, Hans Guski2 and Glen Kristiansen3
(1)
Carl-Thiem-Klinikum, Institut für Pathologie, Cottbus, Germany
(2)
Vivantes Klinikum Neukölln, Institut für Pathologie, Berlin, Germany
(3)
Universität Bonn, UKB, Institut für Pathologie, Bonn, Germany
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Mast Cell Tumors
Mast cell tryptase | ||
Expression pattern: cytoplasmic | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Mast cell tumors | Mast cells | |
Positive control: appendix | ||
Diagnostic Approach
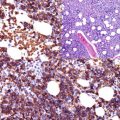
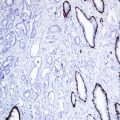
Tryptase is a neutral serine protease and a member of the trypsin-like proteinases. It is one of the mediators of inflammation found in mast cells and basophiles and released in the extracellular matrix in response to activation. Antibodies to tryptase are used as specific markers for mast cells but cannot discriminate between normal and neoplastic mast cells. The aberrant tryptase expression is described in rare types of acute myeloid leukemia.
CD25:
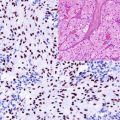
CD25 is a subunit of the interleukin-2 receptor, involved in the differentiation and activation of T lymphocytes, and is normally expressed in a subpopulation of T lymphocytes in addition to myeloid precursors and oligodendrocytes. It is also expressed in viral transformed T and B lymphocytes. CD25 labels the majority of T-cell lymphomas as well as hairy cell leukemia. In mast cell disorders, the expression of CD25 is restricted to neoplastic mast cells and is usually negative in reactive mast cells [6].
CD2:
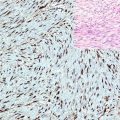
CD2 was listed in a previous chapter. CD2 is normally expressed in different stages of T-cell development and T-cell lymphomas but negative in B lymphocytes, B-cell lymphomas, and normal mast cells, whereas the expression of CD2 in mast cells indicates a neoplastic nature of these cells [3].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree