VII.D.001 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
VII.D.001
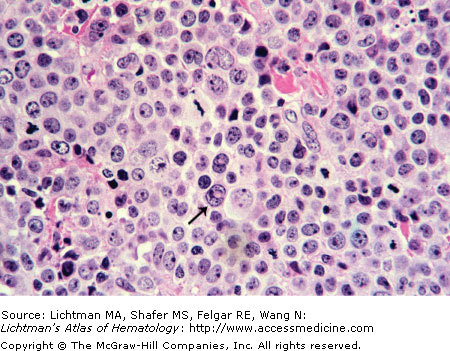
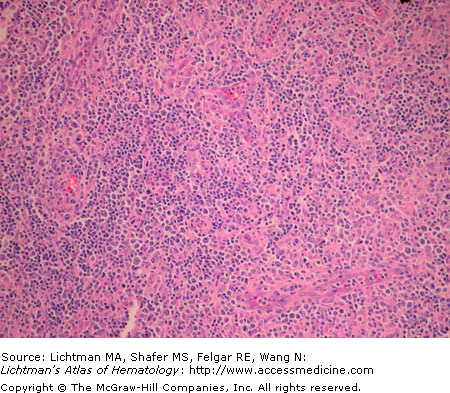
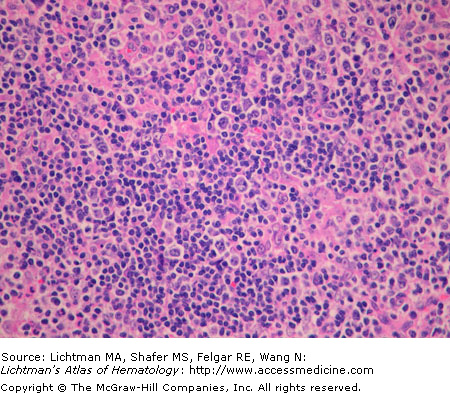
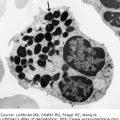
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma. T-cell type. Lymph node biopsy. H & E. Infiltrate of malignant lymphocytes with multiple nucleoli and sometimes abundant cytoplasm. This lymphoma has a varied morphologic appearance but virtually all cases display a proportion of cells (hallmark cells) with horseshoe nuclei or multiple peripheral nuclei in a wreath shape. The arrow points to an example of a hallmark cell.
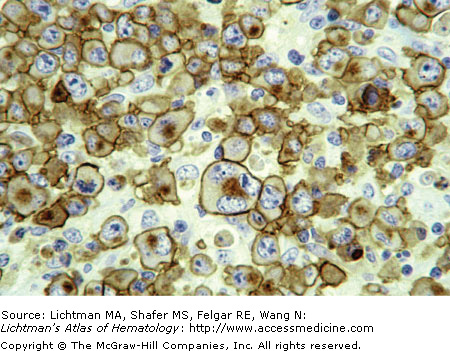
VII.D.002 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: CD30 Immunostain
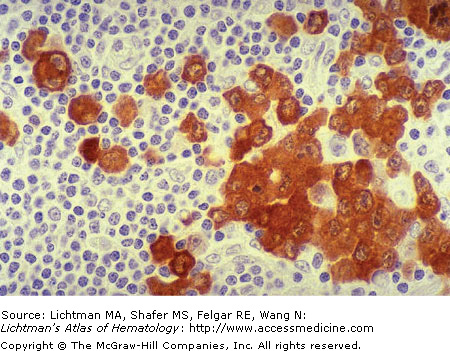
VII.D.003 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Immunostain
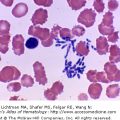
VII.D.003
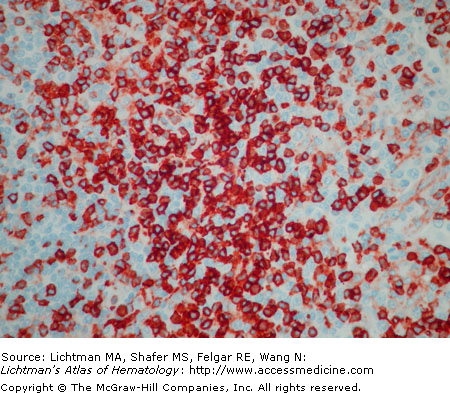
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) immunostain. Lymph node biopsy. This lymphoma is strongly positive when examined for its content of ALK. Here we see a case with strong cytoplasmic staining. In other cases nuclear as well as cytoplasmic staining may be evident.
VII.D.004 Angiocentric T/NK Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type
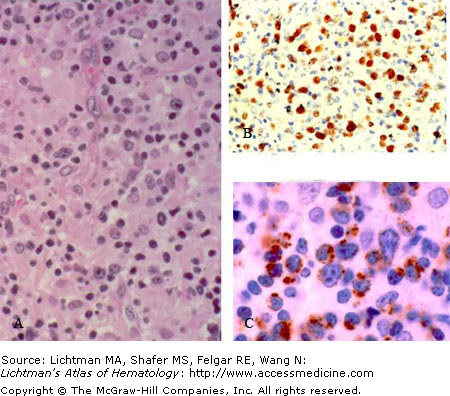
VII.D.004
Angiocentric T/NK cell lymphoma, nasal type. (A) H&E stain. Lymphoma cells may range from large to small with irregular nuclei. Nucleoli are inconspicuous in the small cells but overt in the larger cells. Cytoplasm is abundant and usually clear or pale. Mitotic figures are usually evident. Apoptotic bodies and necrosis is often present. Fibrinoid changes in blood vessel walls can occur. Involvement is diffuse but angiocentric and angionecrotic patterns may be present. (B) In situ hybridization for Epstein-Barr virus early RNA expression (EBER) is evident by nuclear brownish reaction product. (C) T-cell intracellular antigen (TIA-1) immunostain indicates brownish cytoplasmic reaction product confirming a cytotoxic T-cell/NK-cell phenotype.