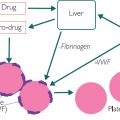
normal other LFT values.)
Troponins peak after seven hours and remain elevated for up to seven days. Troponins are muscle structure (contraction) proteins, which are released into the blood after muscle damage. Troponin I and C are markers of cardiac muscle damage, which is commonly used to differentiate between an angina and a myocardial infarction (MI). MI often results in significant troponin I release compared to angina, although care is needed when making a final interpretation, as some non-myocardial events (like tachycardia) can raise troponins. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may also have increased levels of troponins, given the ischaemic and hypoxic nature of the disorder.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree