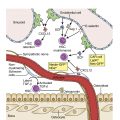
General Overview and Incidence
Pediatric hematology/hematopathology spans the spectrum of benign, malignant, and neoplastic mimickers. Neoplastic lymphoid, myeloid, and histocytic neoplasms follow criteria in the updated World Health Organization (WHO) 2017 classification similar to adults. Examples of common entities or those related to the updated WHO 2017 classification are presented for illustrative purposes. Many of these entities are covered in more depth in Chapter 8, Chapter 9 , 11, 12, and 16.
Etiology
- •
Familial
- •
Genetic predisposition
- •
Sporadic
- •
Immunodeficiency
- •
Posttransplant
- •
Viral cause
Clinical Presentation
- •
Fatigue
- •
Weight loss
- •
Organomegaly
- •
Fever
- •
Malaise
- •
Headache
- •
Rash
Laboratory Manifestations
- •
Leukocytosis ( Fig. 15.1A–C )
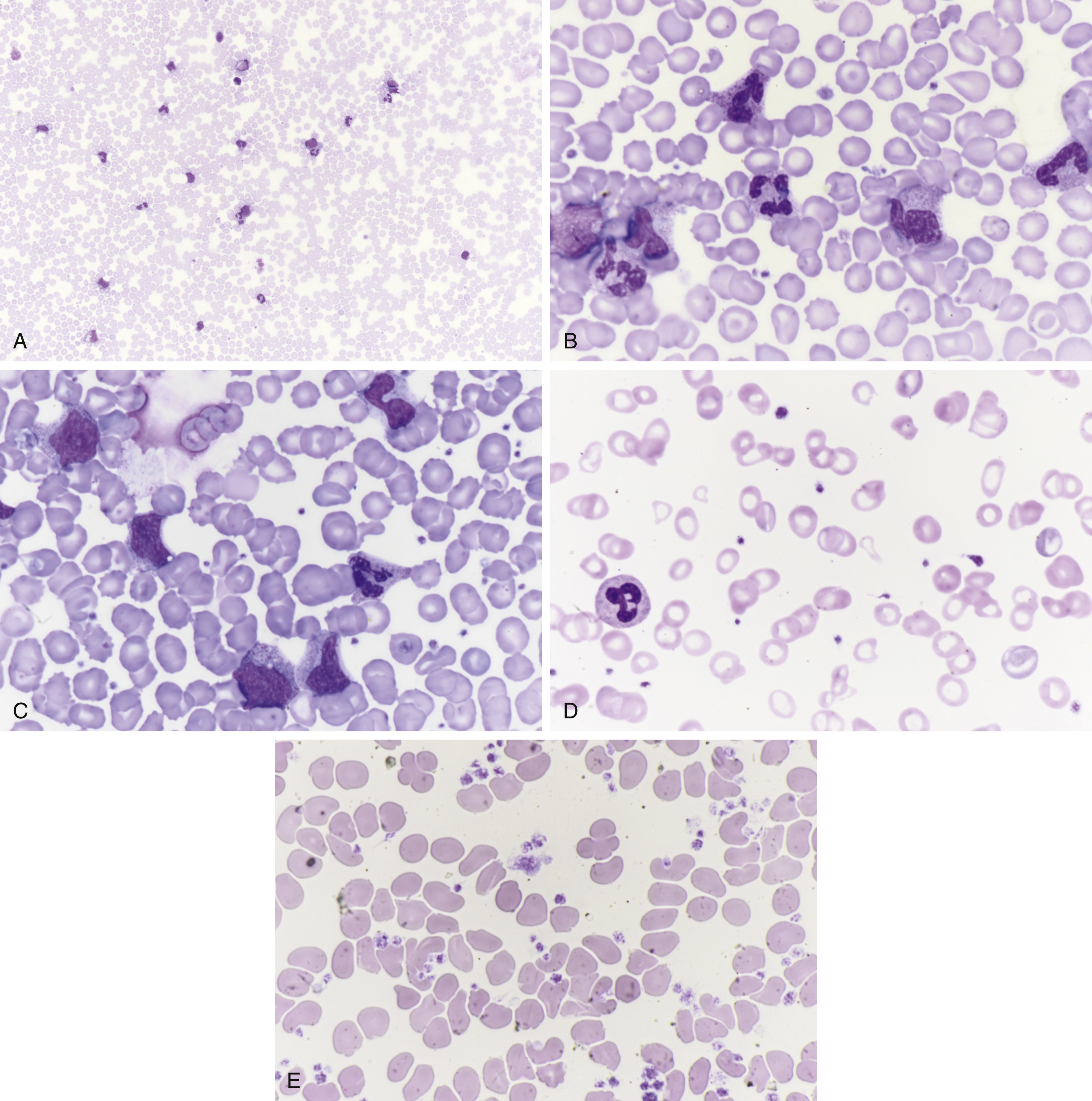
Fig. 15.1
(A) Leukemoid reaction at low power shows myeloid cells, neutrophils, and small lymphocytes. (B) Leukemoid reaction shows myeloid cells, neutrophils. (C) Leukemoid reaction shows myeloid cells, myelocytes, bands, and neutrophils. (D) Iron deficiency anemia with microcytic red blood cells, pale centers, small size, thrombocytosis, and an increase in platelets. (E) Thrombocytosis with increase in platelets with large forms.
- •
Leukemoid reaction versus leukemia
- •
Anemia ( Fig. 15.1D )
- •
Thrombocytopenia
- •
Thrombocytosis ( Fig. 15.1E )
Pediatric Pathologic Disease Entity Examples
- •
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) ( Fig. 15.2A–C )
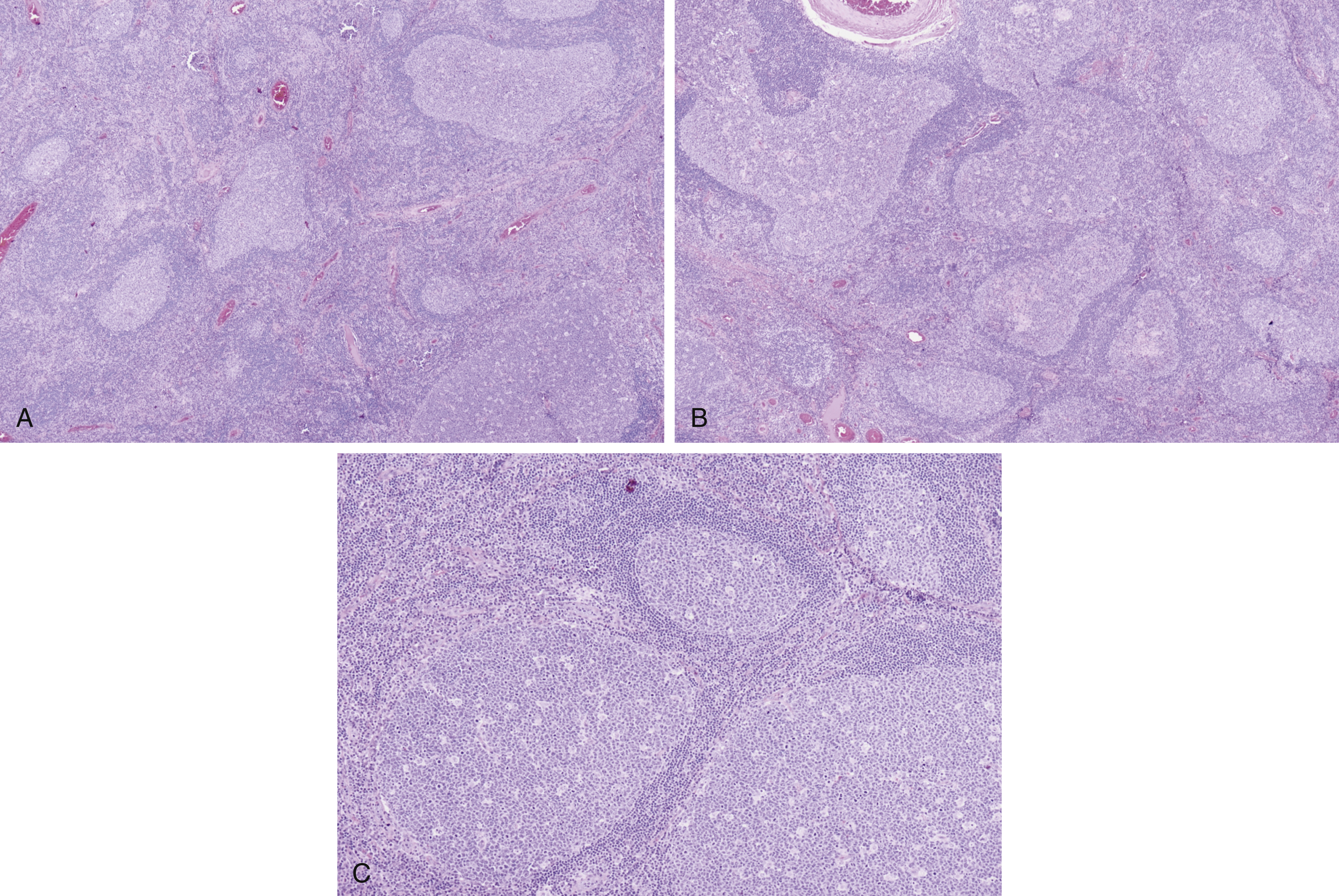
Fig. 15.2
(A) Variably sized germinal centers, ranging from small to large, with retained mantle zones, starry sky pattern, or tingible body macrophages in germinal centers. (B) Irregularly shaped germinal centers, serpentine-appearing, mimicking human immunodeficiency virus lymphadenitis, with retained mantle zones and tingible body macrophages in germinal centers. (C) Back-to-back germinal centers with retained mantle zones, starry sky pattern, and tingible body macrophages; florid follicular hyperplasia.
- •
Castleman disease ( Fig. 15.3A–C )
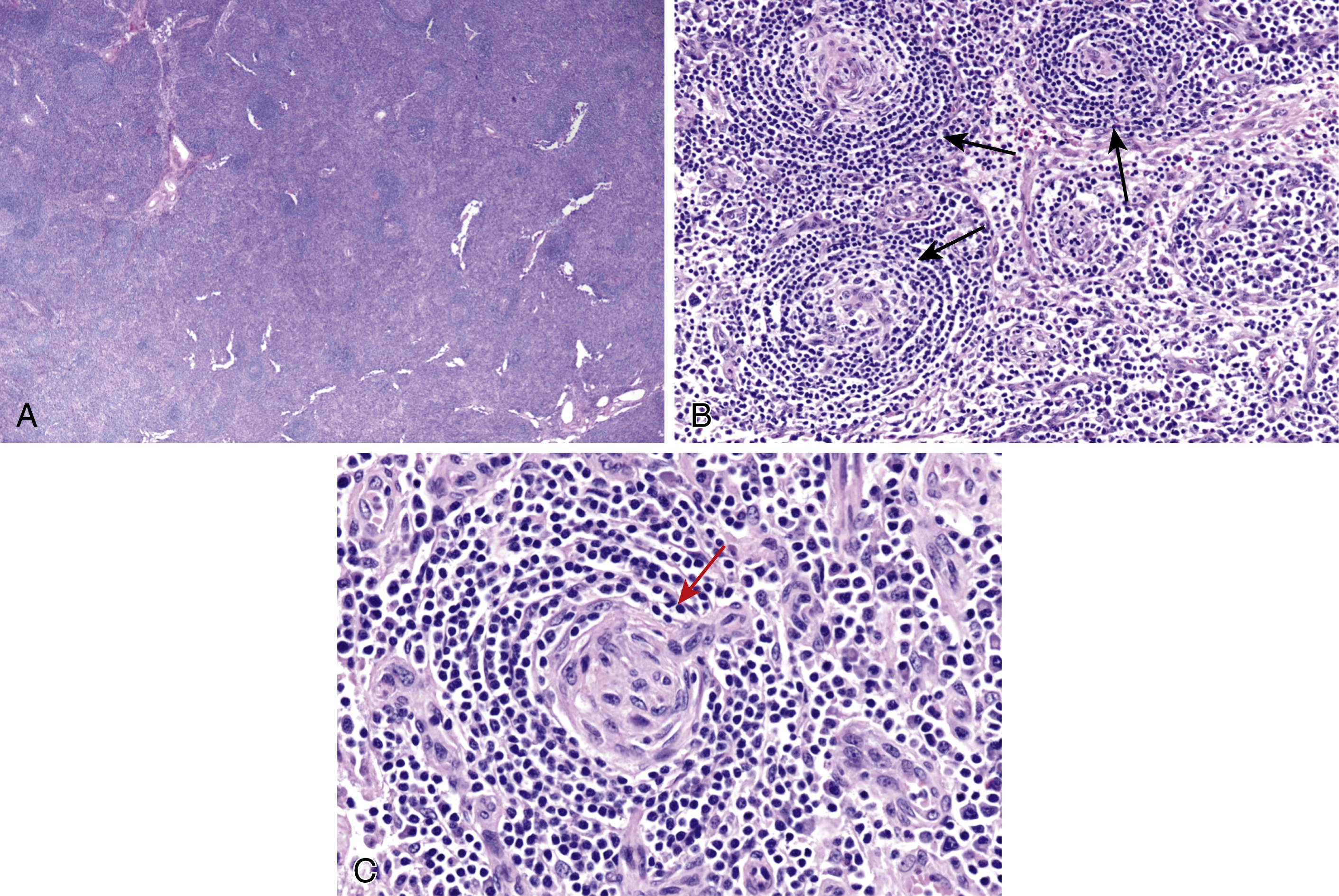
Fig. 15.3
(A) Lymphoid hyperplasia with regressed germinal centers, retained mantle zones, small germinal centers, and hyaline vascular interfollicular proliferation as seen in Castleman disease. (B) Small regressed germinal centers ( arrows , lollipop sign), onion skinning of mantle zone lymphocytes, and interfollicular plasma cells as seen in Castleman disease. (C) Small regressed germinal center, lollipop sign ( arrow ), onion skinning of mantle zone lymphocytes, and scattered plasma cells as seen in Castleman disease.
- •
Follicular lymphoma ( Fig. 15.4A–E )
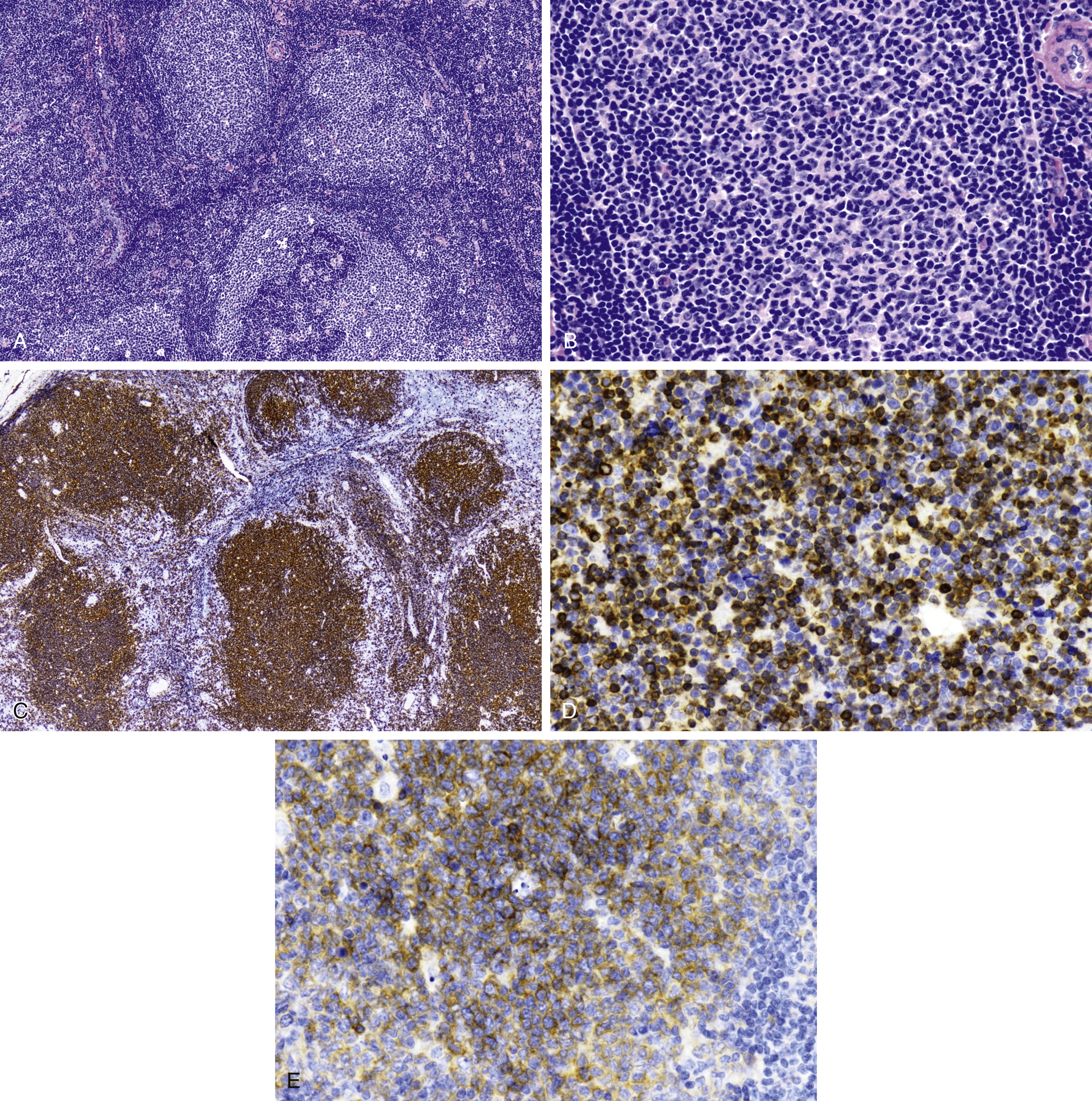
Fig. 15.4
(A) Nodular lymphoid proliferation with back-to-back follicles and attenuated mantle zones. (B) High-power view of neoplastic follicle shows atypical angulated small cleaved lymphocytes, with less than 5 centroblasts per high-power field in follicular lymphoma, grade 1. (C) Follicular or nodular lymphoid growth pattern is highlighted by CD20 in pediatric follicular lymphoma. (D) Neoplastic follicles overexpress BCL2 protein showing cytoplasmic localization. (E) CD10 is expressed in neoplastic lymphoid follicles in this example of pediatric follicular lymphoma.
- •
Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma ( Fig. 15.5A–C )
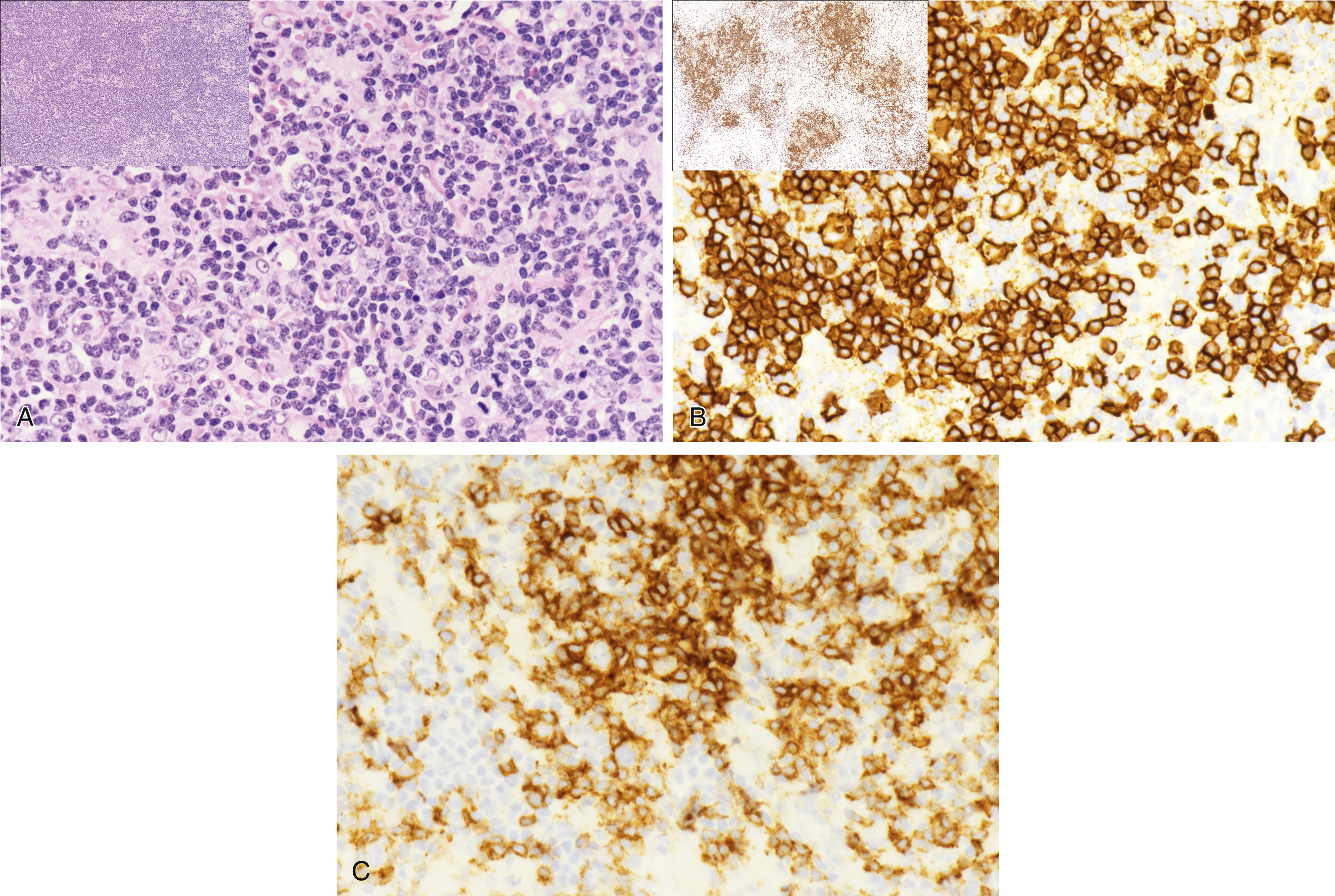
Fig. 15.5
(A) Low-power view shows a mottled lymphoid growth pattern ( upper left inset ). At higher power, L&H cell, popcorn, multilobulated nuclei ( arrow ) with small lymphocytes and histiocytes are seen in the background as seen in nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL). (B) CD20 at low power ( upper left inset ) highlights irregular, mottled expanded lymphoid nodules. At high power, atypical L&H cells are highlighted by CD20, with numerous small B cells in the background as seen in NLPHL. (C) PD-1 rosettes L&H cell in NLPHL. L&H, lymphocytic and histiocytic; PD-1 , programmed death protein 1.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree