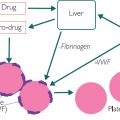
Figure 7.1: Cellular and exudative inflammation
The tissue damage elicits a cellular signal: CRP, to recruit and increase the number of neutrophils. To aid this process, the enzyme COX-2 produces prostaglandins, which cause constriction and dilatation at the site to affect blood flow. This response may cause pain (if a nerve is part of the constricted area), swelling, oedema and redness of skin.
Table 7.1: Inflammation analogies
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is ‘how far red cells (erythrocytes) fall (sediment) in a tube, in an hour’. As the tissue is damaged, fibrinogen is released. Fibrinogen ‘sticks’ red cells together, making them heavy, so they fall further in the test. A high ESR means that more red cells are stuck together by fibrinogen, which results in more cell/tissue damage. ESR is usually raised in inflammation, but it can take time for this ‘sticking process’ to occur and indeed be removed. ESR is therefore not as quick to respond to damage as CRP. In some cases, ESR will rise in anaemia (independently of fibrinogen and inflammation). Large, macrocytic red blood cells will fall more quickly than small or normal-size ones. ESR can also be used to indicate cancer, myeloma and macrocytic anaemia and so could be being used for this reason. ESR also increases with age.
Storytelling: If you went to the top of a tall building and dropped three footballs (red cells), timing how long they took to fall, that would be a normal ESR. If you repeated this exercise, but placed the footballs in a heavy sack (fibrinogen resulting from inflammation), the balls would fall faster. However, as discussed earlier, ESR can also be independent of inflammation. If you repeated the demonstration, but dropped a large medicine ball (a macrocytic red blood cell) instead of three footballs, the large ball would fall faster. In other words, ESR can also be raised in macrocytic anaemia. You could cross-check ESR with mean cell volume (MCV) to find out the size of the red cells.
Plasma viscosity
Plasma viscosity (PV) is a measure of pressure in the blood (not blood pressure). It is measured in mPascals, a unit of pressure. PV is a surrogate marker of material that is not expected to be in the blood. As more white cells, bacteria, antibodies, red cells, in fact any material, build up in the blood, the pressure will rise and so will PV. It’s often described as ‘thick blood’ because more material is present.
Storytelling: Visualise a glass filled with water, and imagine stirring it with a spoon. The amount of pressure or power needed to stir the water is a normal PV. If you add a handful of marbles to the glass, it will be harder to stir because more pressure will be needed. Now imagine the glass is inside a box so you can’t see what is causing it to get harder to stir. It could be marbles (red blood cells), but it could also be stones (white blood cells) or woollen fibres (antibodies) or even sand (bacteria). Hence, an increased PV demonstrates an increase in pressure within the blood. But to determine the cause you’ll need to cross-check with other tests such as full blood count (FBC), looking at WBC, RBC and so on.
PV is mainly used to understand inflammation. It’s used in autoimmune conditions because it can indicate that additional antibodies and white cells are present, thickening or increasing pressure in the blood. PV can also be useful for monitoring against a baseline over time. However, it has limitations in that it is not specific to one disease and is therefore a crude global marker.
CRP
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a molecule that attracts and induces production of white blood cells (usually neutrophils), following inflammation. CRP is a marker for inflammation and infection and it can be used in autoimmune conditions because it can represent cellular signalling. CRP is also being used for chronic disease surveillance, as it is sensitive enough to represent vascular damage (raised CRP) and liver disease (low CRP). However, in some settings it can be expensive. Also, the signal can be lost as CRP is cleared, whilst ESR and PV may remain high for some time after the initial response.
The following storytelling offers a strategy to assist in interpreting a complex and dynamic process.
Storytelling: CRP is the fire alarm that goes off in the building, attracting fire engines (neutrophils/WBC) and causing a traffic jam in the street (PV). The structural support (fibrinogen scaffold) around the building is ESR. It’s unlikely that a small fire, as in the specific connective tissue damage caused by rheumatoid arthritis, will result in the entire building needing scaffolding. ESR is therefore only requested periodically, usually every six months. However, following major surgery or a large muscle trauma, ESR would be required.
Anti-inflammatory treatments
Anti-inflammatory treatments work along the pathways shown in Figure 8.1 (see page 59). Anti-TNF alpha treatments suppress the initial chemoattractant; drugs like methotrexate work by suppressing the neutrophil recruitment and replication (it was originally an anti-cancer cell proliferation drug); and drugs like aspirin and NSAIDS work to inhibit COX-2 and relieve the vasoconstriction.
To summarise, ESR represents tissue repair post-injury (fibrinogen), PV reflects components in the blood due to inflammation (more WBC, more antibodies), and CRP represents the tissue signalling in response to cellular damage.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


 CRP, PV, ESR and white cell type. Increased neutrophils are likely to indicate a bacterial infection or an autoimmune response. Raised lymphocytes are likely to be due to viral infection.
CRP, PV, ESR and white cell type. Increased neutrophils are likely to indicate a bacterial infection or an autoimmune response. Raised lymphocytes are likely to be due to viral infection.