TESTS FOR THE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF HYPERCORTISOLISM
The traditional differential diagnostic tests for adrenal hyper-function, which focus on establishing the presence or absence of an intact feedback loop, are the dexamethasone suppression test and the metyrapone test. These tests are difficult to interpret and are quickly becoming obsolete. Because metyrapone is now hard to obtain, this test is included here mainly for historical interest.
DEXAMETHASONE SUPPRESSION TEST
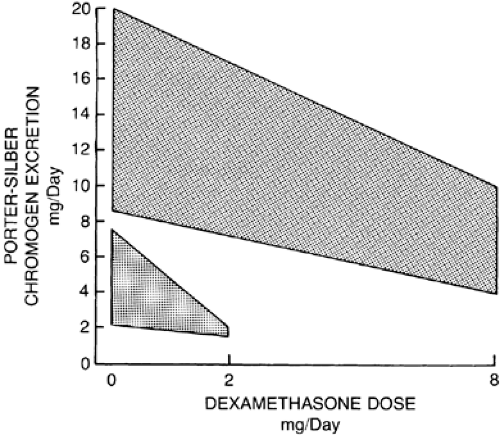
As developed by Liddle and colleagues, the dexamethasone suppression test measures the response of the Porter-Silber chromogens to the exogenous administration of dexamethasone.12 Urine collections are made for 6 days. Basal, or control, collections are made on days 1 and 2 of the test. Dexamethasone is given at a dose of 2 mg per day on days 3 and 4, and 8 mg per day on days 5 and 6. At some point during the test, the excretion of Porter-Silber chromogens is reduced by half in 95% of patients with Cushing disease (Fig. 74-3). It is reduced by less
than half in patients with other causes of Cushing syndrome. The urine free cortisol also can be used as an end point, but must decrease by 80% or more to indicate that suppression has occurred13 (see Chap. 75).
than half in patients with other causes of Cushing syndrome. The urine free cortisol also can be used as an end point, but must decrease by 80% or more to indicate that suppression has occurred13 (see Chap. 75).
METYRAPONE TEST
Metyrapone is a competitive inhibitor of the 11-hydroxylase enzyme (Fig. 74-4). It blocks the biosynthesis of cortisol. This leads to a reduced plasma cortisol concentration. If the feedback axis is intact, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion increases in an attempt to reestablish normal plasma cortisol concentrations. Because large amounts of 11-deoxy-cortisol are produced, 11-deoxycortisol and its metabolites raise the urinary concentration of Porter-Silber chromogens (Fig. 74-5). The traditional rule of thumb is that a doubling of the basal level of Porter-Silber chromogens indicates an intact feedback axis.14
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree