of PAR-1 when bound to EPCR and possibly other receptors.16 Additional dimensions to studies on the protein C pathway include preclinical studies showing beneficial effects of second-generation recombinant APC mutants in sepsis and ischemic stroke, the generation of protein C- or protein S-deficient mice, and the findings that protein S can exert direct receptor-mediated effects on cells.16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,25,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47
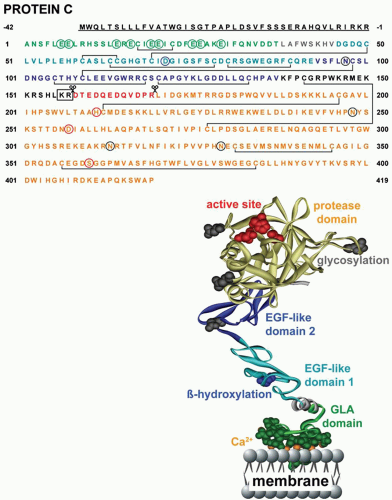
Thrombin cleavage of the zymogen at Arg169 removes the activation peptide and generates APC, a trypsin-like serine protease with a typical serine protease active site triad (His211, Asp257, and Ser360). Endogenous circulating levels of plasma APC are low (<40 pM), and inactivation of APC in plasma is driven by serine protease inhibitors (SERPINs) that contribute to a remarkably long circulation half-life of APC in man of approximately 20 to 25 minutes. Most important inhibitors of APC in plasma are protein C inhibitor (PCI) and α1-antitrypsin and, to a lesser extent, α2-macroglobulin and α2-antiplasmin.
Table 19.1 Characteristics of the protein C pathway components | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
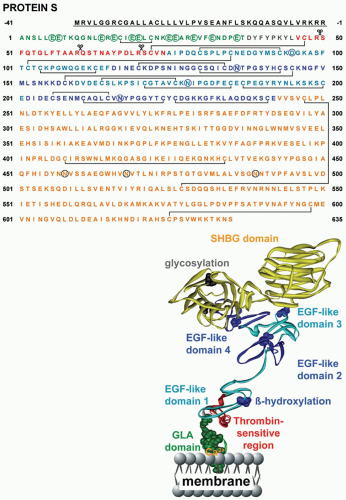
the liver but is also made by endothelium and other cells. Protein S circulates in plasma at a total concentration of 320 nM, and approximately 60% of the protein S is noncovalently complexed with C4b binding protein (C4BP) such that free protein S is 130 nM in plasma.56 C4BP is an octopus-like shaped glycoprotein of approximately 500 to 570 kDa and consists of six or seven disulfide-linked, identical alpha-chains and one smaller beta-chain (see Table 19.1).57 C4BP regulates protein S functions by binding via the beta-chain.58 Protein S binds to the C4BP beta-chain in a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with high affinity (Kd ˜ 0.1 to 0.6 nM).59 Although C4BP is an acute-phase response protein, only alpha-chains are increased causing the levels of free protein S levels to remain stable during an acute-phase response.60
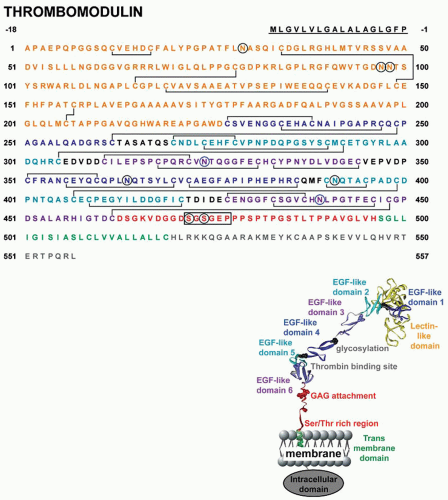
the form of a 60.3-kDa single-chain transmembrane protein.63 Posttranslational O-linked and N-linked glycosylation accounts for approximately 20% of the apparent molecular weight of TM, and other modifications include covalently bound chondroitin sulfate moieties.64
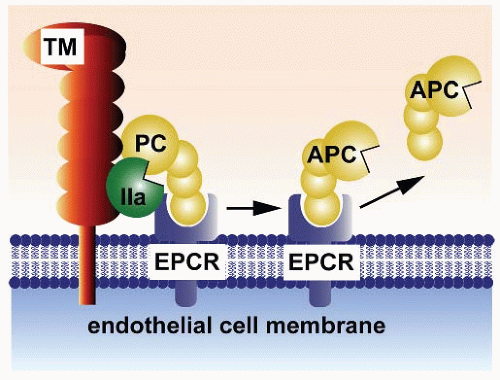
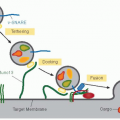
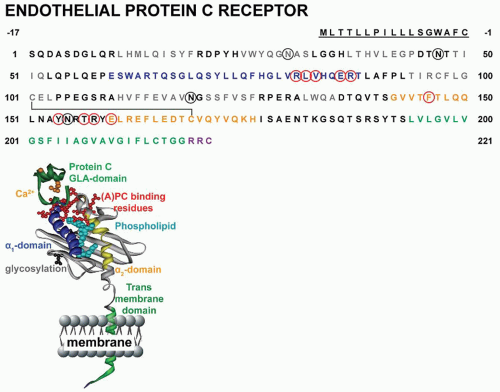 FIGURE 19.4 Amino acid sequence and ribbon polypeptide scheme of the EPCR. Amino acids are numbered from the amino-terminus of the mature protein with the signal peptide sequence underlined. Specific domains are color coded as indicated in the ribbon cartoon. Black circles represent sites of N-linked glycosylation. EPCR residues implicated in binding of APC are indicated in red.54 |
is located along opposing edges of a planar platform generated by an eight-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet. The crystal structure of soluble EPCR revealed that a phospholipid, most likely phosphatidylcholine, was bound in this groove between the two alpha-helices.69,70 EPCR’s short cytoplasmic tail (Arg-Arg-Cys-CO2H) suggests that induction of direct cell signaling is unlikely and that palmitoylation of the C-terminal Cys residue may help localize EPCR to certain lipid rafts or caveolae and facilitate modulation of cell-signaling pathways that depend on EPCR.71,72
is strongly linked to excessive complement activation.143 The lectin-like domain of TM (figure 19.3) can contribute to inhibition of complement activation and provide direct anti-inflammatory activity, although the molecular basis for this remains somewhat unclear.144,145,146,147
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree