Chronic Inflammation and Esophageal Cancer
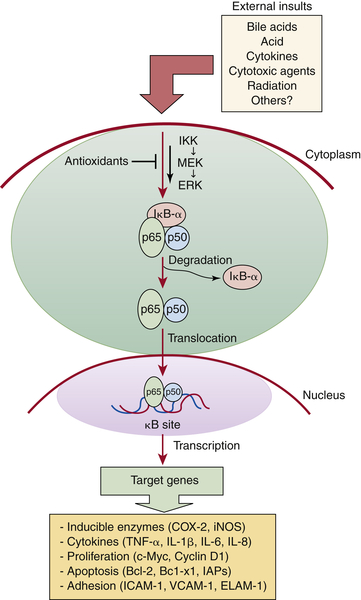
Nuclear Factor-Kappa B
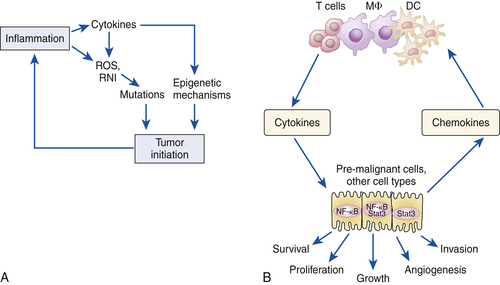
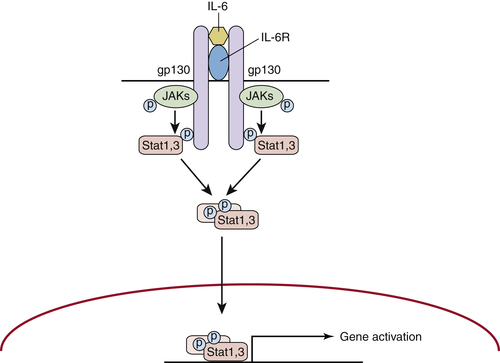
Activation of Additional Inflammatory Mediators and Esophageal Cancer
Environmental Carcinogenic Exposures and Esophageal Cancer
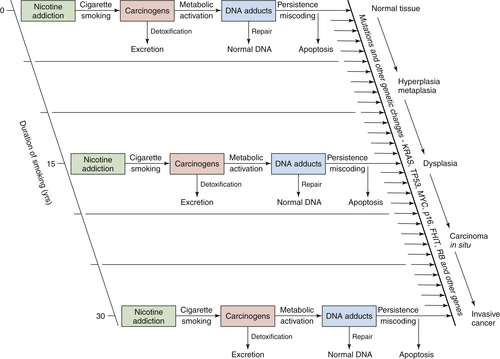
Tobacco Smoking
Alcohol
Diet
1. Global cancer statistics . CA Cancer J Clin . 2011 ; 61 : 69 – 90 .
2. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008 . Int J Cancer . 2010 ; 127 : 2893 – 2917 .
3. Curado M.P., Edwards B., Shin H.R., et al. Cancer Incidence in Five Continents. Vol 9. IARC Scientific Publication No 160; 2009
4. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations). Bethesda, Md: National Cancer Institute. Retrieved from http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09.
5. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of esophageal cancer . Semin Radiat Oncol . 2007 ; 17 : 2 – 9 .
6. Late presentation of esophageal cancer: observations in a multiracial South-East Asian population . J Dig Dis . 2010 ; 11 : 28 – 33 .
7. Tumors of the esophagus . In: Feldman M. , Friedman L.S. , Brandt L.J. , eds. Sleisenger & Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management . 9th ed . Philadelphia, Pa : WB Saunders ; 2010 : 745 – 770 .
8. Molecular evolution of the metaplasia-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence in the esophagus . Am J Pathol . 1999 ; 154 : 965 – 973 .
9. Histological precursors of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: results from a 13 year prospective follow up study in a high risk population . Gut . 2005 ; 54 : 187 – 192 .
10. Molecular biology of esophageal cancer in the genomics era . Surg Clin North Am . 2005 ; 85 : 539 – 553 .
11. Inflammation and cancer . Nature . 2002 ; 420 : 860 – 867 .
12. The contribution of Rudolf Virchow to the concept of inflammation: what is still of importance? J Nephrol . 2006 ; 19 : S102 – S109 .
13. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression . Nature . 2006 ; 441 : 431 – 436 .
14. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer . Cell . 2010 ; 140 : 883 – 899 .
15. Inducibility of κ immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein NF-κB by a post-translational mechanism . Cell . 1986 ; 47 : 921 .
16. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system . Annu Rev Immunol . 1994 ; 12 : 141 – 179 .
17. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors . Oncogene . 1999 ; 18 : 6853 – 6866 .
18. Potential role of NF-κB in esophageal adenocarcinoma: as an emerging molecular target . J Surg Res . 2009 ; 153 : 172 – 180 .
19. Activation of NFκB represents the central event in the neoplastic progression associated with Barrett’s esophagus: a possible link to the inflammation and overexpression of COX-2, PPARγ, and growth factors . Dig Dis Sci . 2004 ; 49 : 1075 – 1083 .
20. Association of activated transcription factor nuclear factor κB with chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in esophageal carcinoma . J Clin Oncol . 2006 ; 24 : 748 – 754 .
21. NF-κB activation in esophageal adenocarcinoma: relationship to Barrett’s metaplasia, survival, and response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy . Ann Surg . 2004 ; 239 : 491 – 500 .
22. Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with Barrett’s esophagus . N Engl J Med . 2011 ; 365 : 1375 – 1383 .
23. The risk of esophageal cancer in patients with achalasia: a population-based study . JAMA . 1995 ; 274 : 1359 – 1362 .
24. High-temperature beverages and foods and esophageal cancer risk-a systematic review . Int J Cancer . 2009 ; 125 : 491 – 524 .
25. Caustic ingestion and oesophageal cancer: intra- and peri-tumoral fibrosis is associated with a better prognosis . Eur J Cardiothorac Surg . 2010 ; 38 : 659 – 664 .
26. Nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway constitutively activated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and inhibition of growth of cells by small interfering RNA . Acta Biochim Biophys Sin . 2006 ; 38 : 318 – 326 .
27. Immunohistochemical study of nuclear factor-kB expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: prognostic significance and sensitivity to treatment with 5-FU . Dis Esophagus . 2012 ; 25 : 716 – 722 .
28. Cyclooxygenase-2 and its regulation in inflammation . Mediat Inflamm . 1996 ; 5 : 305 – 323 .
29. Cyclooxygenase 2 expression in Barrett’s esophagus and adenocarcinoma: ex vivo induction by bile salts and acid exposure . Gastroenterology . 2000 ; 118 : 487 – 496 .
30. Cyclo-oxygenase-2 is overexpressed in Chinese esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and correlated with NF-κB: an immunohistochemical study . Exp Mol Pathol . 2005 ; 79 : 214 – 218 .
31. Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 suppresses growth and induces apoptosis in human esophageal adenocarcinoma cells . Cancer Res . 2000 ; 60 : 5767 – 5772 .
32. COX-2 mRNA expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and effect by NSAID . Dis Esophagus . 2008 ; 21 : 9 – 14 .
33. A preliminary study on the postoperative survival of patients given aspirin after resection for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus or adenocarcinoma of the cardia . Ann Surg Oncol . 2009 ; 16 : 1397 – 1402 .
34. A phase II study of cisplatin, 5 fluorouracil (5-FU), radiation (RT) and celecoxib in patients with resectable esophageal cancer (EC): updated results from the Hoosier Oncology Group (HOG) study . J Clin Oncol . 2004 ; 22 : 4052 .
35. IL-6: from its discovery to clinical applications . Int Immunol . 2010 ; 22 : 347 – 352 .
36. The JAK-STAT signaling pathway: input and output integration . J Immunol . 2007 ; 178 : 2623 – 2629 .
37. IL-6 triggers cell growth via the Ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade . J Immunol . 1997 ; 159 : 2212 – 2221 .
38. Increased expression and secretion of interleukin-6 in patients with Barrett’s esophagus . Clin Cancer Res . 2004 ; 10 : 2020 – 2028 .
39. Bile acid and inflammation activate gastric cardia stem cells in a mouse model of Barrett’s-like metaplasia . Cancer Cell . 2012 ; 21 : 36 – 51 .
