I.B.001 Basophilic Stippling
I.B.001
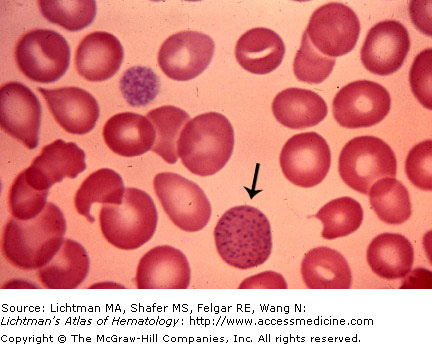
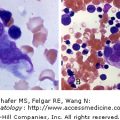
Basophilic stippling. Blood film. The arrow denotes a red cell with numerous, scattered prominent blue inclusions identified with a polychrome stain. Basophilic stippling may be present in a variety of conditions such as clonal sideroblastic anemia, polyclonal sideroblastic anemia, megaloblastic anemia, thalassemia, and others. It is particularly useful in distinguishing iron deficient erythropoiesis from thalassemia minor since it is absent in the former and present in the latter. It is also a marker of red cell dysmorphia in clonal anemia.
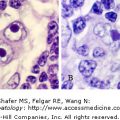
I.B.002 Basophilic Stippling
I.B.002
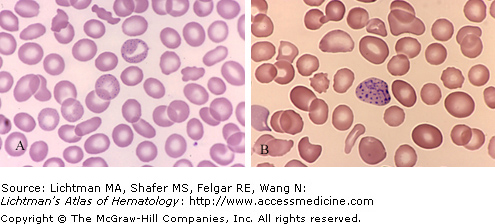
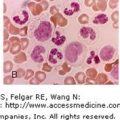
Basophilic stippling. Blood films. (A) Red cell with fine basophilic stippling at center top of field in patient with beta-thalassemia minor. (B) Red cell with coarse basophilic stippling in sideroblastic anemia. Basophilic stippling is a very important marker of disordered erythropoiesis seen notably in thalassemia and sideroblastic and megaloblastic anemia as well as other erythroid disorders. It is not present in iron deficiency anemia and helps in distinguishing that hypochromic-microcytic anemia from thalassemia minor in which careful examination of the blood film will usually permit identification of stippled red cells.