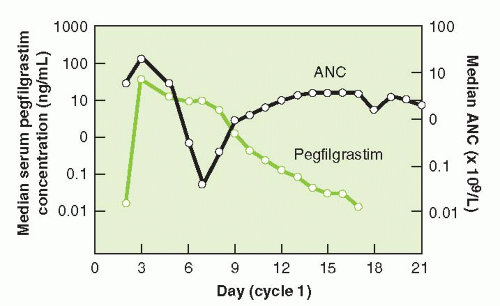
and functional activation of neutrophils. The half-life of pegfilgrastim is approximately 33 hours. Pegfilgrastim has saturable and self-regulating neutrophil-mediated elimination where neutrophil production is stimulated when neutrophil counts are low and rapid clearance of the agent occurs as neutrophil counts recover providing fresh receptors for binding. G-CSF receptor knockout mice exhibit a significantly slower clearance, longer half-life, and greater area under the curve (AUC) than wild-type mice for both filgrastim and pegfilgrastim.9 Similar concentration-time profiles of pegfilgrastim are observed in nephrectomized rats while nephrectomy results in a 60% to 70% decreased clearance of filgrastim.10 In clinical observations, serum clearance of pegfilgrastim decreased with increasing dose, consistent with neutrophil-mediated elimination while the elimination of pegfilgrastim is prolonged after chemotherapy, when the myeloid mass was reduced11 (Fig. 38-2). The apparent neutrophil-dependent clearance of pegfilgrastim results in prolonged circulation and action during recovery from neutropenia. Pegfilgrastim, like filgrastim, binds to cell surface G-CSF receptors and increases differentiation and functional activation of neutrophils.12
TABLE 38.1 Pharmaceutical characteristics of hematopoietic growth factors | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
by monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and conditioned lymphocytes.6,7 GM-CSF gene knockout mice exhibit normal hematopoiesis suggesting that it has minimal role in leukocytosis in the steady state.6,7 The GM-CSF receptor is expressed on neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, myeloid progenitors, myeloid leukemia cells, T lymphocytes, and dendritic cells. The GM-CSF receptor is composed of two subunits: an a subunit that is GM-CSF specific encoded on chromosome X/Y and a β subunit shared by other cytokines encoded on chromosome 22q31. Binding of GMCSF to its receptor leads to downstream signaling mainly through the JAK-STAT pathway but also through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK).6,7 GM-CSF stimulates the functional activity of
neutrophils, macrophages, monocytes, and eosinophils enhancing phagocytosis. Recombinant GM-CSF is available as sargramostim (yeast derived) and molgramostim (Escherichia coli derived) and is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (SCT), and stem cell mobilization. It is used experimentally as a vaccine adjuvant.
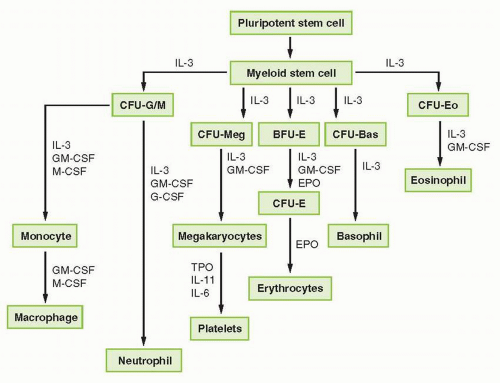 FIGURE 38-1 Representation of myeloid hematopoietic differentiation. Cytokines capable of stimulating specific cells are listed below such cells. See Table 38-2 for other names of cytokines shown here. BFU-E, burst-forming unit, erythroid; CFU-GEMM, colony-forming unit-granulocyte-erythrocyte-megakaryocyte macrophage; CFU-GM, colony-forming unit-granulocyte-macrophage; EPO, erythropoietin; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; SCF, stem cell factor; TPO, thrombopoietin. |
TABLE 38.2 Pharma cokinetic studies of hematopoietic growth factors | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
antibody formation that neutralized physiologic TPO occurred in 13 of 325 healthy volunteers and 4 of 650 oncology patients receiving as few as two doses of PEG-rHuMGDF.34 Therefore, alternative TPO agonists have been sought, lacking any sequence homology with endogenous TPO. These new agents include TPO peptide mimetics, nonpeptide mimetics, and agonist antibodies.35
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree