, Hans Guski2 and Glen Kristiansen3
(1)
Carl-Thiem-Klinikum, Institut für Pathologie, Cottbus, Germany
(2)
Vivantes Klinikum Neukölln, Institut für Pathologie, Berlin, Germany
(3)
Universität Bonn, UKB, Institut für Pathologie, Bonn, Germany
9.1 Hepatocellular Tumors
Diagnostic Antibody Panel for Hepatocellular Tumors
Hepatocyte-specific antigen (Hep Par-1) | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: cytoplasmic (granular) | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatoblastoma | Adrenal gland tumors, mucosal intestinal metaplasia and small intestinal adenocarcinoma, signet ring cell carcinoma, tumors with hepatoid differentiation, yolk sac tumor | Hepatocytes, intestinal enterocytes |
Positive control: liver tissue | ||
Diagnostic Approach
Hepatocyte paraffin-1 (Hep Par-1 ) reacts with a urea cycle enzyme located on the mitochondrial membrane of hepatocytes that is also found in the mitochondria of intestinal epithelium and cells of renal tubules. Hep Par-1 is a specific marker for liver tissue and hepatocellular tumors; however, it also labels small intestinal mucosa and small intestinal adenocarcinomas in addition to gastric and esophageal intestinal metaplasia including Barrett’s mucosa [3–7].
Diagnostic Pitfalls
Generally, extrahepatic tumors with hepatoid differentiation have the same immunoprofile as hepatocellular tumors and can be positive for Hep Par-1, AFP, and CD10 [8]. The expression of Hep Par-1 is also reported in tumors of adrenal cortex and adenocarcinomas of the stomach and small intestine, but these tumors are negative for arginase [9].
False-positive results in the immunostaining of liver tissue can be caused by the high biotin activity of the hepatocytes; thus, the inactivation of endogenous biotin is recommended to eliminate the biotin background. The use of a polymer detection system is also effective.
Arginase-1:
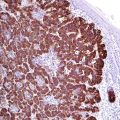
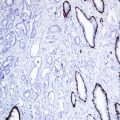
Arginase -1 is a manganese urea cycle metalloenzyme that catalyzes the conversion of arginine to ornithine and urea. In gastrointestinal system, the expression of arginase-1 is limited to hepatocytes, whereas bile duct epithelial, sinusoidal, and endothelial cells lack the expression of this enzyme. Arginase-1 is more specific for hepatocytes and hepatocellular carcinomas than Hep Par-1 and found in 85–100% of primary and metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma, whereas the expression intensity correlates with differentiation grade of the tumor [10]. BSEP, HSP70, glypican-3, and CD34 (Fig. 9.1) can be used in a panel to support the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinomas [11].

Fig. 9.1
CD34 highlighting sinusoidal cells in hepatocellular carcinoma
Various expression levels of Arginase-1 are also found in myeloid cells and macrophages.
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) | ||
|---|---|---|
Expression pattern: cytoplasmic | ||
Main diagnostic use | Expression in other tumors | Expression in normal cells |
Hepatocellular carcinoma, yolk sac tumor | Tumors with hepatoid differentiation, pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma, pancreatoblastoma | Fetal liver |
Positive control: fetal liver | ||
Diagnostic Approach
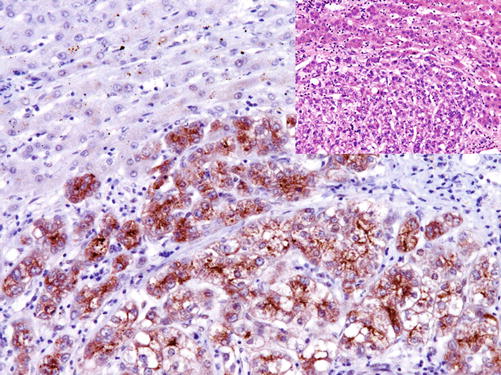
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is an oncofetal protein found in fetal liver, fetal gastrointestinal track, yolk sac, and fetal plasma. AFP is also present in a very low concentration in adult plasma. In the majority of cases, hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a high expression level of AFP, and a lesser expression degree is found in germ cell tumors, i.e., yolk sac tumor (Fig. 9.2).
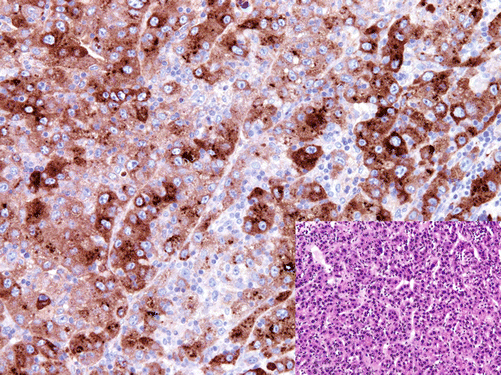

Fig. 9.2
Neoplastic cells of hepatocellular carcinoma with strong AFP expression
Diagnostic Pitfalls
It is important to consider that about 5% of hepatocellular carcinoma is negative for AFP. Low expression level of AFP is reported in pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma, pancreatoblastoma, and renal cell carcinoma.
Bile Salt Export Pump (BSEP) and Multidrug Resistance Protein 3 (MDR-3):
BSEP is a member of the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter family encoded by the ABCB11 gene. BSEP is a membrane-associated ATP-dependent bile salt transporter protein localized on the canilicular microvilli and subcanilicular vesicles of hepatocytes and responsible for the transport of bile-conjugated salts out of hepatocytes into the canaliculus system [12].
The multidrug resistance protein 3 (MDR-3) is another member of the same transporter family and a transmembrane protein also involved in the transport of bile salts from hepatocytes. Both BSEP and MDR-3 are expressed exclusively on the membrane of hepatocytes and used as sensitive and specific markers for hepatocytes and hepatocellular tumors. These markers can be also used to differentiate between hepatocellular and bile duct tumors [13].
Glypican-3:
Glypican-3 is a membrane and extracellular heparan sulfate glycoprotein that regulates signaling during embryogenesis. Glypican-3 is normally expressed in fetal tissue and trophoblasts. In adult tissue, the expression of glypican-3 is restricted to few tissue types, namely, gastric glands and renal tubules. Glypican-3 is also expressed in a wide range of epithelial and mesenchymal tumors including pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatoblastoma, acinar carcinoma of the pancreas, neuroblastoma, Wilms’ tumor, yolk sac tumor and choriocarcinoma, liposarcoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma. Glypican-3 is a helpful marker to distinguish between hepatocellular carcinoma and benign liver tissue, but it is important to consider that it could be focally positive in cirrhotic liver tissue, active chronic hepatitis C, and dysplastic liver nodules (Fig. 9.3). Embryonal carcinoma and seminoma lack the expression of glypican-3.