Chapter 50 Human Blood Group Antigens and Antibodies
Table 50-1 Blood Group Systems, Antigens, Expression, and Disease Associations
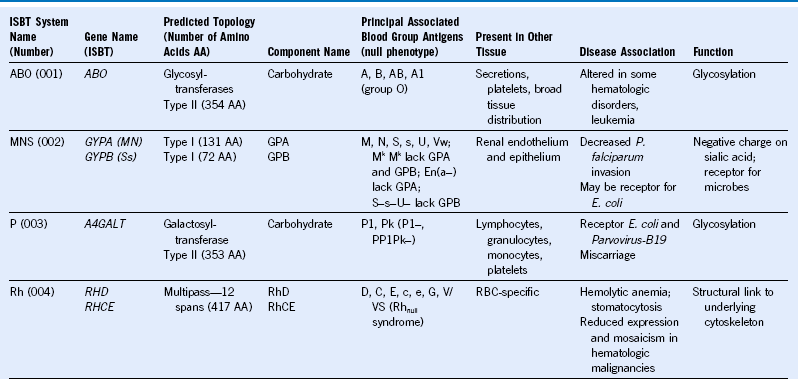
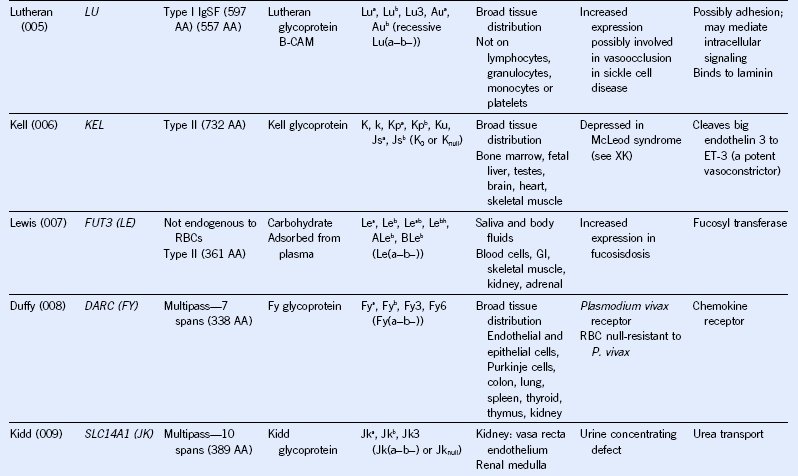
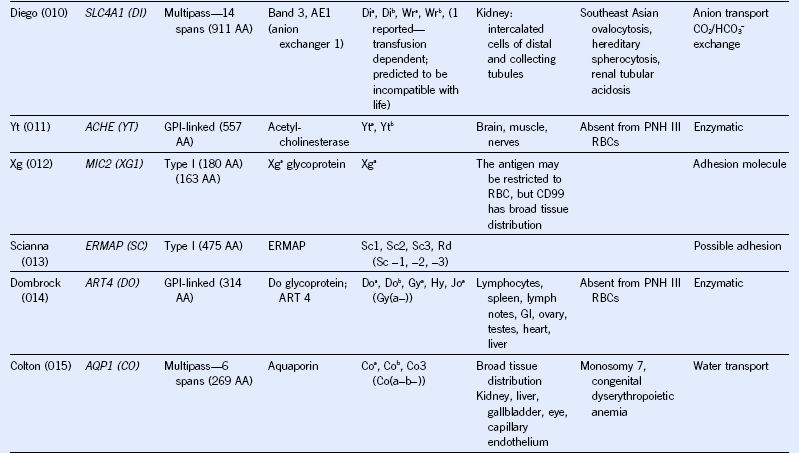
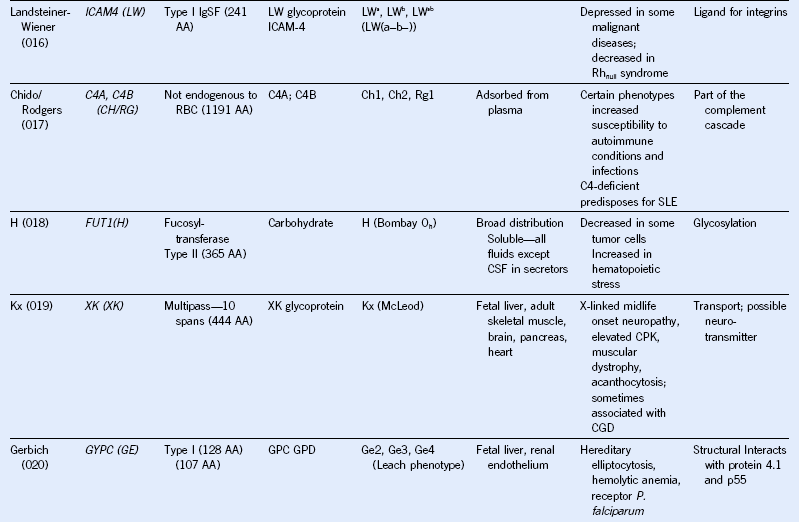
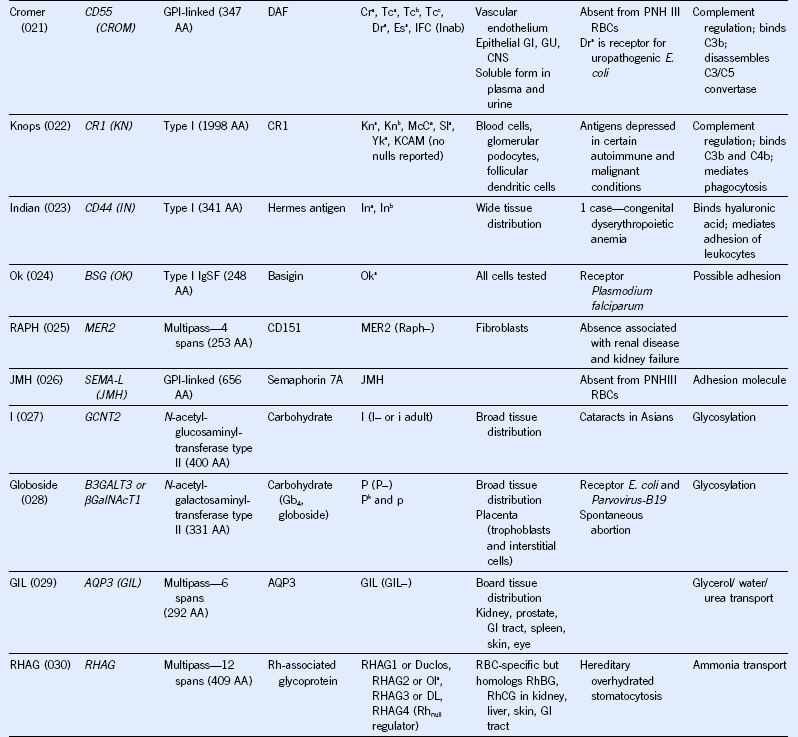
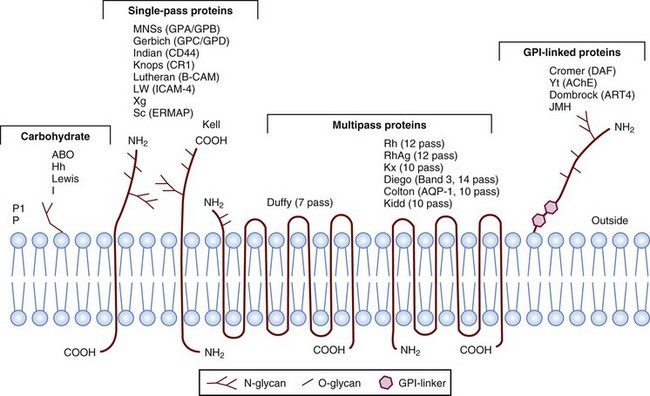
IgSF, Immunoglobulin super family; ISGN, International Society for Gene Nomenclature; type I, protein with a single pass through the RBC lipid bilayer with its amino terminus to the outside of the cell; type II, protein with a single pass through the RBC lipid bilayer with its amino terminus to the inside of the cell.
Table 50-2 Uses of DNA-Based Genotyping Assays for Transfusion Medicine