© Springer-Verlag Italia 2015
Raul Mattassi, Dirk A. Loose and Massimo Vaghi (eds.)Hemangiomas and Vascular Malformations10.1007/978-88-470-5673-2_3030. Principles of Treatment
(1)
Department of Vascular Surgery, Center for Vascular Malformations “Stefan Belov”, Clinical Institute Humanitas “Mater Domini”, Castellanza (Varese), Italy
(2)
Section Vascular Surgery and Angiology, Facharztklinik Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
(3)
Department of Vascular Surgery, A.O.G. Salvini Hospital, Garbagnate Milanese, Italy
Keywords
TruncularVascular malformationsExtratruncularSclerosisInterstitial laserIntroduction
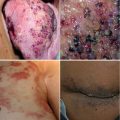
The decision process about the best treatment in congenital vascular malformations (CVM) should consider several factors: symptoms, possible complications of treatment, hemodynamic correction expected, invasivity of the procedure and others (see Chap. 24 for more details about clinical conditions and treatment). In other words, a balance between risks and advantage of the treatment is mandatory, as in any therapy. However, that decision may be much more difficult in CVM, due to the great variability of the disease. Several techniques are available, and often, best result is obtained by a combination of those procedures and also by a correct timing.
Truncular vascular dysplasia of veins and arteries is mainly treated by conventional vascular techniques, like revascularization surgery or reflux control surgical techniques in venous truncular dysplasia. Specific reconstructive techniques are available for some cases of truncular lymphatic defects (see Chap. 51). In arteriovenous truncular fistulas, complex devascularization techniques or, sometimes, endovascular procedures can be used.
Extratruncular forms are much more frequent and variable and have a tendency to recur because they are composed by a remnant of embryonic cells. To prevent recurrence, the ideal treatment should be a radical surgical removal, rather than a simple occlusion, that close the lumen of the dysplastic vessels but let the abnormal cells in site. Limited forms can be treated by surgery or by occlusion. In extensive infiltrations of organs, surgical resection is performed according to general surgical techniques. Occlusion techniques, by catheter or percutaneous, are available as an alternative or a combination with surgery.
Truncular CVM
Treatment of truncular CVM should be addressed to the correction of the hemodynamic disorder. Treatment options are the following [1, 2]:
Revascularization techniques (repair of a vascular defect), mainly surgical, (bypass, vascular plastics) are indicated in cases of congenital aneurysma, hypoplasia, or aplasia of the arteries and veins. Endovascular techniques, like covered stent implantation or balloon techniques, are also useful in these instances.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree