Plasma Cell Disorders
MGUS AND MULTIPLE MYELOMA (MM)
Patrick W. Burke
Hani Hassoun
Definition
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS): Premalignancy w/clonal plasma cell (PC) proliferation. No e/o other B-cell disease. <10% monoclonal PCs in BM, <3 g/dL serum M-protein, & no MM-related organ dysfunction s/s.
Multiple myeloma (MM): Malignant neoplasm of clonal PC. Almost always in BM plus Ig or light chain production → M-protein in blood/urine. Arises from MGUS.
Plasma cell Leukemia: Rare variant of MM (2-4% of MM) w/↑ aggressive course. Leukemic phase of MM → either 1° or 2° (antecedent MM). ↓↓ OS.
Epidemiology
MGUS: ↑ incidence w/age & in Western countries → 3% of adults >50 y.
7.5% in adults >85 y. ˜0.5-3% per y progress to MM.
MM: 1% all neoplasms. 13% of heme malignancies (2nd highest incidence in Western
World. ˜5.6/100000/y). 2% of all CA death.
U.S. 2012: ˜21700 new Dx. ˜10,710 death. ˜63000 total cases.
↑ Incidence African-Americans, Afro-Caribbeans, & Pacific Islanders.
Possible familial predisposition. Possible exposure risk (pesticides/herbicide).
Biology/Pathogenesis (N Engl J Med 2011;364:1046)
Multistep progression of genetic & BM microenvironment changes.
CG: 50% hyperdiploid (48-74 chromosomes); 50% nonhyperdiploid.
Translocations at IgH switch region: Chromosome 14(q32.33) → IgH gene enhancers/promoter juxtaposed in proximity to oncogene locus.
Three common translocation partners: MAF → t(14;16)(q32.33;q23); MMSET→ t(4;14)(p16;q32.33) (deregulation of MMSET & FGFR3); CCND1 → t(11;14) (q13;q32.33).
Molecular: ↑ expression of cyclins (D1, D2, & D3) & transcription factors.
MM: CG: Hyperdiploidy & nonhyperdiploid (hypodiploid, near tetraploid, & pseudohypodiploid) & IgH translocations seen.
Presentation
Workup
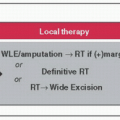
Initial H&P, CBC, basic metabolic profile (BMP), LFTs, electrolytes (esp. serum Ca), SPEP, UPEP, quantitative Igs, urine immunofixation (UIF), serum immunofixation (SIF), serum free light chain assay (SFLC), 24-h urine protein quantification, β2-microglobulin, albumin, BM aspirate & Bx (w/IHC, morphology, flow cytometry + CG w/karyotype + FISH), & x-ray skeletal survey. MRI or PET if bone sxs but negative skeletal survey.
Staging
Durie-Salmon (DS): MM “cell mass” c/w prognosis (response to CT & OS). 5 criteria (anemia, serum Ca, bone disease, M-protein, & serum Cr). Significantly c/w MM cell mass & prognosis. DS staging performed at Dx. 3 prognostic categories: Low (Stage 1), INT (Stage 2), & High (Stage 3).
Durie-Salmon MM Staging Criteria (Cancer 1975;36:842)
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
All criteria
– Hb > 10 g/dL
– Serum Ca nl (< 12 mg/dL)
-X-ray: Nl bone structure or solitary bone plasmacytoma
– ↓ M-Protein production rate
– IgG < 5 g/dL
– IgA < 3 g/dL
– Urine light chain
M-Component on electrophoresis < 4g/24 h
Meeting criteria neither for stages 1 or 3.
≥1 criterion
– Hb < 8.5 g/dL
– Serum Ca > 12 mg/dL
– Adv lytic bone lesions
– ↑ M-Protein production rate
– IgG > 7 g/dL
– IgA > 5 g/dL
– Urine light chain
M-Component on electrophoresis > 12 g/24 h
Subclassification
A: Serum cr < 2 mg/dL
B: Serum cr ≥ 2 mg/dL

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree