and World Health Organization define AML. The malignant promyelocytes need to be considered as part of the total blast count to establish a diagnosis of AML. Malignant promyelocytes may be slightly larger than their normal counterpart. Such cells are heavily granulated: the granules often obscure the nucleus, making the nucleocytoplasmic border somewhat indistinct. In addition, the nucleus may be folded or bilobed. The cytoplasm often contains vacuoles, and distinctive Auer rods are frequently visible. Auer rods are coalesced primary granules and may be abundant. Multiple Auer rods clustered together within a single cell resemble a bundle of sticks or twigs, and such cells have been labeled
faggot cells (after the French term for
bundle of sticks). Globular cytoplasmic inclusions (pseudo-Chédiak-Higashi inclusions) have also been described. The term
flaming promyelocyte has been coined to describe cells that appear to be “breaking apart,” taking on a vibrant reddishpurple hue with the apparent liberation of granules into the surrounding cellular matrix.
Identification of the microgranular variant (M
3V) according to the FAB classification system) may be more problematic.
14,16 This entity generally constitutes about 20% to 30% of APL cases. It was first recognized because it shared some clinical features as well as the typical t(15;17) with the hypergranular form of APL. The granules in the microgranular variant are less prominent, are somewhat dispersed, and may be difficult to visualize using light microscopy. Instead, the granulation may be fine and the cells may appear “dusky” or “hazy.” The shape of the nucleus, which has a characteristic bilobed, folded appearance, is often the key in identifying this disorder. Auer rods may be present but are generally less plentiful than the hypergranular variety. Another clue to
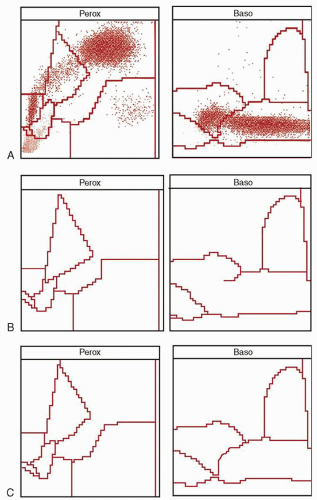
diagnosis is the finding of a few of the more typical hypergranulated forms in the bone marrow. Although diminished in number, their presence helps distinguish this disorder from leukemias of monocytic origin. The peripheral white blood cell count may be higher than the classic variety, and any hypergranulated promyelocytes are less likely to be found in the peripheral blood. The characteristic cytogram found via flow cytochemistry (
Fig. 78.1B) will be preserved in the microgranular variant, providing useful rapid confirmation of the diagnosis before the cytogenetic or molecular results are available.
17A third morphologic form of APL, the hyperbasophilic variant, has been described.
17 This is a relatively uncommon form of APL that some experts group within the M3V category. However, the morphologic features are distinct enough to warrant separate consideration. The cells in this disorder have few, if any, granules. Instead, the cytoplasm is deeply basophilic and may be noted to have small blebs, buds, or projections, making the appearance reminiscent of micromegakaryocytes. The nucleus tends to occupy most of the cell and has an irregular lobulated appearance. Both the microgranular and hyperbasophilic variants can be mistaken for an acute monocytic leukemia. A variant form of AML associated with CD56 expression and natural killer (NK) cell lineage has been confused with M3V but lacks the defining t(15,17) cytogenetic abnormality.
37 More recently, a European consensus group has described distinctive morphologic features of APL variants associated with the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger gene (
PLZF)/retinoic acid receptor-
α (
RARα) fusion products (see below) and have proposed a new morphologic category, M3r. These leukemias exhibit cells that lack a folded or bilobed nucleus but instead have a regular round or oval appearance. An increased number of Pelger-like cells reminiscent of those found in a myelodysplastic syndrome can also be seen. Auer rods are generally rare and the cytoplasmic granularity is intermediate between M3 and M2 varieties of AML.
36Although not diagnostic for APL, cytochemistry and immunophenotyping may help characterize APL. The cytochemical properties of the abnormal promyelocytes are consistent with a diagnosis of AML.
14,16,17,35,38 The hypergranular variety stains intensely with Sudan black, MPO, or chloroacetate esterase. The microgranular variant retains this staining pattern, although the degree of positivity may be less intense. As discussed above, the high MPO content of abnormal promyelocytes may be detected in the peripheral blood using modern blood analyzers. Less useful is the observation that nonspecific esterase activity has been noted in some abnormal promyelocytes, further confusing the differentiation between acute monocytic leukemia and some forms of APL.
39 These reactions are weaker than those found in monocytes, and some forms of the isoenzymes found in monocytes are absent in the abnormal promyelocytes. Metachromatic staining with toluidine blue has been reported in cases of APL with basophilic differentiation.
Immunophenotyping is also useful in confirming the diagnosis of APL.
38,40 Promyelocytes are partially differentiated cells that are reflected in the immunophenotype. The cells express the early myeloid marker CD33 but lack human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR, a marker often associated with some earlier progenitor cells. It is important to emphasize that this immunophenotypic profile is characteristic but not diagnostic of APL. Up to 20% of other types of AML may express CD33 but not HLA-DR. The marker CD9 is expressed in APL but not in other AML subtypes.
41 Unfortunately, this finding is not clinically useful as few screening panels used for diagnosis contain CD9 as part of the initial workup. The stem cell marker C34 is generally not expressed, whereas the myeloid lineage marker CD13 is occasionally observed and possibly associated with the development of retinoic acid syndrome (RAS).
42 The T-cell marker CD7 is negative, as are the myelomonocytic markers CD11b and CD14. CD11b is also an indicator of myeloid maturation and, along with CD16, a surface marker found on granulocytes, can be induced with differentiation therapy. The aberrant expression of the T-cell marker CD2 has been correlated with the microgranular variant, as well as a shorter duration of remission.
43 Reports of a correlation with the short form of the promyelocytic leukemia (
PML)/
RARα fusion transcripts have been mixed.
44,45,46,
47 Expression of the P-glycoprotein associated with the MDR phenotype is generally not found in APL. The NK marker CD56 has been reported in true APL (as opposed to NK-AML) and has been associated with a poor prognosis.
48,49
Cytogenetics and Molecular Biology
Despite the minor variations in phenotype discussed above, APL as a clinical syndrome is defined by its cytogenetics. The balanced translocation between chromosomes 15 and 17 characterizes over 95% of cases of APL.
50,51 The breakpoints for the translocation usually occur at q22 loci on chromosome 15 and q21 on chromosome 17. The t(15;17) is generally detected by conventional cytogenetic techniques and provides definitive evidence of the diagnosis of APL. The molecular consequence of this translocation results in a fusion of a portion of the gene for the
RARα on chromosome 17 to part of the
PML gene on chromosome 15.
50,
52, 53 and 54 Although the break within the
RAR gene is invariable within the second intron of the gene, the point of rearrangement within the
PML gene can occur at two major breakpoints, resulting in three isoforms of the transcript. Breakpoints within
PML intron 3 (bcr3) generally yield a shorter messenger RNA transcript, whereas breakpoints within intron 6 (bcr1) result in the long form of the transcript.
46 Breakpoints within intron 6 of
PML can also occur at a second site (bcr2) and result in a transcript
of variable length. The site of the breakpoint has been reported to have prognostic implications as newly diagnosed patients with the short isoform appear to have a shorter disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) compared with the long isoform in some series.
42,
46,55 Other authors have correlated the isoform with various other prognostic factors but discount an independent effect on outcome.
56 In all cases, the chimeric gene products that result from this translocation have fundamental implications for the cell and are thought to be causative in producing the malignant phenotype. Variations of this translocation exist, and in some instances have profound clinical implications.
Although the t(15;17) is the defining cytogenetic abnormality in APL, other additional chromosomal abnormalities can be found in 30% to 40% of patients with APL.
57,58 The most common among these are trisomy 8 and isochromosome 17. Additional chromosomal abnormalities do not have a negative impact on the overall prognosis.
58,59 Complex translocations involving other chromosomes in addition to 15 and 17 can occur. Masked translocations, where pieces of chromosome 15 and 17 are transposed but escape detection by conventional techniques, have been reported.
60,61 In most of these cases, the molecular abnormality, either the
PML-RARα or the reciprocal
RARα-PML transcript, can be detected. Expression of the fusion gene product ultimately results in the clinical syndrome identified with APL despite the lack of gross chromosomal changes.
Variant translocations also exist and are rare as clinical entities but are instructive in helping define the biology of APL. The most common variants involve translocations between chromosome 17 and either chromosome 5 or 11.
62,63,64,65 These variant translocations retain the same break within the
RARα intron but differ in the molecular partner gene (X gene), which may account for some of the differences regarding their functional effects on the cell. The individual variants are summarized in
Table 78.2. The structural changes within these genes may affect the normal function of the wildtype product, resulting in the phenotypic abnormality, which is expressed as the leukemia. Most notable among the variants is the t(11;17) (q23q21) because this entity is resistant to the differentiation effects of ATRA. This chromosomal translocation results in a fusion of the
RAR gene with
PLZF. PLZF is similar to
PML in that it has profound implications for the cell with regard to regulation of transcription of target genes resulting in differentiation. However,
PLZF is distinctly different from
PML in that properties of this gene product interact differently with retinoic acid, rendering it ineffective.
66 This form of APL also has a poor response to standard chemotherapy, underscoring the multiple differences in biology between these two entities.
In addition to variant chromosome translocations in APL, it has been discovered that APL commonly harbors co-existing mutations that may have biologic and clinical impact. To date, internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutations of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (
FLT3) gene are the most frequent concurrent mutational events in APL, occurring at a frequency of 21% to 32%.
67,68,69,70 Constitutive activation of the FLT3 receptor via this mutation is known to confer a proliferative and survival advantage to AML blasts.
71,72 In non-M3 AML, this mutation occurs at a similar frequency and is generally associated with worse DFS and OS than occurs in
FLT3-ITD wildtype AML.
74,75 The adverse effect of this mutation in APL is less clear, with most series suggesting that the mere presence of an
FLT3-ITD mutation does not independently affect survival, although it does associate with other known adverse factors, such as elevated WBC. However, quantitatively higher expression levels of
FLT3-ITD and longer transcript length may have a negative impact on DFS.
68,70 Given the recent influx of clinically available pharmacologic inhibitors of FLT3, such inhibitors may eventually become incorporated into standard therapy for selected patients with APL whose disease harbors a
FLT3 mutation.
Based on experimental data generated in cell lines, transgenic mice, and correlations with clinical treatment data, a model for leukemogenesis in APL has been developed (
Fig. 78.3).
73,74,75,76,77 On the most basic level, this hypothesis states that APL results from transcriptional dysregulation of differentiation produced by the
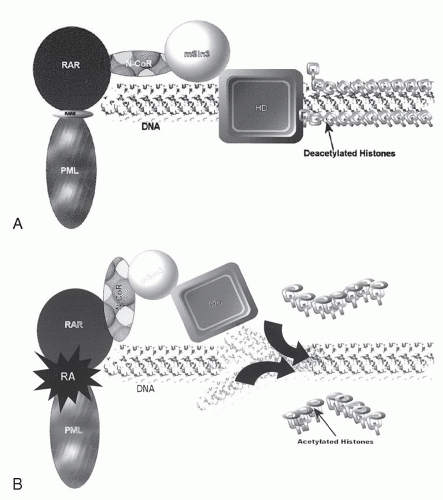
PML-RARα gene product. In the normal cell,
RARα plays an important role in modulating myeloid differentiation by virtue of its ability to recruit various nuclear co-repressors such as SMRT/N-CoR and mSin3. These transcription co-repressors, in turn, bind various histone deacetylases, affecting chromatin conformation and resulting in repression of transcription of target genes fundamental to the differentiation process. Under physiologic conditions, binding of retinoic acid causes dissociation of the co-repressor complex, recruits transcriptional activators, and “opens” the chromatin, facilitating the transcription of the various target genes and allowing normal maturation. The PML-RAR
α fusion protein has an increased affinity for the N-CoR co-repressor complex such that physiologic doses of RA <(10
-8 M) fail to produce a dissociation of the complex, resulting in continued transcriptional repression and a maturational block. Instead, supraphysiologic doses achieved by the administration of ATRA are required to recapitulate the behavior of the wildtype receptor. In the PLZF-RAR
α variant, there is a second binding site for the co-repressor proteins within the PLZF portion of the fusion protein
that is not sensitive to retinoic acid. Hence, even supraphysiologic doses are unable to free the co-repressor complex and permit the conformational changes in the histones necessary for permitting differentiation to occur. This may be an explanation for the clinical resistance of t(11;17) to ATRA and has led investigators to explore compounds such as histone deacetylase inhibitors that bypass co-repressor binding as defined by the activity of RARs and directly effect transcriptional activation.
Although the model of transcriptional repression through chromatin remodeling may rest on the interaction of the aberrant RAR
α fusion protein with key regulatory genetic elements, the primary partners in the molecular fusion proteins, namely PML and PLZF, are important in leukemogenesis and may also serve to amplify dysregulation of transcription.
66,73 PML does not directly bind DNA but has been found to regulate transcription through interaction with a number of transcription factors and repressors.
78,79,80 In the normal cell, PML is localized in discreet subnuclear structures called PML oncogenic domains or PML nuclear bodies (PNBs). These PNBs may functionally regulate transcription by either binding various transcription activators/repressors or sequestering them from circulating in the nucleoplasm, thereby preventing any interaction with other regulatory elements, or by providing an environment where the various regulatory factors can interact or be modified. This function, in turn, may affect fundamental cellular processes such as growth, senescence, and apoptosis. PML-RAR disrupts the organization and function of the PNBs and displaces PML, forming a microspeckled pattern in the nucleus. Treatment with RA causes the PNBs to reorganize and presumably restores not only the structure, but also the functional activity.
Less is known regarding the function of PLZF. It also modulates transcriptional repression through multiple interactions with SMRT/N-CoR/mSin3/HDAC complexes and may localize in structures similar to the PNBs. Some of the mediators with which PLZF interacts are insensitive to modulation by RA, and these properties are retained in the PLZF-RAR fusion product, resulting in clinical ATRA resistance.
In addition to providing an understanding of the underlying biology of leukemia with possible application to cancer as a whole, the molecular genetics of APL also provide a useful tool for the clinician in confirming the diagnosis and planning therapy. As discussed above, the vast majority of APL is characterized by the t(15;17), resulting in a PML-RAR fusion product. These genetic changes are specific for APL and, using the modern molecular technique, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), are easily detectable.
81,82,83 RT-PCR has become a standard tool in the management of APL. It is now readily available in commercial laboratories, and there is usually a rapid turnaround time. RT-PCR is useful in confirming the diagnosis of APL, particularly in cases where morphology is problematic. In addition, this unique molecular “signature” can be used to monitor response and test for minimal residual disease (MRD).
55,81,82,83,84,85,86 This ability to have an effective method for detecting MRD is in sharp contrast to the other forms of AML, where response is assessed primarily through morphologic examination of the bone marrow and blood. Therefore, in APL, the concept of remission can be redefined to include a molecular response. Molecular relapse can be detected before it is clinically apparent, and this information can be used to guide therapy. An effective treatment regimen will render the RT-PCR assay for
PML-RAR negative. The conversion from a negative result to positive that is reproducible on two sequential assays is predictive of clinical relapse. Some groups have reported highly successful results treating the disease in molecular relapse prior to the occurrence of the full-blown clinical syndrome
87 This has led to the standard recommendation that patients with APL be serially monitored via RT-PCR for
PML-RAR every 3 months during the first 2 years after remission is achieved, when the risk of relapse is the greatest.
55 It is important to note, however, that there are different forms of PCR analysis with different sensitivities, and the clinical results have only been validated with RT-PCR assays having relatively low sensitivities. More recently, the low relapse rate following modern treatment regimens has caused some investigators to question the need for a monitoring strategy, instead reserving such strict monitoring to those defined as having poor-risk disease. The role of real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR) as part of any monitoring strategy has yet to be defined and is currently under investigation.