There should be histological confirmation of the disease. The regional lymph nodes are those appropriate to the site of the primary tumour. See Regional Lymph Nodes under Skin Tumours. The extent of the tumour is classified after excision, see pT, page 000. Note The pT classification of malignant melanoma considers the following histological criteria: Note * pTX includes shave biopsies and curettage that do not fully assess the thickness of the primary. The pN categories correspond to the N categories. (Figs. 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 362, 364, 365, 366, 367). Note
MALIGNANT MELANOMA OF SKIN (ICD‐O‐3 C44, C51.0, C60.9, C63.2)
Rules for Classification
Regional Lymph Nodes
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
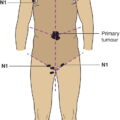
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
Metastasis in one regional lymph node or intralymphatic regional metastasis without nodal metastasis
N1a
Only microscopic metastasis (clinically occult) (Fig. 357)
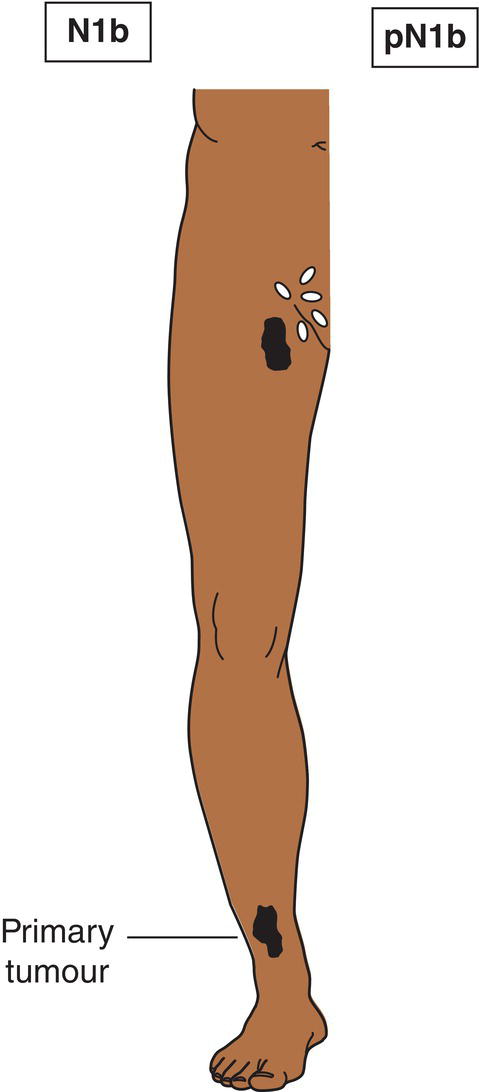
N1b
Macroscopic metastasis (clinically apparent) (Fig. 358)
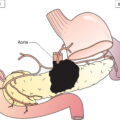
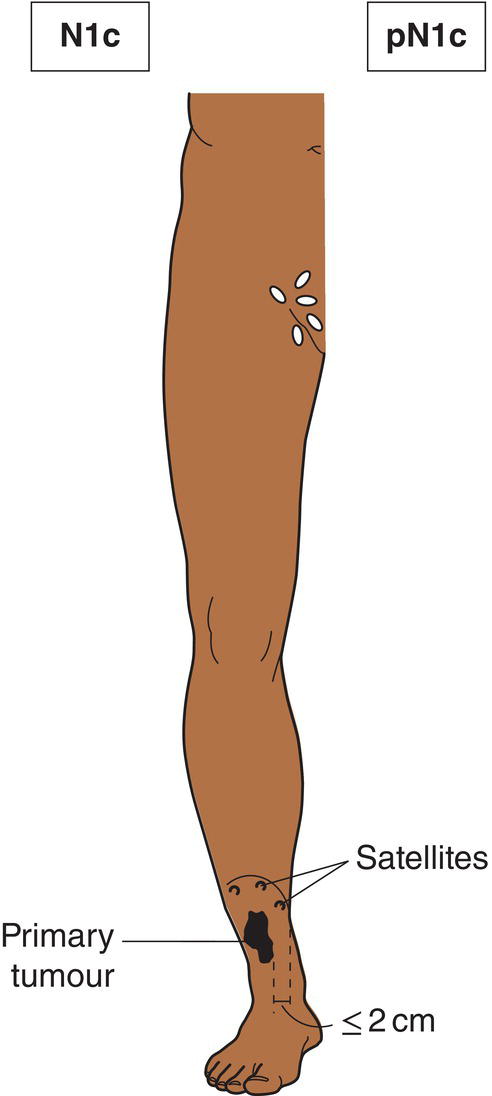
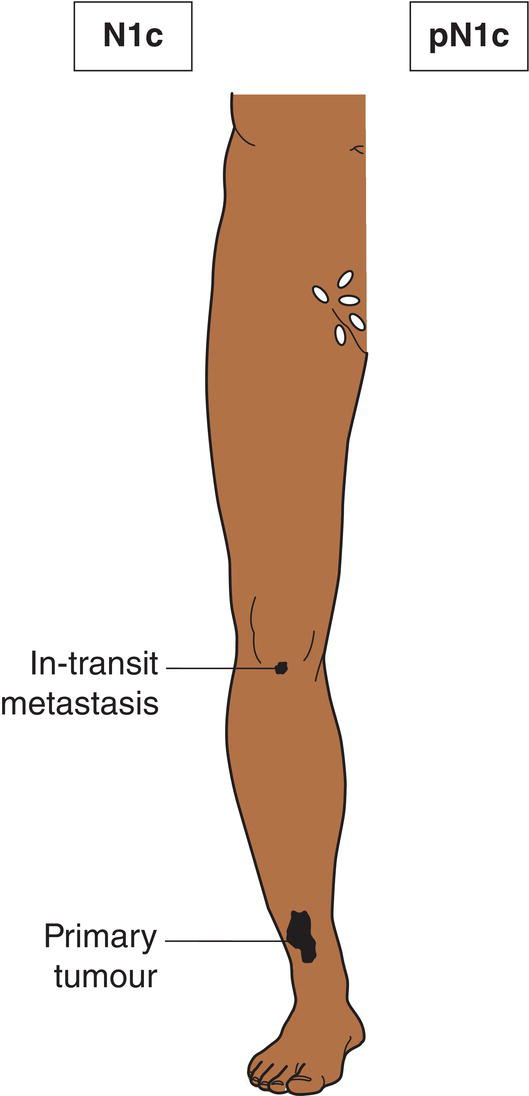
N1c
Satellite or in‐transit metastasis without regional nodal metastasis (Figs. 359, 360)
N2
Metastasis in two or three regional lymph nodes or intralymphatic regional metastasis with regional metastasis
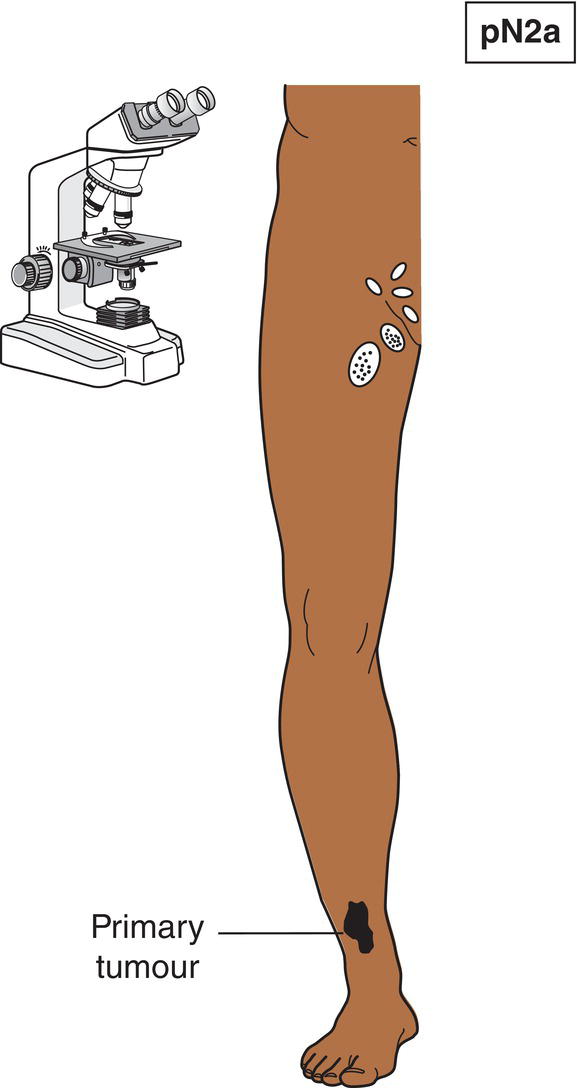
N2a
Only microscopic nodal metastasis (Fig. 361)
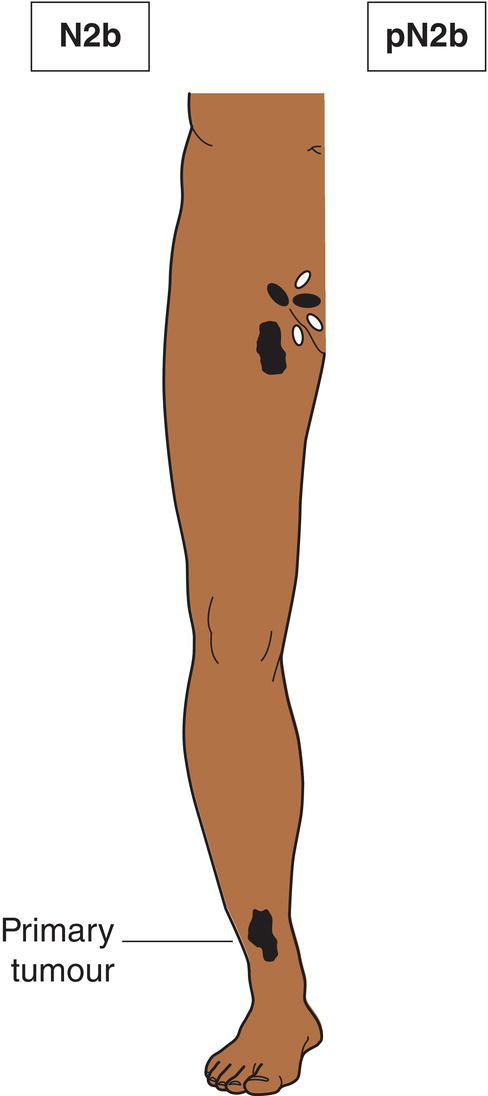
N2b
Macroscopic nodal metastasis (Fig. 362)
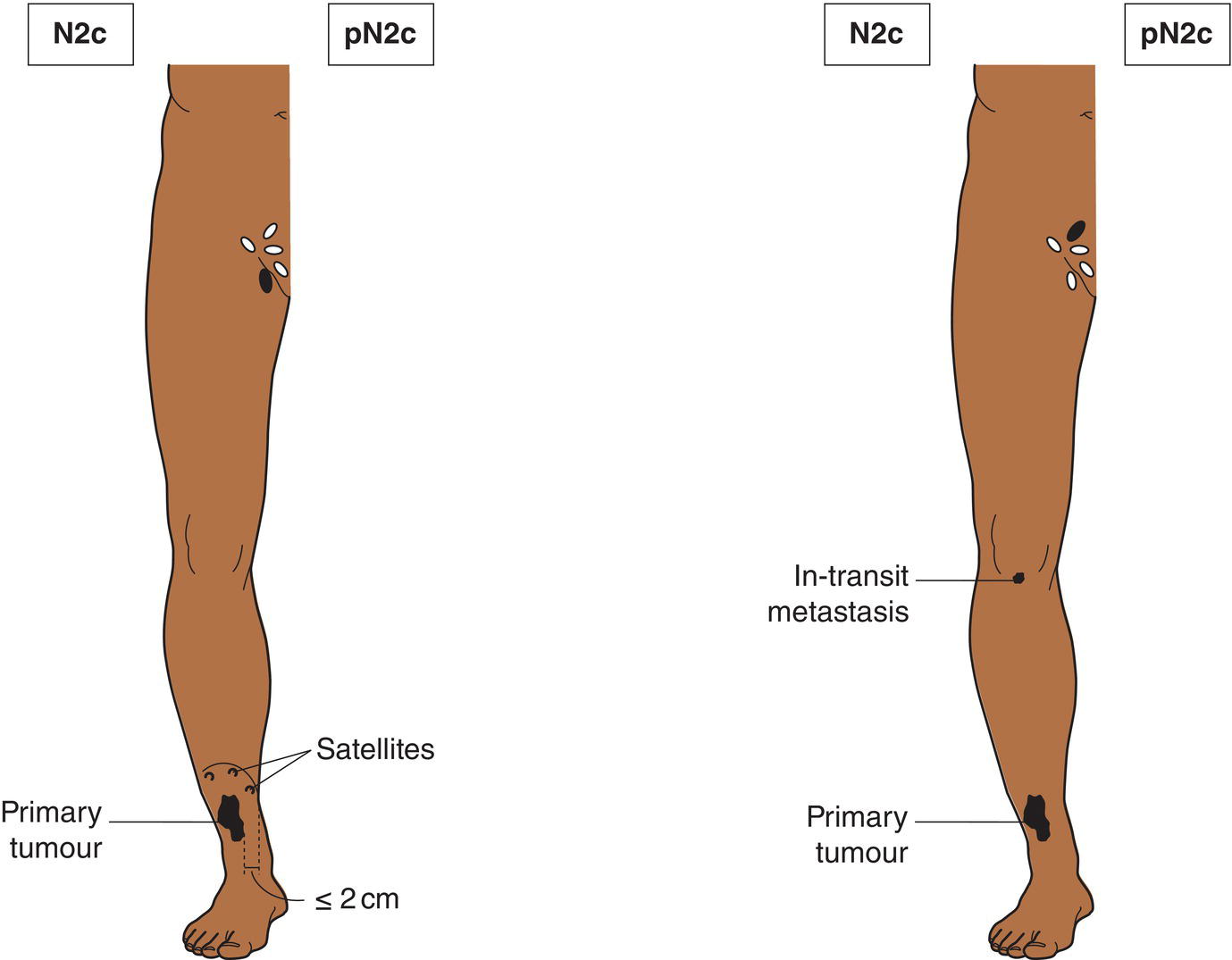
N2c
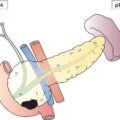
Satellite or in‐transit metastasis with only one regional nodal metastasis (Fig. 363)
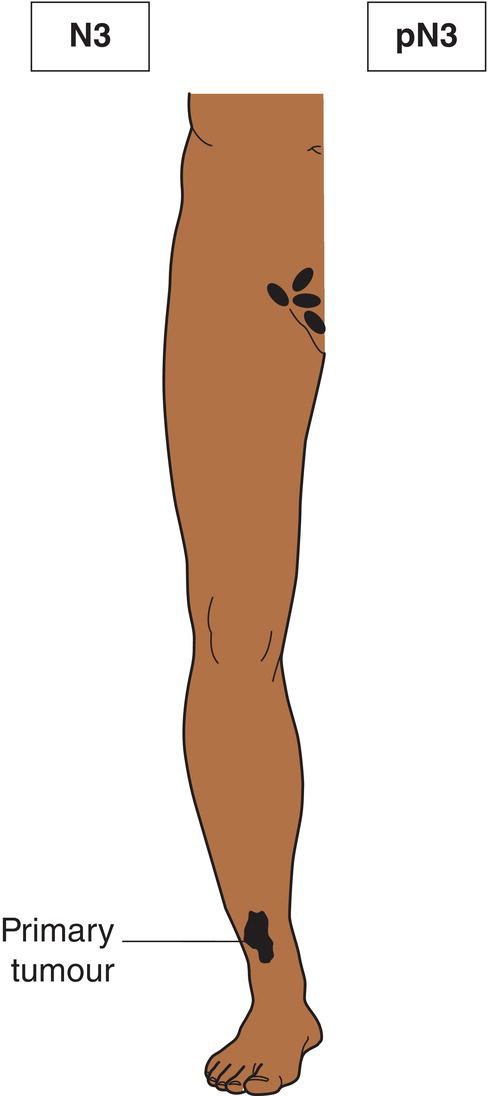
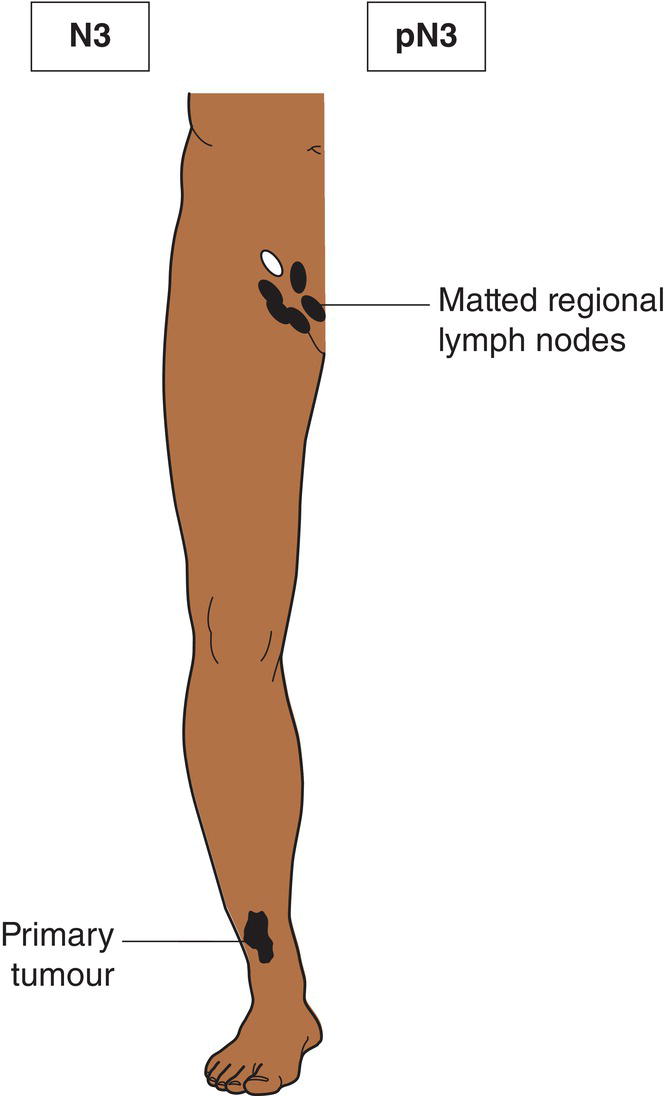
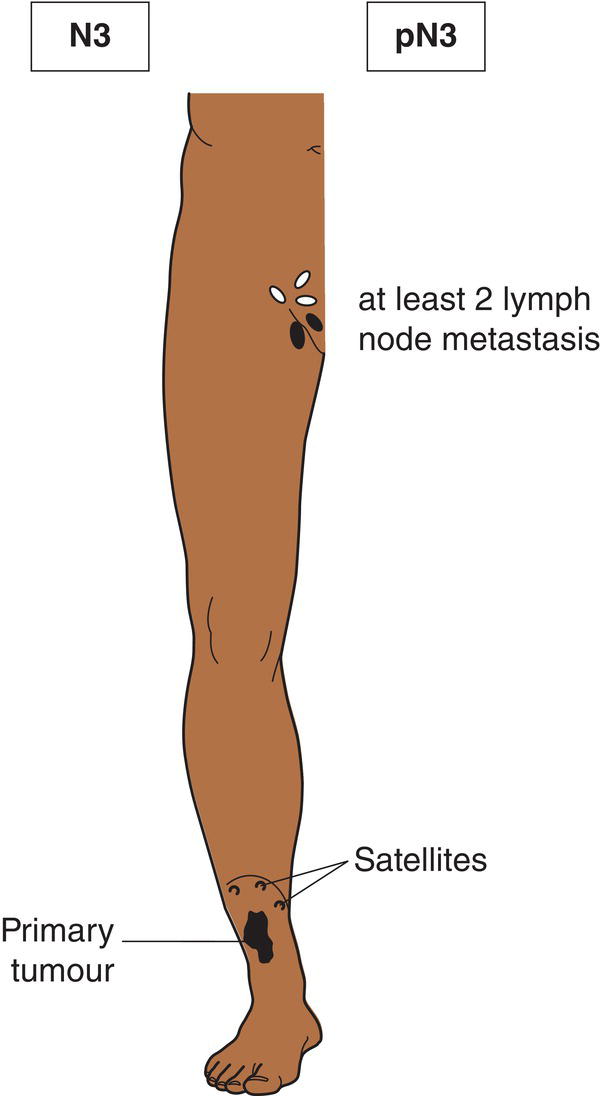
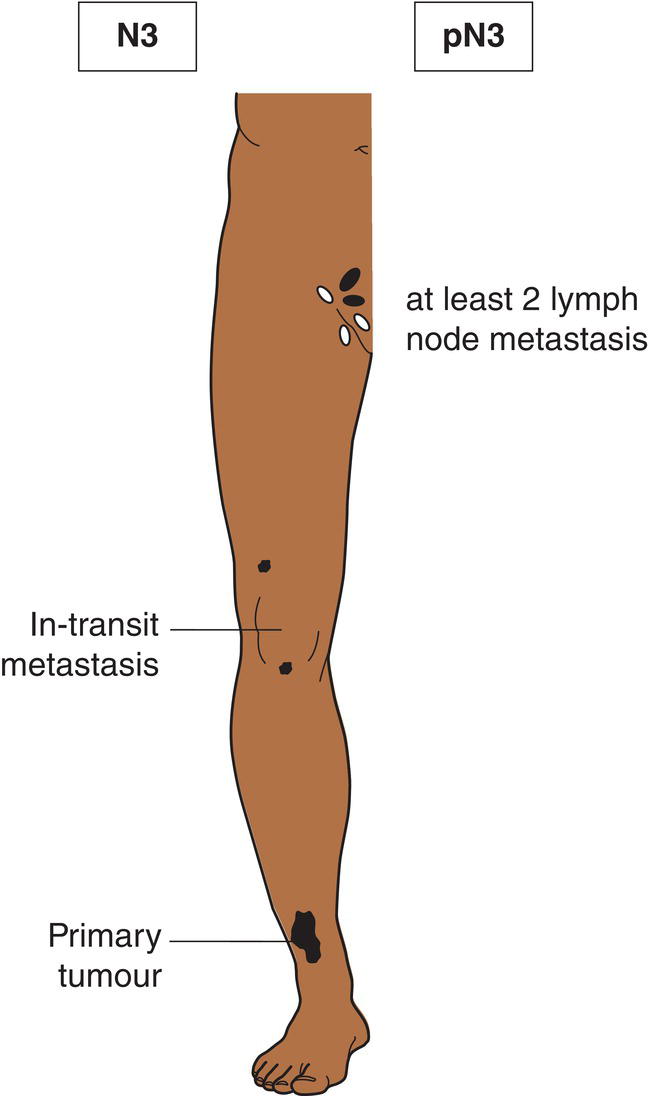
N3
Metastasis in four or more regional lymph nodes (Fig. 364), or matted metastatic regional lymph nodes (Fig. 365), or satellite(s) or in‐transit metastasis with metastasis in regional lymph node(s) (Figs. 366, 367)
Satellites are tumour nests or nodules (macro‐ or microscopic) within 2 cm of the primary tumour. In‐transit metastasis involves skin or subcutaneous tissue more than 2 cm from the primary tumour but not beyond the regional lymph nodes.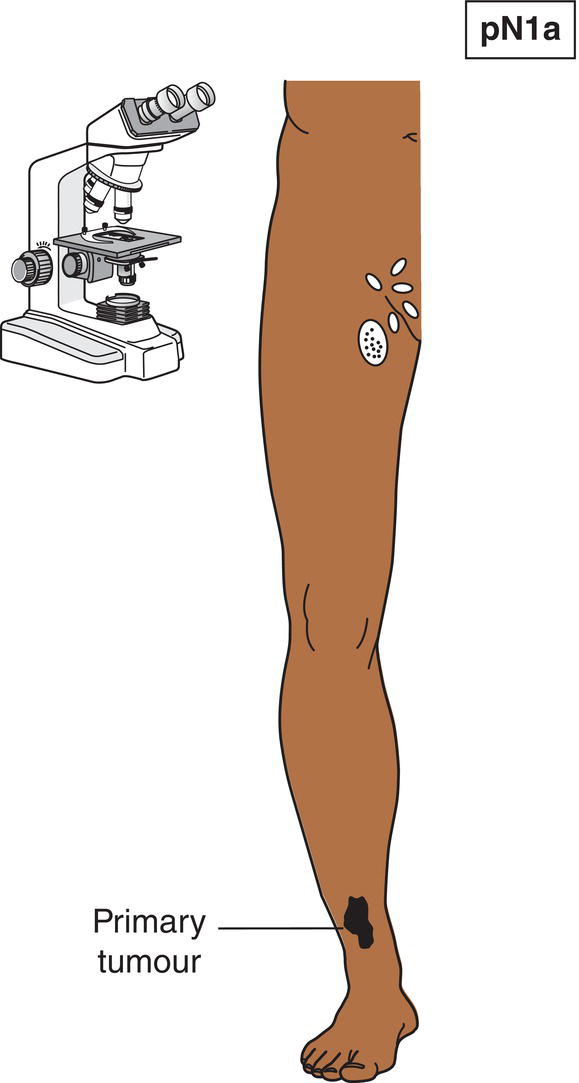
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis
M1a
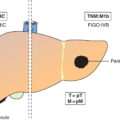
Skin, subcutaneous tissue or lymph node(s) beyond the regional lymph nodes (Figs. 324, 325, 326, 327)
M1b
Lung
M1c
Other sites, or any site with elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
pTNM Pathological Classification
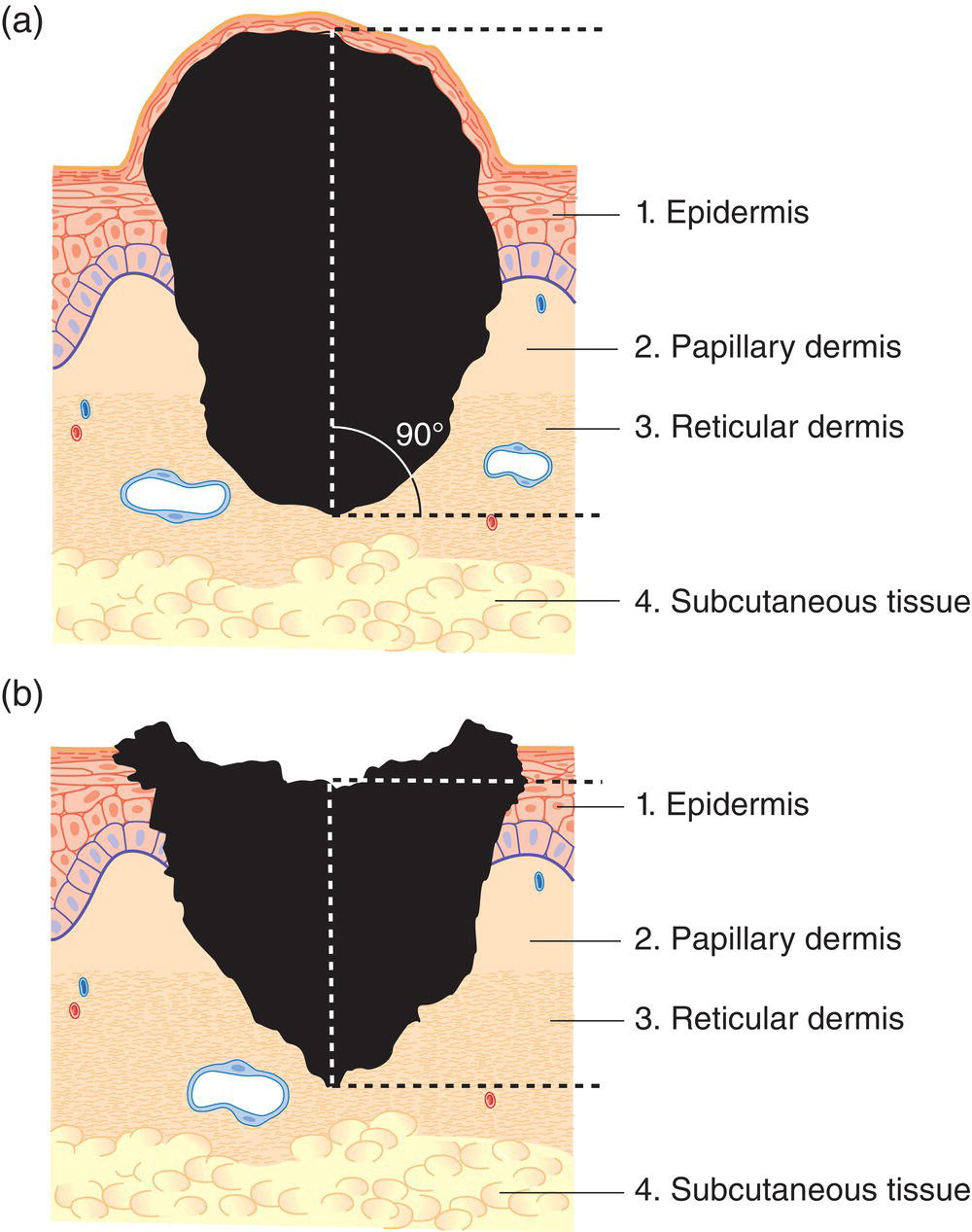
pT – Primary Tumour
pTX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed*
pT0
No evidence of primary tumour
pTis
Melanoma in situ (Clark level I)
pT1
Tumour 1 mm or less in thickness
pT1a
Less than 0.8 mm thickness without ulceration (Fig. 369)
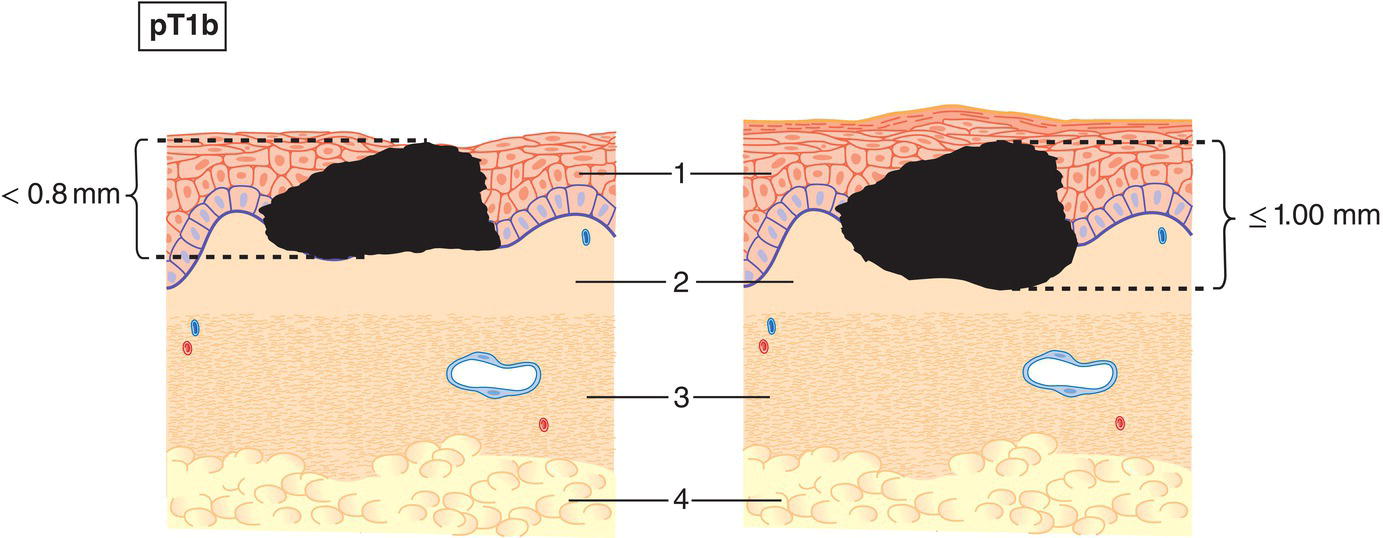
pT1b
Less than 0.8 mm in thickness with ulceration or 0.8 mm or more but no more than 1 mm in thickness, with or without ulceration (Fig. 370)
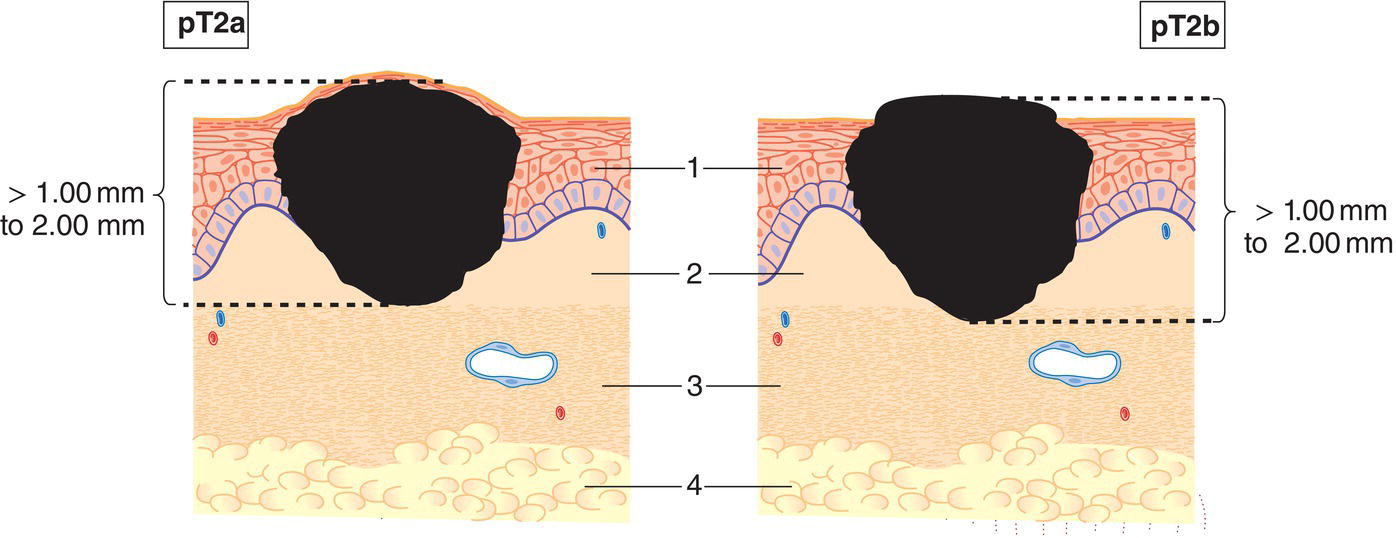
pT2
Tumour more than 1 mm but not more than 2 mm in thickness (Fig. 371)
pT2a
without ulceration
pT2b
with ulceration
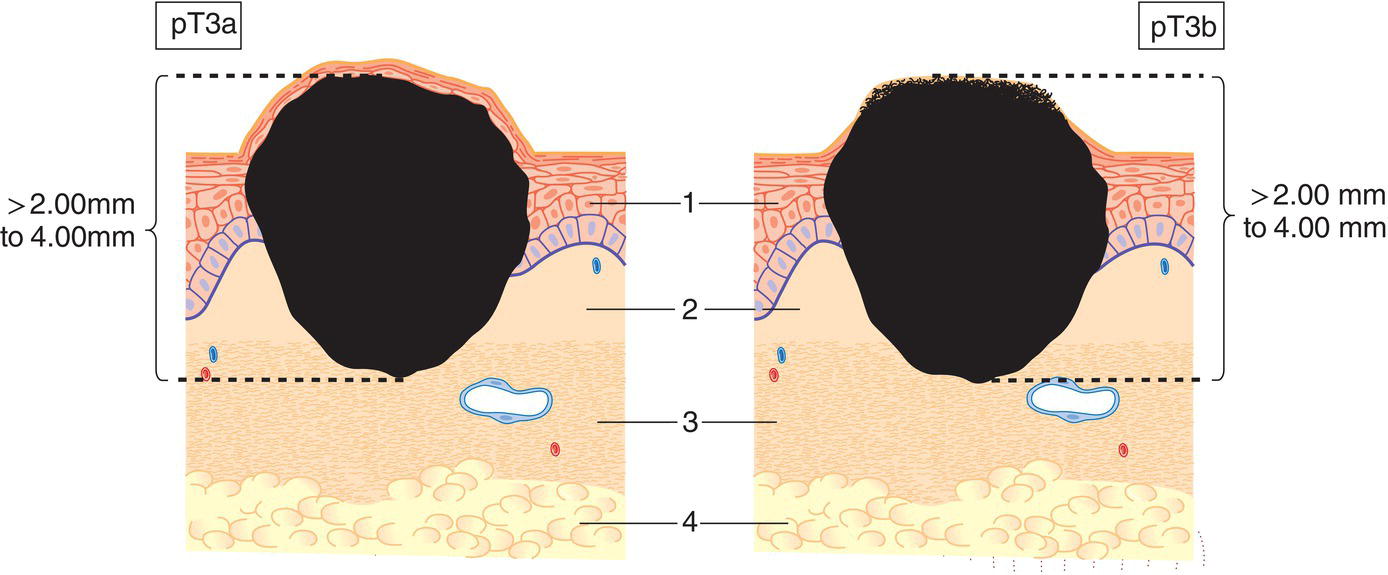
pT3
Tumour more than 2 mm but not more than 4 mm in thickness (Fig. 372)
pT3a
without ulceration
pT3b
with ulceration
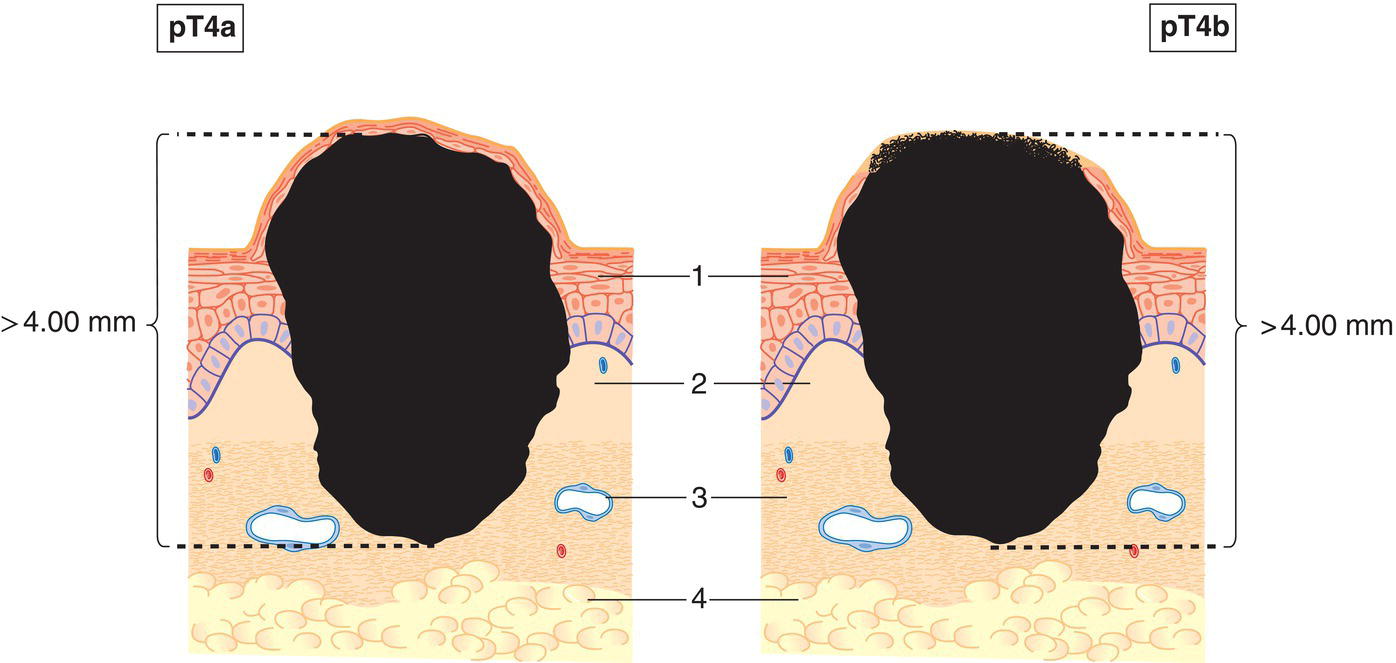
pT4
Tumour more than 4 mm in thickness (Fig. 373)
pT4a
without ulceration
pT4b
with ulceration 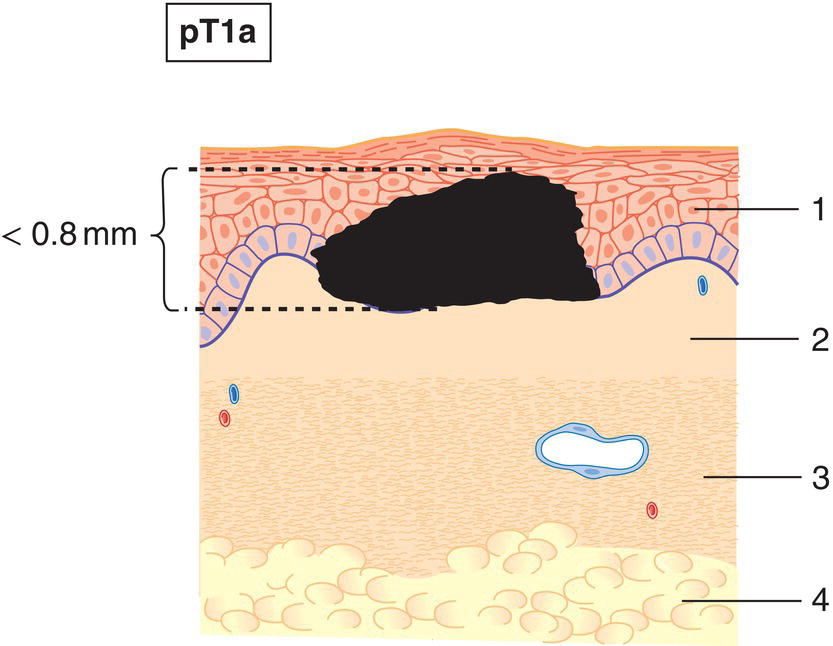
pN – Regional Lymph Nodes
pN0
Histological examination of a regional lymphadenectomy specimen will ordinarily include 6 or more lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are negative, but the number ordinarily examined is not met, classify as pN0. Classification based solely on sentinel node biopsy without subsequent axillary lymph node dissection is designated (sn) for sentinel node, e.g., pN1(sn). (See Introduction.)
pM – Distant Metastasis
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree