CHAPTER 1 The Importance of Nutrition
1.2 THE IMPORTANCE OF NUTRITION FOR HEALTH
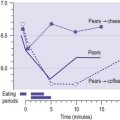
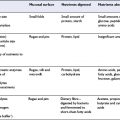
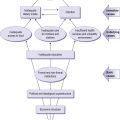
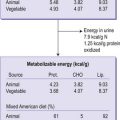
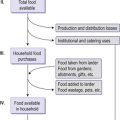
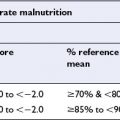
In developing countries, poverty and disease result in a significant proportion of the population consuming diets deficient in energy (overall calories from food whether fat, protein or carbohydrate) and specific vitamins and minerals. These diets have many adverse effects both in the short term and the long term. Growth in infancy and childhood is very often impaired, and this can affect education, ability to work, and childbearing, so that the long-term consequences are manifold. Additionally, vitamin or mineral deficiencies can lead to a range of conditions such as anaemia, bone abnormalities, increased susceptibility to infection, even blindness. Levels of child and maternal mortality in these countries are high.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree