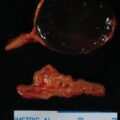
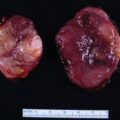
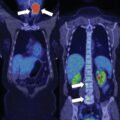
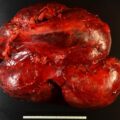
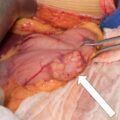
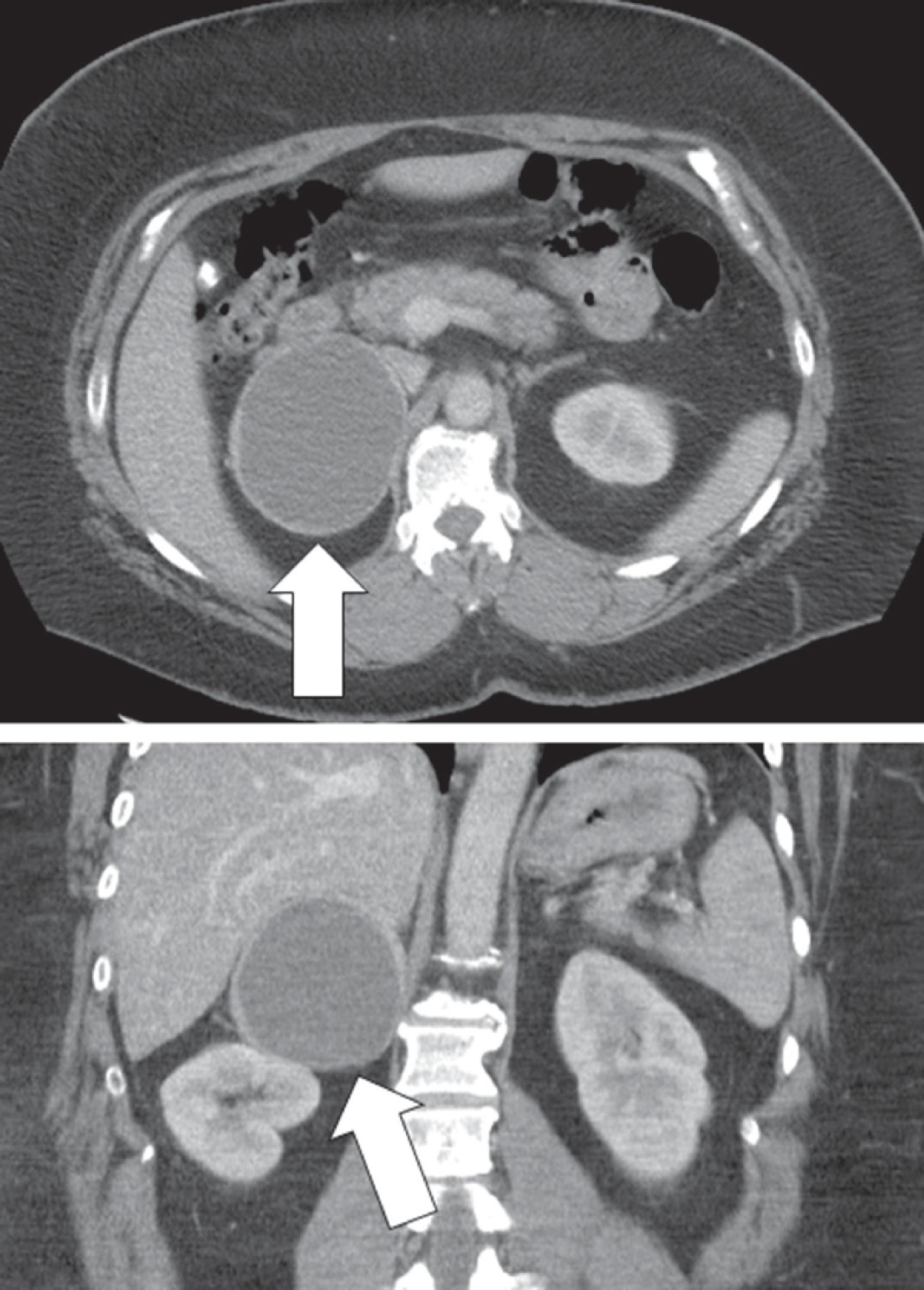
As pheochromocytomas enlarge, they develop areas of hemorrhagic necrosis. Most pheochromocytomas >4 cm in diameter have some cystic component that is evident on computed cross-sectional imaging. Some pheochromocytomas become progressively cystic to the point that the radiologist interprets them as adrenal cysts. Such a case is reported herein.
Case Report
The patient was a 50-year-old woman who presented with persistent and recurrent emesis that led to abdominal computed tomography (CT). Incidentally discovered on the CT scan was a 7 × 8.3–cm cystic right adrenal mass ( Fig. 43.1 ). The patient was morbidly obese (body mass index 51.6 kg/m 2 ). She had well-controlled hypertension of 7 years, duration that was treated with a β-adrenergic blocker (atenolol 100 mg daily) and an angiotensin receptor antagonist (valsartan 80 mg daily). She also had type 2 diabetes mellitus diagnosed 5 years previously and treated with metformin 500 mg once daily. Her blood pressure was 136/76 mmHg and heart rate was 76 beats per minute.
INVESTIGATIONS
The plasma fractionated metanephrines and 24-hour urine for fractionated metanephrines and catecholamines unequivocally confirmed the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma ( Table 43.1 ).
| Biochemical Test | Result | Reference Range |
| Sodium, mmol/L | 141 | 135–145 |
Potassium, mmol/L | 4.0 | 3.6–5.2 |
Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 | 0.6–1.04 |
Glycosylated hemoglobin, % | 7.0 | 4.2–5.6 |
Plasma metanephrine, nmol/L | 1.1 | <0.5 |
Plasma normetanephrine, nmol/L | 14.0 | <0.9 |
Aldosterone, ng/dL | 10 | ≤21 ng/dL |
Plasma renin activity ng/mL per hour | 14 | ≤0.6–3 |
24-Hour urine: | ||
Metanephrine, mcg | 1022 | <400 |
Normetanephrine, mcg | 6761 | <900 |
Norepinephrine, mcg | 239 | <80 |
Epinephrine, mcg | 9.1 | <20 |
Dopamine, mcg | 219 | <400 |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree