IODINE-INDUCED AUTOIMMUNITY
Part of “CHAPTER 37 – ADVERSE EFFECTS OF IODIDE“
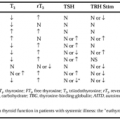
Investigators have speculated that increased iodine intake may contribute to the prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disease. Individuals with Hashimoto disease are well known to be sensitive to the effects of iodine and vulnerable to iodine-induced hypothyroidism. Less well known is that iodine exposure may induce a lymphocytic thyroiditis in a variety of experimental animals (rat, hamster, dog) as well as in humans.9,52 A few studies have examined the greater prevalence of thyroid antibodies after increases in iodine exposure.53 Specific histologic features of iodine-induced goiter have been described in one study of 28 patients, with half the biopsies also showing typical lymphocytic infiltration.54
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree