RENAL OSTEODYSTROPHY
Kevin J. Martin
Esther A. Gonzalez
Eduardo Slatopolsky
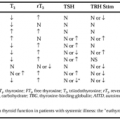
The association of skeletal disease with renal failure has been recognized for many years. The term renal osteodystrophy is used to encompass the many complex disorders of the skeleton that occur in patients with chronic renal disease and includes disorders with high bone turnover such as osteitis fibrosa as well as disorders with abnormally low bone turnover such as adynamic bone and osteomalacia; in addition, osteoporosis and, in children, growth retardation may be seen. Areas of osteosclerosis as well as cystic bone lesions may also be present. These disorders may occur together to variable degrees in any given patient. Thus, to prevent and treat bone disease in patients with renal failure, an understanding of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of the various types of bone disease is essential. The prevalence of the various types of bone disease encountered in patients with end-stage renal disease differs somewhat according to the modality of dialysis used, as illustrated in Figure 61-1.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree