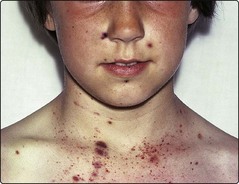
34 Thrombocytopenia can be simply defined as a blood platelet count of below 150 × 109/L. With the routine measurement of platelet number by automated cell counters it is a relatively common laboratory finding. Before initiating further investigations it is important to confirm that a low platelet count is genuine by careful inspection of the blood sample and film. Either a small clot in the sample or platelet clumping (Fig 34.1) can cause artefactual thrombocytopenia. Fig 34.1 Blood film showing clumping of platelets. Major causes of thrombocytopenia are listed in Table 34.1. Many of the diseases and syndromes are discussed elsewhere. Table 34.1 ITP, immune thrombocytopenia; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation. In general terms there are four possible processes leading to thrombocytopenia: Patients with thrombocytopenia are particularly prone to bleeding from mucous membranes. It should be emphasised that spontaneous bleeding is usually only seen with platelet counts of less than 10–20 × 109/L, although patients with associated platelet dysfunction may bleed at higher counts. Conjunctival haemorrhage, nose and gum bleeding and menorrhagia are all relatively common, with haematuria and melaena less frequent. Intracranial bleeding is of serious import but, thankfully, is rare. Possible examination findings include purpura and more extensive petechial haemorrhages involving the skin and mucous membranes (Fig 34.2). The retina should be routinely inspected for haemorrhages.
Thrombocytopenia
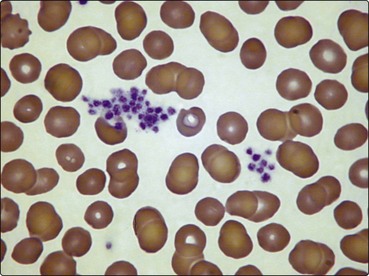
This phenomenon causes an artefactual thrombocytopenia in the automated blood count.
Causes
Pathogenesis
Disease examples
Failure of production
Leukaemia, myelodysplasia, aplastic anaemia, megaloblastic anaemia, myelofibrosis, malignant infiltration, infection, drugs1
Shortened lifespan
Immune
ITP, drugs1, connective tissue disorders, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, infection, post-transfusion purpura, neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia
Non-immune
DIC, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Sequestration
Hypersplenism, cardiopulmonary bypass surgery
Dilution
Massive blood transfusion
 Failure of marrow production. The bone marrow failure of haematological disease (e.g. aplastic anaemia, leukaemia) usually causes pancytopenia. However, thrombocytopenia may be the only sign of intrinsic marrow disease or marrow suppression associated with infection or chemotherapy.
Failure of marrow production. The bone marrow failure of haematological disease (e.g. aplastic anaemia, leukaemia) usually causes pancytopenia. However, thrombocytopenia may be the only sign of intrinsic marrow disease or marrow suppression associated with infection or chemotherapy.
 Shortened lifespan. Platelets can be destroyed in the circulation. The most common mechanism is an immunological reaction in clinical syndromes such as immune thrombocytopenia.
Shortened lifespan. Platelets can be destroyed in the circulation. The most common mechanism is an immunological reaction in clinical syndromes such as immune thrombocytopenia.
 Sequestration. Splenomegaly can cause low platelet counts because of pooling in the enlarged organ. The spleen is not necessarily massively enlarged.
Sequestration. Splenomegaly can cause low platelet counts because of pooling in the enlarged organ. The spleen is not necessarily massively enlarged.
 Dilution. Normal platelets are diluted by massive blood transfusion.
Dilution. Normal platelets are diluted by massive blood transfusion.
Clinical presentation
Thrombocytopenia