and hemostasis within the local environment of the growing platelet thrombus. As some of these markers are also soluble and specific to the megakaryocyte-platelet lineage, their measurement provides a way to systemically and specifically measure the degree of platelet activation occurring in various disease states. Platelet-derived α-granular markers are now usually measured by ELISAs that have superseded radioimmunoassays. Of these molecules, the most commonly and traditionally measured markers of platelet activation are the α-granular soluble constituents, β-thromboglobulin (β-TG),8,9 and platelet factor 4 (PF4).8,9 More recently, some α-granular membrane proteins have been found to be expressed on the surface of activated platelets where they are rapidly cleaved by proteases and are shed into the plasma. These include soluble P-selectin10,11 and soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L)12 (see the platelet “sheddome” section below). However, as a result of the obligatory plasma separation procedures, all of these assays are vulnerable to artifactual in vitro platelet activation.8,9
Table 67.1 Summary of laboratory markers of platelet activation | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
been traditionally used for measurement of PF4 and β-TG to help minimize any additional ex vivo platelet activation. Soluble P-selectin in plasma may also be of endothelial cell origin although it is thought that this is a predominant marker of platelet activation.10
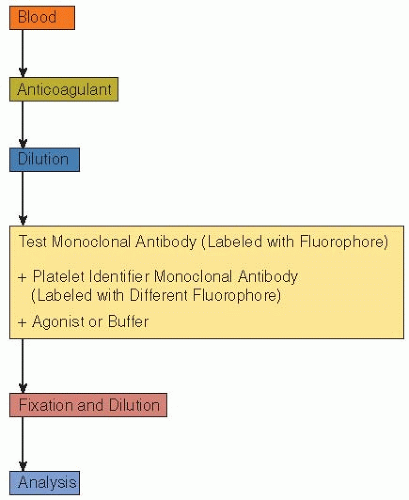 FIGURE 67.1 A typical schema of sample preparation for analysis of platelets by whole blood flow cytometry. |
copy density can also be detected on activated platelets. This is normally reflected as an increase in mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) with most fluorescent antibodies against this receptor. Although the vWF receptor GPIb is also expressed at high copy density on resting platelets, changes also occur after activation. As the protein can be internalized into the OCS and/or cleaved to form soluble glycocalicin, significant downregulation in the copy density of this receptor can occur with a decrease in MFI, although the percentage of positive platelets remains 100%.41,42
Table 67.2 Activation-dependent monoclonal antibodies, that is, antibodies that bind to activated but not resting platelets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
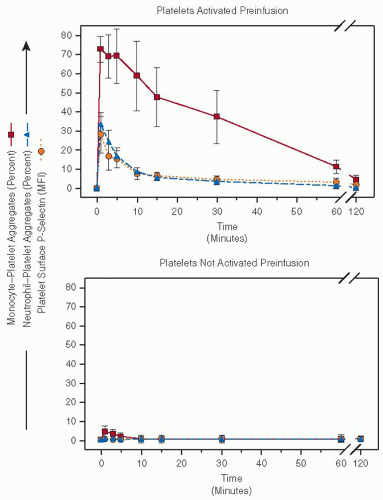
neutrophil-platelet aggregates are readily and easily identified by whole blood flow cytometry.34,48 These interactions are important in cardiovascular disease and many other clinical disorders in which platelets are activated (see section on platelet activation in clinical disorders below).49,50,51
and absence of ADP. PGE1 and ADP (acting via P2Y12) have opposite effects on VASP with either promotion or inhibition of phosphorylation respectively. Therefore the nonphosphorylated VASP correlates with the activity of P2Y12. Interference with the activity of this receptor by the active metabolites of thienopyridines (e.g., clopidogrel or prasugrel) or direct antagonists (e.g., ticagrelor or cangrelor) results in persistent VASP phosphorylation induced by PGE1 even when the platelets are stimulated with ADP. By comparing the level of VASP phosphorylation in whole blood samples stimulated with either PGE1 or a combination of PGE1 and ADP, it is possible to derive a platelet reactivity index (%).53 The assay provides the most direct and specific measurement of the activity of P2Y12 and can be used to monitor the efficacy of antiplatelet drugs that target this receptor.54,55 Accordingly, the VASP phosphorylation assay has been used to monitor the effects of clopidogrel in humans, and an impaired restoration of VASP phosphorylation by clopidogrel has been shown to be associated with subacute stent thrombosis following PCI.54,55 Further work is required to determine whether this indicates that a high level of receptor blockade is required to prevent stent thrombosis, particularly as the assay has been reported to be insensitive to low levels of P2Y12 inhibition.
been successfully used, for example, corn trypsin inhibitor (an inhibitor of activated factor XII).75 The strong calcium chelator ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) should be avoided, because it can dissociate αIIbβ3. Nonchelating anticoagulants like PPACK (a direct thrombin inhibitor) or hirudin may be preferable for the monitoring of GPIIb-IIIa antagonist therapy.76 Citrate has also recently been shown to interfere with in vitro but not ex vivo measurement of P2Y12 inhibition by low concentrations of cangrelor and the prasugrel metabolite.77 Another alternative anticoagulant available is EDTA-CTAD.78 Platelet count, mean platelet volume (MPV), number of platelet clumps, mean platelet component, numbers of P-selectin-positive platelets, and platelet-leukocyte aggregates have all been shown to be stable for 360 minutes in blood samples kept at 4°C.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree