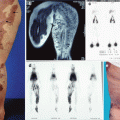
Fig 19.1
PHACE syndrome in a young girl. A large, plaque-like hemangioma is affecting the central part of the face and it was particularly aggressive on the nose. Unfortunately this patient had also lissencephaly that caused major neurodevelopmental problems
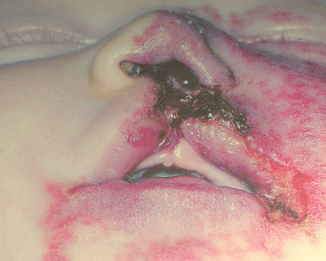
Fig 19.2
Another case of PHACE syndrome in an infant. This picture illustrates dramatically the involvement of the nose and the upper lip with significant loss of tissue in both. These complications will require a future reconstructive approach
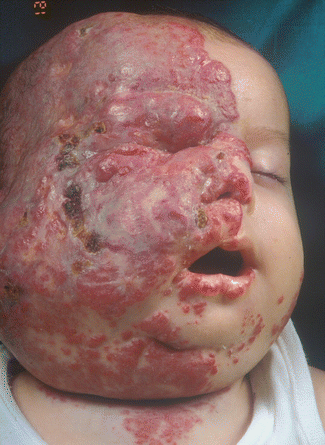
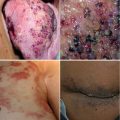
Fig 19.3
This case summarizes some of the possible findings in PHACE syndrome: a large plaque-like hemangioma involves the right half of the face (closing the visus of the right eye) and, bilaterally, the “beard” area (with a possible involvement of the airways)
Table 19.1
Medical findings associated with PHACE syndrome
Posterior fossa anomalies-brain structure |
Dandy-Walker complex |
Cerebellar hypoplasia |
Unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia |
Subependymal or arachnoid cysts |
Dilated lateral ventricles |
Hypoplasia of cerebrum |
Hypoplasia of corpus callosum |
Hypoplasia of septum pellucidum |
Hypoplasia of vermis |
Absent foramen lacerum |
Polymicrogyria |
Microcephaly |
Heterotopia |
Absent pituitary or partially empty sella turcica |
Arterial lesions-cerebrovascular |
Dysplasia of the large cerebral arteriesa |
Stenosis, occlusion, absence or moderate to severe hypoplasia of the large cerebral arteriesa |
Aberrant origin or course of the large cerebral arteriesa |
Saccular aneurysms |
Persistent embryonic arteries |
Cerebral sinus malformations |
Sinus pericranii |
Dural arteriovenous malformations |
Moyamoya vasculopathy |
Acute arterial stroke |
Cardiac/aortic coarctation/cardiovascular |
Coarctation or interrupted aortic arch |
Aneurysms of aortic arch |
Right aortic arch |
Double aortic arch |
Congenital valvular aortic stenosis |
Aberrant origin of a subclavian with or without a vascular ring |
Subclavian steal syndrome |
Anomalous coronary arteries |
Patent ductus arteriosus |
Anomalous pulmonary veins |
Patent foramen ovale |
Cor triatriatum |
Tricuspid atresia/stenosis |
Dextrocardia |
Persistent left superior vena cava |
Ventral and atrial septal defects |
Pulmonary stenosis |
Tetralogy of Fallot |
Ectopia cordis or Cantrell’s syndrome |
Arteriovenous shunting |
Eye abnormalities |
Posterior segment abnormalities |
Retinal vascular abnormality |
Persistent fetal retinal vessels |
Iris vessel hypertrophy |
“Morning-glory” disk |
Peripapillary staphyloma |
Optic nerve hypoplasia |
Anterior segment abnormalities |
Microphthalmos |
Coloboma |
Congenital cataracts. |
Sclerocornea |
Iris hypoplasia |
Exophthalmos |
Congenital third nerve palsy |
Horner syndrome |
Other associated anomalies |
Ventral developmental |
Partial or complete agenesis of sternum |
Sternal cleft or pit |
Sternal papule |
Lingual ectopic thyroid |
Supraumbilical raphe |
Omphalocele |
Miscellaneous |
Pituitary insufficiency |
Micrognathia |
Auricular hypoplasia or agenesis/“low-set” ears |
Orofacial clefting |
Airway hemangioma |
Carcinoid endobronchial tumor |
Spina bifida occulta |
Esophageal diverticulum |
Cervical cyst |
Ipsilateral sensorineural hearing loss |
Congenital scrotal/hemiscrotal agenesis |
Hemangioma of the liver
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|