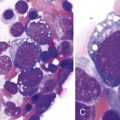
Chapter 57 Thrombocytopenia Caused by Platelet Destruction, Hypersplenism, or Hemodilution
Table 57-1 Mechanisms of Platelet Destruction or Consumption
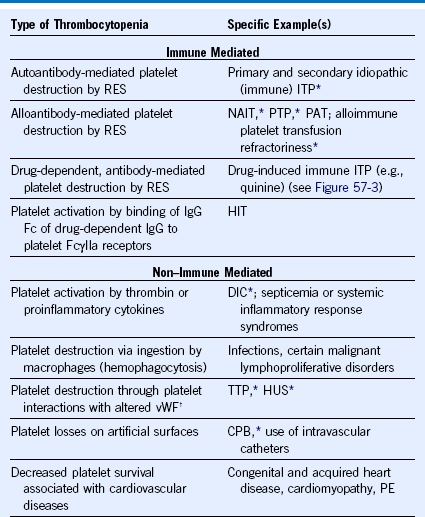
CPB, Cardiopulmonary bypass surgery; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; HIT, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; HUS, hemolytic uremic syndrome; IgG, immunoglobulin G; ITP, Idiopathic (immune) thrombocytopenic purpura; NAIT, Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia; PAT, passive alloimmune thrombocytopenia; PE, pulmonary embolism; PTP, posttransfusion purpura; RES, reticuloendothelial system; TTP, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
* See Chapter 56 for a discussion of thrombocytopenia in these disorders.
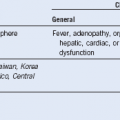
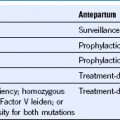
Table 57-2 Differential Diagnosis of Thrombocytopenia in Pregnancy
DIC, Disseminated intravascular coagulation; HUS, hemolytic uremic syndrome; TTP, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
*Preeclampsia or eclampsia usually is not associated with overt DIC.
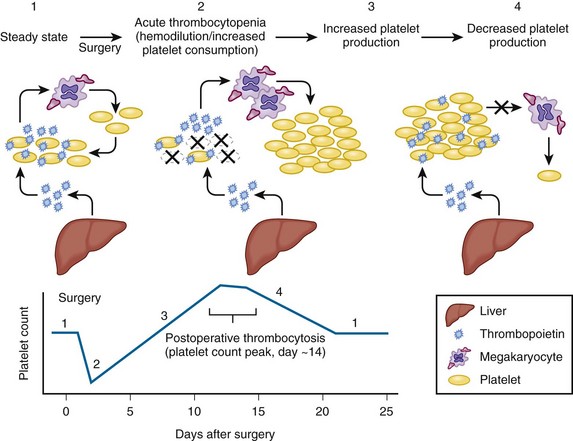
Figure 57-1 POSTSURGERY PLATELET COUNT CHANGES.
(Reprinted, with modifications, with permission, from Arnold DM, Warkentin TE: Thrombocytopenia and thrombocytosis. In Wilson WC, Grande CM, Hoyt DB, editors: Trauma: Critical care, vol 2. New York, 2007, Informa Healthcare, p 983.)
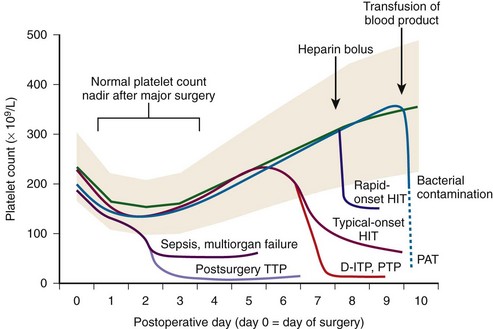
Figure 57-2 TIMING OF ONSET AND SEVERITY OF THROMBOCYTOPENIA: IMPLICATIONS FOR DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS.
(Reprinted, with permission, from Greinacher A, Warkentin TE: Acquired non-immune thrombocytopenia. In: Marder VJ, Aird WC, Bennett JS, et al, editors: Hemostasis and thrombosis: Basic principles and clinical practice, ed 6. Philadelphia, 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, in press.)
Table 57-3 Laboratory Tests Used to Investigate a Patient With Thrombocytopenia
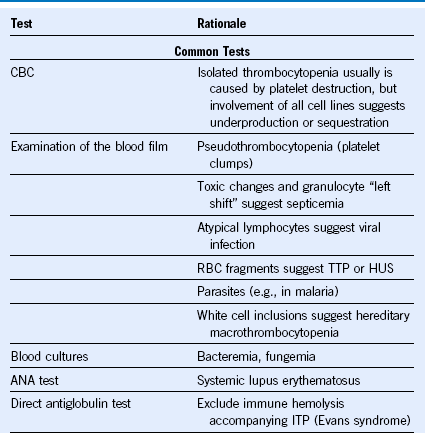
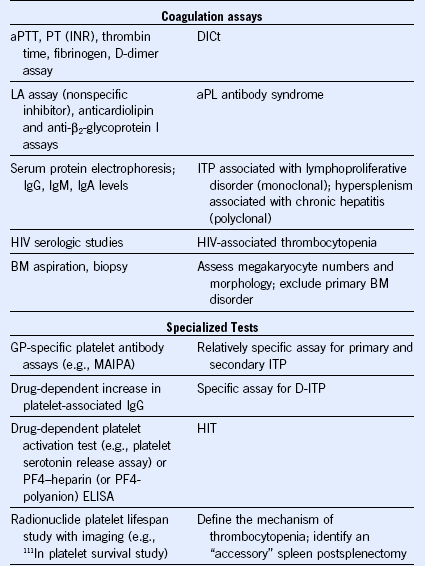
ANA, Antinuclear antibody; aPL, antiphospholipid; aPTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; CBC, complete blood count; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; D-ITP, drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GP,
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree