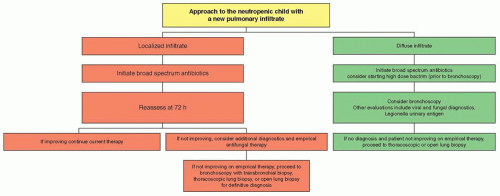
Figure 40.1 Effect of patient and pathogen factors on the host defense system that result in the immunocompromised host. |
(GVHD) may also compromise GI mucosal integrity and permit bacteria and/or fungi to translocate from the mesenteric capillary bed and portal venous system.
immunity, the TLR system may be especially relevant to immunocompromised patients when adaptive immunity is significantly suppressed. For instance, one study suggests an association between a donor TLR4 haplotype and the risk of invasive aspergillosis among recipients of hematopoeitic stem cell transplants from unrelated donors.15 Similarly, other TLR4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms have been associated with susceptibility to infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria,16 C. albicans,17 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).18
culturing in patients with cancer with Vascular Access Devices (VADs). Obtaining blood cultures from a peripheral site concomitantly with blood cultures from the central venous catheter may be helpful in differentiating central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLA-BSI) from non-CLA-BSI.29 This distinction may be important in optimizing management and identifying patients who could safely undergo catheter salvage from those who would benefit from catheter removal or adjunctive therapies.
ensure compliance with oral therapy, and the availability of transportation to a medical facility.
Several regimens, usually consisting of a cephalosporin, an aminoglycoside, and extended-spectrum penicillin, have been employed.
TABLE 40.1 Predominant Pathogens in Pediatric Cancer Patients | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TABLE 40.2 Commonly Used Antimicrobial Agents for Pediatric Cancer Patients | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
the fluoroquinolones and other antibiotics is uncommon. Fluoroquinolones are usually active against multiresistant organisms; ciprofloxacin, for example, exhibits activity against many of the resistant Gram-negative rods, including P. aeruginosa, Serratia, Enterobacter, and Klebsiella species that are responsible for serious infections in neutropenic and otherwise immunocompromised patients. Ciprofloxacin activity against streptococcal species, particularly α-hemolytic streptococci (e.g., Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus sanguis), is often inadequate.
associated with cisplatin or ifosfamide. Although azotemia in most pediatric patients is usually reversible, renal function may not return to normal levels after cessation of D-AmB in children who have received previous repeated or prolonged courses of this polyene. Moreover, return to pretreatment levels may require several months in some cases.
events, cutaneous reactions, and visual hallucinations. Hepatic enzyme abnormalities (elevated aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase) are dose-limiting adverse events for voriconazole. Transient altered perception of light, photopsia, or photophobia may occur following oral or IV dosing; these visual effects tend to appear and resolve early in the course of therapy over several days. Erythematous macular and desquamative rashes, most of which are mild, may occur in as many as 15% to 20% of patients receiving voriconazole. However, severe cutaneous reactions, including Stevens-Johnson, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and intense photosensitivity reactions may occur.80 Visual hallucinations occur significantly more often in patients receiving voriconazole versus L-AmB81; these hallucinations are distinct from the infusion-related visual side effects and may be dose related.
(HSV, CMV, varicella zoster virus [VZV], human herpesvirus 6 [HHV-6], and Epstein-Barr virus [EBV]), community-acquired respiratory viruses (influenza, parainfluenza, and RSV), adenoviruses, and polyoma viruses (JC virus [JCV] and BK virus [BKV]).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree