, Hans Guski2 and Glen Kristiansen3
(1)
Carl-Thiem-Klinikum, Institut für Pathologie, Cottbus, Germany
(2)
Vivantes Klinikum Neukölln, Institut für Pathologie, Berlin, Germany
(3)
Universität Bonn, UKB, Institut für Pathologie, Bonn, Germany
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Keratinocytic (Epidermal) Tumors:
Cytokeratin profile, EMA, epithelial specific antigen (Ber-EP4), p16, p53, HPV, and Ki-67 (Fig. 20.1).
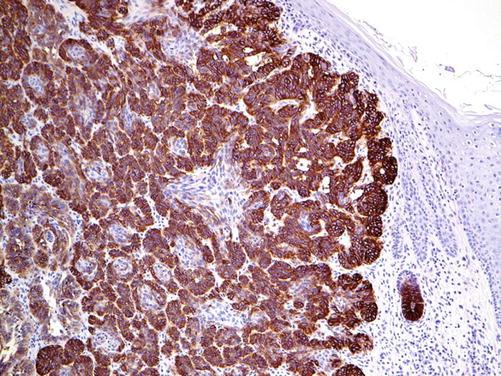

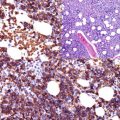
Fig. 20.1
Basal cell carcinoma with strong EPCAM (clone Ber-EP4) expression. Note negative stain of epidermal cells
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Sweat Gland Tumors (Apocrine and Eccrine Differentiation):
Cytokeratin profile, p63, CEA, EMA, CD15, GATA-3, S100, ER, PgR, androgen receptors, and GCFP-15
Analogous to normal sweat glands, eccrine and apocrine gland tumors have the same cell components. Generally, they are composed of luminal cells and basal-type/myoepithelial cells but with disturbed distribution and morphology, which correlates with the differentiation grade of the tumor. The immunohistochemical expression profile of these tumors shows a mixture of both cell types with variable distribution and expression intensity in addition to the expression of CEA, steroid hormone receptors, and frequently GATA-3 [1–4]. Additionally, many sweat gland tumors have the same morphology and immunoprofile as salivary gland tumors such as adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Hair Follicle (Pilar) Tumors:
Cytokeratin profile, p63, EMA, HKN, HHK, and Ber-EP4
The hair-specific keratins including the hair keratins (HKN) 5, 6, and 7 in addition to human hair keratin (HHK) are specific markers for pilar tumors.
Among the different cytokeratins, CK15 is the most specific cytokeratin for hair follicles, nails, and hair follicle tumors. CK15 is a marker of epidermal stem cells, and the expression of CK15 in stratified epithelium is restricted to the basal cell layer. Sebaceous tumors usually lack the expression of CK15.
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Sebaceous Tumors:
Adipophilin | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: membranous/cytoplasmic | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Sebaceous neoplasia, xanthelasma | Burkitt lymphoma, renal cell carcinoma | Adrenal cortex, glands of lactating breast, Sertoli cells |
Positive control: skin | ||
Diagnostic Approach
Adipophilin is a lipid droplet-associated protein expressed on the surface of intracytoplasmic lipid droplets in various normal human cell types including acinar cells of lactating breast, zona fasciculate of adrenal glands, and Sertoli cells, whereas adipocytes lack the expression of adipophilin. Adipophilin labels lipid droplets containing neoplastic cells and is a specific marker for sebaceous neoplasia. Studies on the expression of adipophilin in sebaceous and other cutaneous tumors with clear cell histology mimicking sebaceous neoplasms reveal that adipophilin was positive in 92% of sebaceous carcinoma and all cases of sebaceous adenoma and xanthelasma and in 65% of metastatic renal cell carcinoma [7]. All other tumors with clear cell appearance including squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, trichilemmoma, and clear cell hidradenoma lack the expression of adipophilin [4]. Adipophilin is also a marker of Burkitt lymphoma because of the presence of intracytoplasmic lipid vacuoles.
Lipid Droplet-Associated Protein (Perilipin):
Perilipin is a further marker for sebaceous tumors. Perilipin is located on the surface of lipid droplets and plays a role of lipid metabolism. It is normally expressed in the cells of adrenal cortex, Leydig cells, and brown and adult fat. Perilipin is expressed in about one-third of sebaceous tumors but lacks the specificity as it can be also expressed in other tumors with clear cell morphology [8].
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Melanocytic Tumors
See next chapter.
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Cytokeratin profile, Merkel cell polyomavirus, EMA, CD56, and NSE
The exact histogenesis of Merkel cell carcinoma is not clarified, but the tumor could develop from skin-derived precursors or dermal stem cells. Recently, pro- or pre-B lymphocytes are discussed as the origin of Merkel cell carcinoma. Merkel cell carcinoma is generally associated/induced by the Merkel cell polyomavirus, which can be detected by immunohistochemistry or molecular biology.
Immunoprofile of skin tumors
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|
|---|