MESSENGER RNA PROCESSING
The hnRNA product of gene transcription is rapidly processed in the nucleus with a half-time (t1/2) of 5 to 20 minutes (Fig. 3-8).22 Three major events transform the large heterogeneous RNA precursors into the mature RNA. First, at the 5′ end of hnRNA, a 7methylguanosine residue is added to the first nucleotide of the transcript by means of a 5′-5′ triphosphate bond after 20 to 30 nucleotides have been polymerized. This reaction is rapid (t1/2 < 1 minute) and is catalyzed by the 5′-capping enzyme, including guanylyl and methyl transferases. The 5′-methyl cap associates with 5′-cap binding proteins, which favors the formation of a stable 40S translation-initiation complex and increases the stability and efficiency of translation of the eventual mature mRNA.23
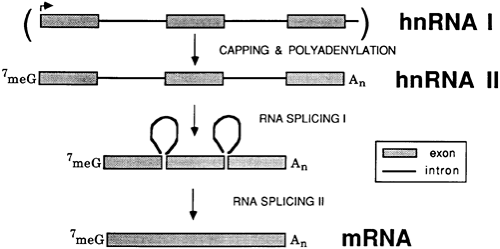 FIGURE 3-8. Gene transcription and RNA processing. The initial RNA transcript is known as heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA I). It contains exons and introns of the structural region and rapidly undergoes 5′ capping with 7methylguanosine (7meG) and 3′ polyadenylation (An) (hnRNA II). Little heterogeneous nuclear RNA has been detected without 5′ cap or 3′ polyadenylated (poly[A]) tails. In a slower process, introns are removed by RNA splicing followed by religation of exon sequences. The mature messenger RNA (mRNA) is composed of fused exon sequences and contains a 5′ cap and a 3′ poly(A) tail.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|