Model name
Company
Patient port size [mm]
PET detector ring
FDA cleared
PET
CT
Diameter [mm]
[year]
ECAT Accel
CTI (Siemens)
562
N/A
824
2000
Discovery LS
GE Healthcare
600
700
927
2001
Biograph Duo
Siemens Healthcare
700
700
824
2002
Discovery ST
GE Healthcare
700
700
886
2003
Aquiduo
Toshiba Medical Systems
700
720
830
2005a
GEMINI TF Big Bore
Philips Healthcare
850
850
900
2009
Biograph TruePoint 16
Siemens Healthcare
700
700
842
2009
Ingenuity TF
Philips Healthcare
700
700
900
2011
TruFlight Select
Philips Healthcare
700
700
2011
Discovery PET/CT 600
GE Healthcare
700
700
810
Discovery PET/CT 610
GE Healthcare
700
700
886
2012
Discovery PET/CT 690
GE Healthcare
700
700
886
Discovery PET/CT 710
GE Healthcare
700
700
886
2012
Biograph mCT
Siemens Healthcare
780
780
842
2012
Celesteion
Toshiba Medical Systems
880
900
907
2014
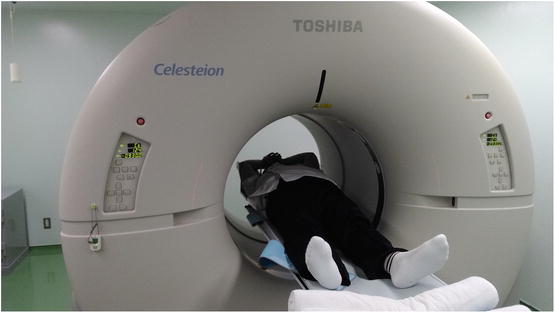
Fig. 10.1
The subject, who weighed 100 kg and was 176 cm tall, was larger than the average of Japanese male. However, there was plenty of space inside the gantry of the Celesteion to accommodate him
10.2 The Celesteion
The Celesteion PET/CT scanner combines a high-speed helical 16-slice CT scanner with a newly designed PET scanner, which harbors a lutetium–yttrium oxyorthosilicate (LYSO) scintillator block detector. The CT scanner has 16 rows of tube detectors with 994 detector cells per row, and each revolution of a detector can cover up to 32 mm. The scintillator block detector system of the PET scanner contains LYSO crystals arranged in 48 rings. The crystals have a transaxial length of 4 mm and an axial length of 4 mm, which are arranged in detection units (blocks) consisting of 48 × 16 crystals coupled to a photomultiplier. The 48-ring system can obtain 95 PET images (48 direct and 47 cross plane), separated by 2 mm and covering an axial FOV of 19.6 cm. The PET scanner can acquire data in three-dimensional (3D) configurations. The energy window of the system is set to 425–650 keV, and the coincidence time window is set to 1.6–4.2 ns, depending on the size of the FOV. The temporal resolution of the TOF is <450 ps.
10.2.1 Spatial Resolution
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) NU 2 2012 protocol [2] recommends using an F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) point source (size <1×1 ×1 mm) inside a 75-mm-long glass capillary tube with an inner diameter of 0.9–1.0 mm and a 0.4-mm-thick wall. The total activity should be low enough to keep dead-time losses and randomness below 5% of the total events. Data were acquired at three transaxial locations (x,y), i.e., (1,0, 10,0, 20,0) cm, and at two axial positions (z) within the PET FOV, i.e., center FOV. At least 2×106 coincidence events were acquired at each position. TOF information was not used in this measurement. No attenuation and scatter correction and no post-smoothing filter were applied. The transverse and axial resolutions at the different positions of the point source are summarized in Table 10.2, which lists the full width at half-maximum (FWHM) values at 1, 10, and 20 cm. These data are provided by Toshiba Medical Systems.
Table 10.2




Spatial resolution measured for the PET component of the Celesteion system (NEMA NU2-2012)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree