PHYSIOLOGY OF ALDOSTERONE
Part of “CHAPTER 80 – HYPERALDOSTERONISM“
SYNTHESIS
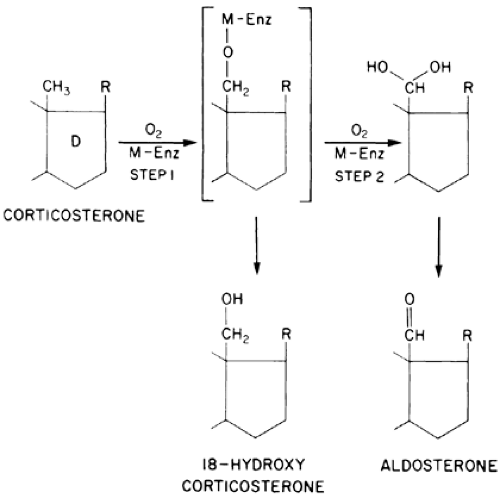
The zona glomerulosa cells of the adrenal cortex synthesize aldosterone from corticosterone in a two-step, mixed function oxidation reaction that is catalyzed by the enzyme corticosterone
methyl oxidase1 (Fig. 80-2). Normally, the adrenal glands secrete 60 to 200 μg aldosterone each day, depending on the state of sodium chloride and water balance of the body; the steroid circulates in the blood either free or loosely bound to albumin. Although some of the circulating aldosterone may be excreted in the urine in the free form, most of it is metabolized by the liver to tetrahy-droaldosterone and by the kidneys to aldosterone-18-glucuronide. Measurement of the excretion of the 18-glucuronide metabolite has been used as an index of aldosterone production; values obtained by this method range from 1 to 15 μg per day in normal persons receiving an unrestricted sodium chloride intake.
methyl oxidase1 (Fig. 80-2). Normally, the adrenal glands secrete 60 to 200 μg aldosterone each day, depending on the state of sodium chloride and water balance of the body; the steroid circulates in the blood either free or loosely bound to albumin. Although some of the circulating aldosterone may be excreted in the urine in the free form, most of it is metabolized by the liver to tetrahy-droaldosterone and by the kidneys to aldosterone-18-glucuronide. Measurement of the excretion of the 18-glucuronide metabolite has been used as an index of aldosterone production; values obtained by this method range from 1 to 15 μg per day in normal persons receiving an unrestricted sodium chloride intake.