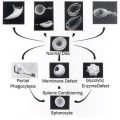
IV.A.001 Bernard-Soulier Disease
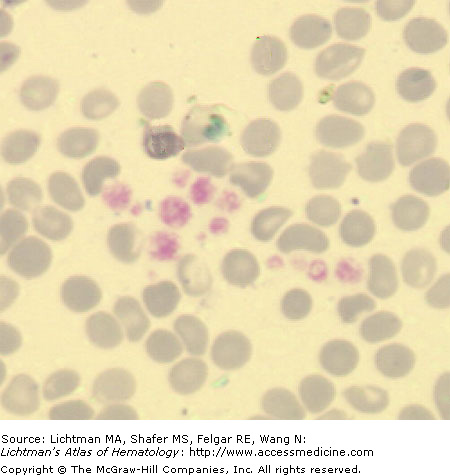
IV.A.002 Gray Platelet Syndrome (α-Granule Deficiency)
IV.A.003 Gray Platelet Syndrome (α-Granule Deficiency)
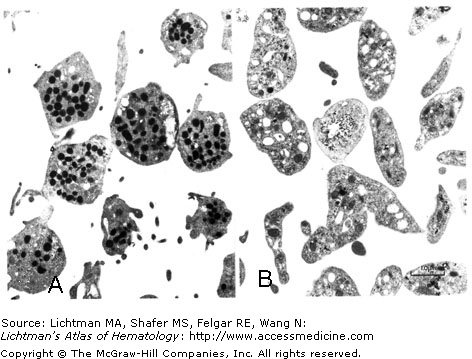
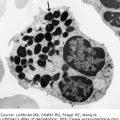
IV.A.004 Gray Platelet Syndrome: Transmission Electron Microscopy
IV.A.004
Gray platelet syndrome: Transmission electron microscopy. (A) Normal platelets. (B) Gray platelet syndrome. Note absence of α-granules, which imparts a bland gray appearance to platelets in the blood film. Occasional radio-opaque bodies are dense bodies. The platelets are rich in glycogen granules and are strongly periodic acid Schiff positive.
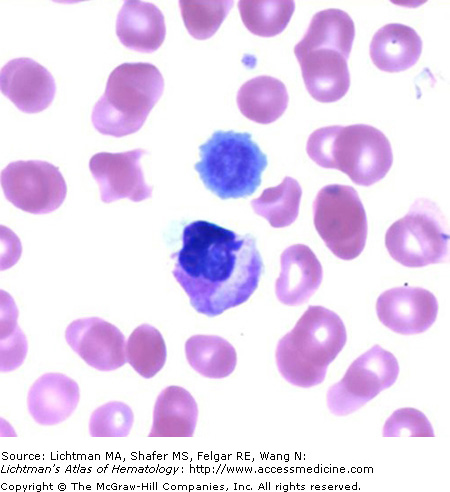
IV.A.005 May-Hegglin Anomaly
IV.A.005
May-Hegglin anomaly. A characteristic giant platelet. An abnormal neutrophil with classic gray-blue inclusions. Patients have a mutation of the MYH9 gene at chromosome region 22q12-13. The mutation results in disordered production of non-muscle myosin heavy-chain type IIA. This leads to macrothrombocytopenia, secondary to defective megakaryocyte maturation and fragmentation. Thrombocytopenia occurs in almost all patients, but severe bleeding is unusual. Individuals may bruise easily, and they may have recurrent epistaxis, gingival bleeding, menorrhagia, or excessive bleeding associated with surgical procedures. The neutrophil inclusions are precipitates of non-muscle myosin heavy-chain type IIA
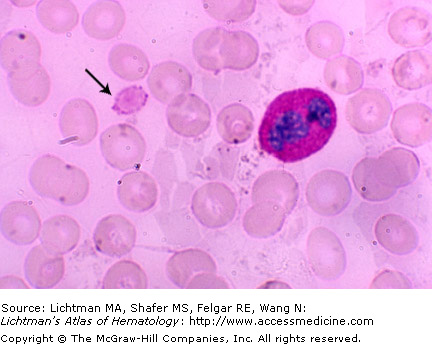
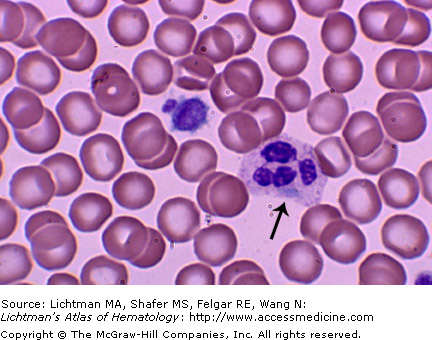
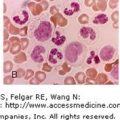
IV.A.006 May-Hegglin Disease
IV.A.006
May-Hegglin disease. Blood film. Gray-blue giant neutrophil inclusion (arrow) and a giant platelet, the size of a red cell. Patients have a mutation of the MYH9 gene at chromosome region 22q12-13. The mutation results in disordered production of non-muscle myosin heavy-chain type IIA. This leads to macrothrombocytopenia, secondary to defective megakaryocyte maturation and fragmentation. Thrombocytopenia occurs in almost all patients, but severe bleeding is unusual. Individuals may bruise easily, and they may have recurrent epistaxis, gingival bleeding, menorrhagia, or excessive bleeding associated with surgical procedures. The neutrophil inclusions contain precipitates of non-muscle myosin heavy-chain type IIA.
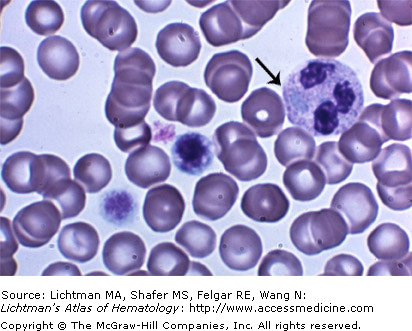
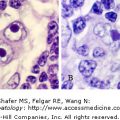
IV.A.007 May-Hegglin Disease
IV.A.007
May-Hegglin disease. Blood film. Gray blue giant neutrophil inclusion (arrow) and giant platelets, the size of a red cell. Patients have a mutation of the MYH9 gene at chromosome region 22q12-13. The mutation results in disordered production of non-muscle myosin heavy-chain type IIA. This leads to macrothrombocytopenia, secondary to defective megakaryocyte maturation and fragmentation. Thrombocytopenia occurs in almost all patients, but severe bleeding is unusual. Individuals may bruise easily, and they may have recurrent epistaxis, gingival bleeding, menorrhagia, or excessive bleeding associated with surgical procedures. The neutrophil inclusions contain precipitates of non-muscle myosin heavy-chain type IIA.
IV.A.008 Megathrombocyte