40. Higher importance of interleukin 6 than classic tumor markers (carcinoembryonic antigen and squamous cell cancer antigen) in the diagnosis of esophageal cancer patients . Dis Esophagus . 2012 ; 25 : 242 – 249 .
41. The hallmarks of cancer . Cell . 2000 ; 100 : 57 – 70 .
42. Loss of heterozygosity involves multiple tumor suppressor genes in human esophageal cancers . Cancer Res . 1992 ; 52 : 6525 – 6530 .
43. Alterations in p53 and pRb pathways and their prognostic significance in oesophageal cancer . Eur J Cancer . 2002 ; 38 : 832 – 841 .
44. Prospective study of cyclin D1 overexpression in Barrett’s esophagus: association with increased risk of adenocarcinoma . J Natl Cancer Inst . 2000 ; 92 : 1316 – 1321 .
45. The less harmful cigarette: a controversial issue. A tribute to Ernst L. Wynder . Chem Res Toxicol . 2001 ; 14 : 767 – 790 .
46. A prospective study of tobacco, alcohol, and the risk of esophageal and gastric cancer subtypes . Am J Epidemiol . 2007 ; 165 : 1424 – 1433 .
47. Tobacco smoke carcinogens, DNA damage and p53 mutations in smoking-associated cancers . Oncogene . 2002 ; 21 : 7435 – 7451 .
48. Platinum-DNA adduct, nucleotide excision repair and platinum based anti-cancer chemotherapy . Cancer Treat Rev . 1998 ; 24 : 331 – 344 .
49. DNA damage control by novel DNA polymerases: translesion replication and mutagenesis . J Biol Chem . 2001 ; 276 : 25639 – 25642 .
50. Smoking, type of alcoholic beverage and squamous-cell oesophageal cancer in northern Italy . Int J Cancer . 2000 ; 86 : 144 – 149 .
51. Carcinogenetic impact of alcohol intake on squamous cell carcinoma risk of the oesophagus in relation to tobacco smoking . Eur J Cancer . 2007 ; 43 : 1188 – 1199 .
52. Acetaldehyde: a cumulative carcinogen in humans . Addiction . 2009 ; 104 : 551 – 553 .
53. Genetic polymorphisms and esophageal cancer risk . Int J Cancer . 2007 ; 121 : 1643 – 1658 .
54. High salivary acetaldehyde after a moderate dose of alcohol in ALDH2-deficient subjects: strong evidence for the local carcinogenic action of acetaldehyde . Alcohol Clin Exp Res . 2000 ; 24 : 873 – 877 .
55. Genetic polymorphisms of ADH2 and ALDH2 association with esophageal cancer risk in southwest China . World J Gastroenterol . 2007 ; 13 : 5760 – 5764 .
56. Alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase gene polymorphisms and oropharyngolaryngeal, esophageal and stomach cancers in Japanese alcoholics . Carcinogenesis . 2001 ; 22 : 433 – 439 .
57. Epidemiologic evidence of the protective effect of fruit and vegetables on cancer risk . Am J Clin Nutr . 2003 ; 78 : 559 – 569 .
58. Fruit and vegetable intake and esophageal cancer in a large prospective cohort study . Int J Cancer . 2007 ; 121 : 2753 – 2760 .
59. Ecological study on the risks of esophageal cancer in Ci-Xian, China: the importance of nutritional status and the use of well water . Int J Cancer . 1999 ; 83 : 620 – 624 .
60. Nitrosamine and related food intake and gastric and oesophageal cancer risk: a systematic review of the epidemiological evidence . World J Gastroenterol . 2006 ; 12 : 4296 – 4303 .
61. Preformed N-nitroso compounds in foods and beverages . Cancer Surv . 1989 ; 8 : 295 – 321 .
62. Ghavamzadeh A, Moussavi A, Jahani M, et al. Esophageal cancer in Iran. Semin Oncol. 200;28:153-157.
63. The relationship between the ingestion of hot coffee and intraesophageal temperature . Gut . 1972 ; 13 : 24 – 30 .
64. Thermal irritation and esophageal cancer in northern Iran . Cancer . 1987 ; 60 : 1909 – 1914 .
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree