, Hans Guski2 and Glen Kristiansen3
(1)
Carl-Thiem-Klinikum, Institut für Pathologie, Cottbus, Germany
(2)
Vivantes Klinikum Neukölln, Institut für Pathologie, Berlin, Germany
(3)
Universität Bonn, UKB, Institut für Pathologie, Bonn, Germany
6.1 Odontogenic Tumors and Tumors of the Oral Cavity
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Odontogenic Tumors and Tumors of the Oral Cavity
Cytokeratin profile, p63, p40, EBV, p16
Immunoprofile of odontogenic tumors and tumors the oral cavity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Tumor type | + in >90% (+) | + in 50–90% (±) | + in 10–50% (∓) | + in <10% (−) |
Basal cell carcinoma | Epithelial specific antigen (BerEP4), bcl-2, androgen receptors | EMA, CEA | ||
Squamous cell carcinoma | CK5/6, CK8, CK14, CK18, CK19, p63, p40 | EBV | CK7, CK20 | |
Sebaceous carcinoma | Adipophilin, EMA, androgen receptors, CEA | |||
Ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor of the tongue | GFAP, Pan-CK, vimentin | S100 | Actin | EMA, CK7, p63, calponin, desmin |
Ameloblastoma | Pan-CK, CK5, CK14, vimentin | Calretinin | ||
Clear cell odontogenic carcinoma | CK8, CK 13, CK14, CK18, CK19, EMA | Vimentin, desmin, actin, S100, HMB45 | ||
Granular cell tumor | S100, SOX-10, CD56, CD68, NSE, vimentin | Inhibin | Pan-CK, actin, HMB-45 | |
The immunoprofile of miscellaneous soft tissue tumors arising in the oral cavity are listed in related sections.
6.2 Salivary Gland Tumors
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Salivary Gland Tumors
Cytokeratin Profile
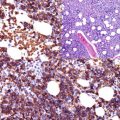
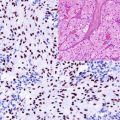
Salivary glands are composed of luminal cells including ductal and acinar cells in addition to the myoepithelial cells. The cytokeratin profile is an important tool to highlight the different cell types forming salivary gland units or tumors derived from these cell types. High molecular weight cytokeratins (CK5/10/14) label the myoepithelial and basal cells. p63, actin, and myosin are also additional markers that label these cells. Recently Sox-10 is also found to label the myoepithelial cells. Cytokeratin 7 is a marker for acinar and ductal cells. The atypical distribution of these cell types is clearly seen in tumors composed of both cell types (Fig. 6.1).
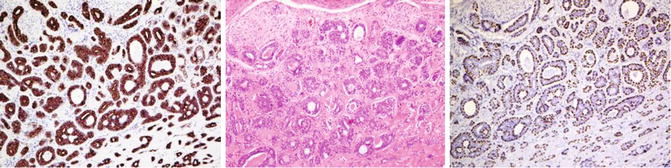

Fig. 6.1




Cytokeratin expression pattern in adenoid cystic carcinoma; CK7, HE, p63. Lumenal ductal cells positive for CK7 (left), basal cells labeled by p63 (right)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree