Myogenic, Lipogenic, and Neural Tumors
Sean V. McGarry
C. Parker Gibbs
Myogenic, lipogenic, and neural tumors affecting bone are much less common than they are in soft tissues. The three most common benign bone lesions that fall into these categories are leiomyoma of bone, lipoma of bone, and schwannoma. Lipoma of bone, also commonly referred to as intraosseous lipoma, has both intramedullary and parosteal subtypes. Only the bone lesions will be discussed here; their soft tissue counterparts are discussed in Chapter 11, Benign Soft Tissue Tumors.
Pathogenesis
Etiology
The etiology for this group of rare tumors is unknown. Chromosomal abnormalities well described in soft tissue lipomas have been reported in some parosteal lipomas.
Epidemiology
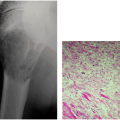
Leiomyoma of bone
Very rare
Age: Adults >30 (only exceptionally in children)
Gender: male = female
Common locations: facial bones (#1 = mandible) outweigh extragnathic bones (#1 tibia)
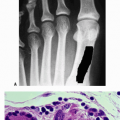
Lipoma of bone (intrausseous lipoma)
Rare (<0.1% primary bone tumors)
Majority intramedullary; few parosteal
Intramedullary lipoma
Age: second to eighth decade, with median age in 40s
Male:female 1.6:1
Common locations
Metaphyseal in long bones: proximal femur > tibia > fibula
Calcaneus
Parosteal lipoma
Age: peaks in fifth and sixth decades
Male > female (small difference)
Common locations
Diaphyseal in long bones: femur > humerus > tibia
Schwannoma
Very uncommon (<1% primary bone tumors)
Only benign osseous neurogenic tumor
Neurofibromas do NOT arise within bone.
Bone lesions in patients with neurofibromatosis-1 are NOT usually neurogenic tumors.
Common locations
Mandible and sacrum or spine
Pathophysiology
Same as for soft tissue counterparts (see Chapter 11)
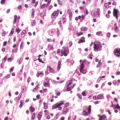
Histopathology
Leiomyoma of bone (see Fig. 11-30 in Chapter 11)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree