Chapter 71 Hematologic Manifestations of HIV/AIDS
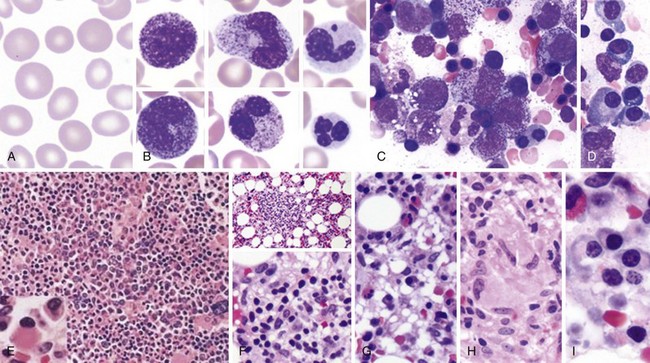
Peripheral Blood Smear and Bone Marrow Morphology in HIV/AIDS
AIDS, Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
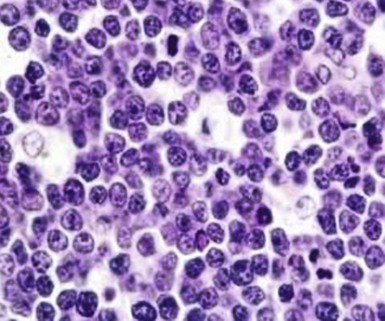
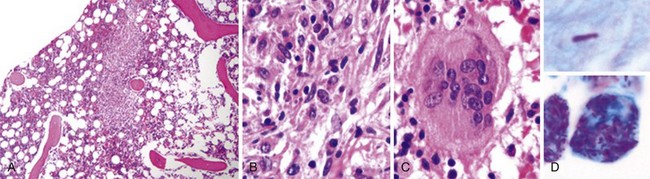
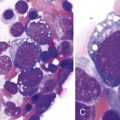
Figure 71-3 BURKITT LYMPHOMA INVOLVING THE BONE MARROW OF A PATIENT WITH ACQUIRED IMMUNODEFICIENCY SYNDROME (AIDS).
(Zhao X, Sun NC, Witt MD, et al: Changing pattern of AIDS: A bone marrow study. Am J Clin Pathol 121:393, 2004.)
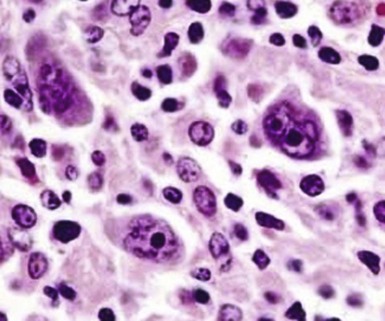
Figure 71-4 CLASSIC HODGKIN LYMPHOMA INVOLVING THE BONE MARROW OF A PATIENT WITH ACQUIRED IMMUNODEFICIENCY SYNDROME (AIDS).
(Zhao X, Sun NC, Witt MD, et al: Changing pattern of AIDS: A bone marrow study. Am J Clin Pathol 121:393, 2004.)
Table 71-1 Surveillance Case Definition for HIV Infection in Adults and Adolescents (Age Over 13 Years)
| Stage | Laboratory Evidence | Clinical Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Stage1 | Laboratory confirmation of HIV infection and CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of ≥500 cells/µL or CD4+ T-lymphocyte percentage of ≥29* | No AIDS-defining condition (see Table 71-2) |
| Stage 2 | Laboratory confirmation of HIV infection and CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of 200-499 cells/µL or CD4+ T-lymphocyte percentage of 14-28* | No AIDS-defining condition (see Table 71-2) |
| Stage 3 | Laboratory confirmation of HIV infection and CD4+ T-lymphocyte count of <200 cells/µL or CD4+ T-lymphocyte percentage of <14* | Documentation of an AIDS-defining condition with laboratory confirmation of HIV infection (see Table 71-2) |
| Stage unknown | Laboratory confirmation of HIV infection and no information on CD4+ T-lymphocyte count or percentage | No information on presence of an AIDS-defining condition |
AIDS, Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
*The CD4+ T-lymphocyte percentage is the percentage of the total lymphocyte count.
Table 71-2 Surveillance Definitions of AIDS-Defining Conditions
Pneumocystis jiroveci (carinii) Candidiasis: esophageal and systemic Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree


|