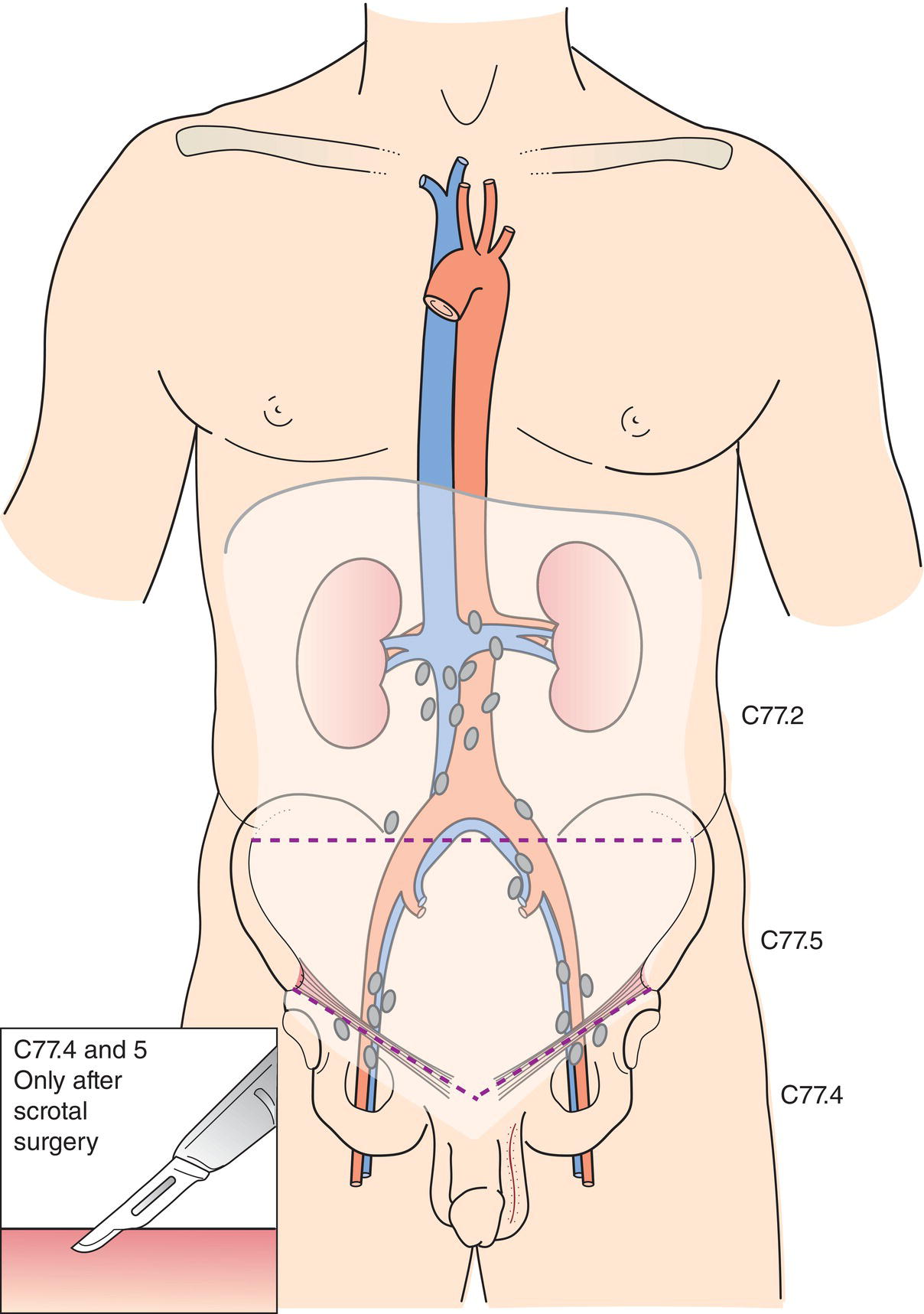
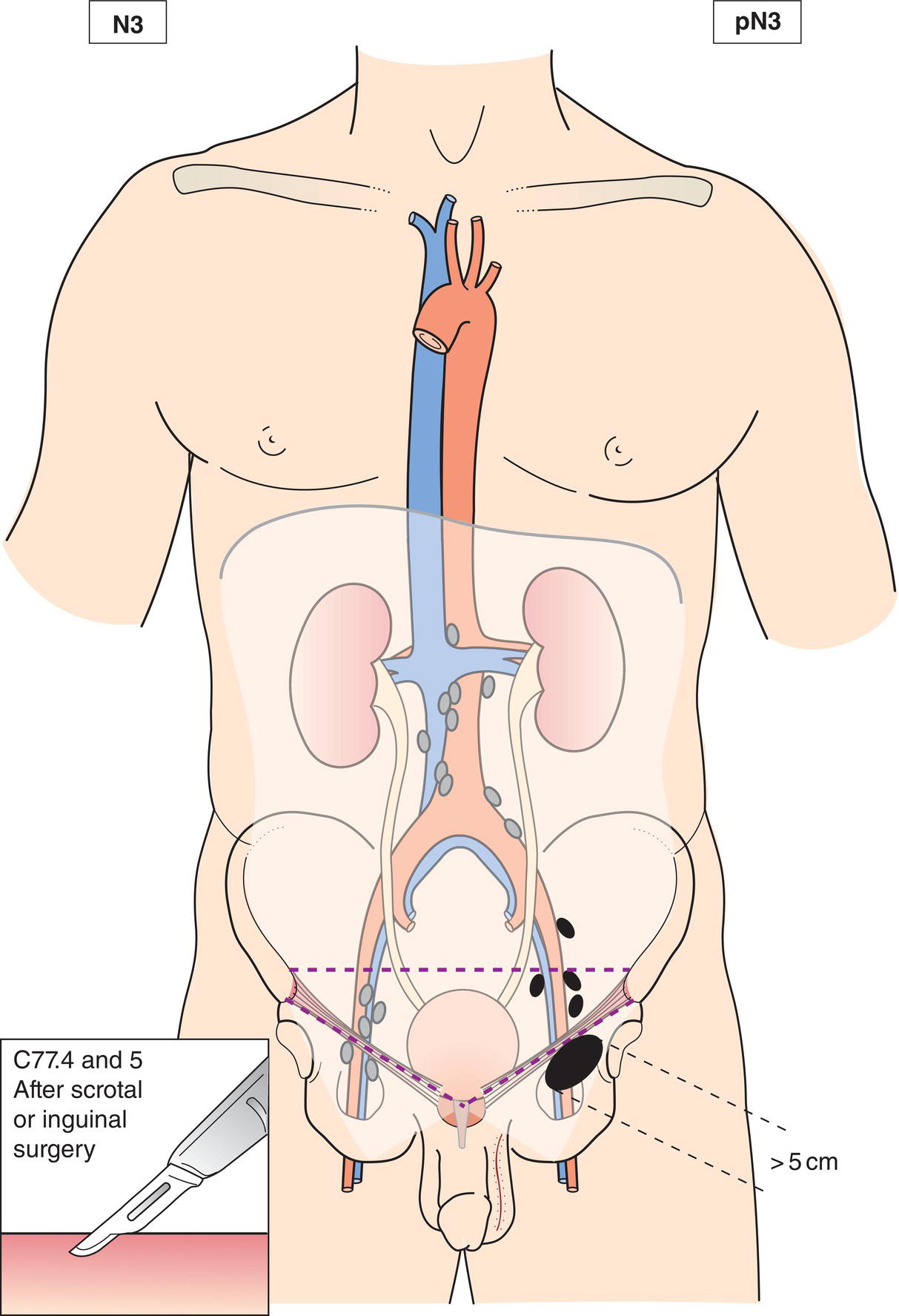
The classification applies only to germ cell tumours of the testis. There should be histological confirmation of the disease and division of cases by histological type. Histopathological grading is not applicable. The regional lymph nodes are the abdominal para‐aortic (periaortic), preaortic, interaortocaval, precaval, paracaval, retrocaval, and retroaortic nodes. Nodes along the spermatic vein should be considered regional. Laterality does not affect the N classification. The intrapelvic nodes and the inguinal nodes are considered regional after scrotal or inguinal surgery. Except for pTis and pT4, where radical orchiectomy is not always necessary for classification purposes, the extent of the primary tumour is classified after radical orchiectomy; see pT. In other circumstances, TX is used if no radical orchiectomy has been performed. Note
TESTIS (ICD‐O‐3 C62) (Fig. 489)
Rules for Classification
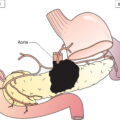
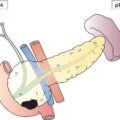
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 490)
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
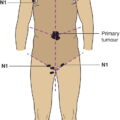
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
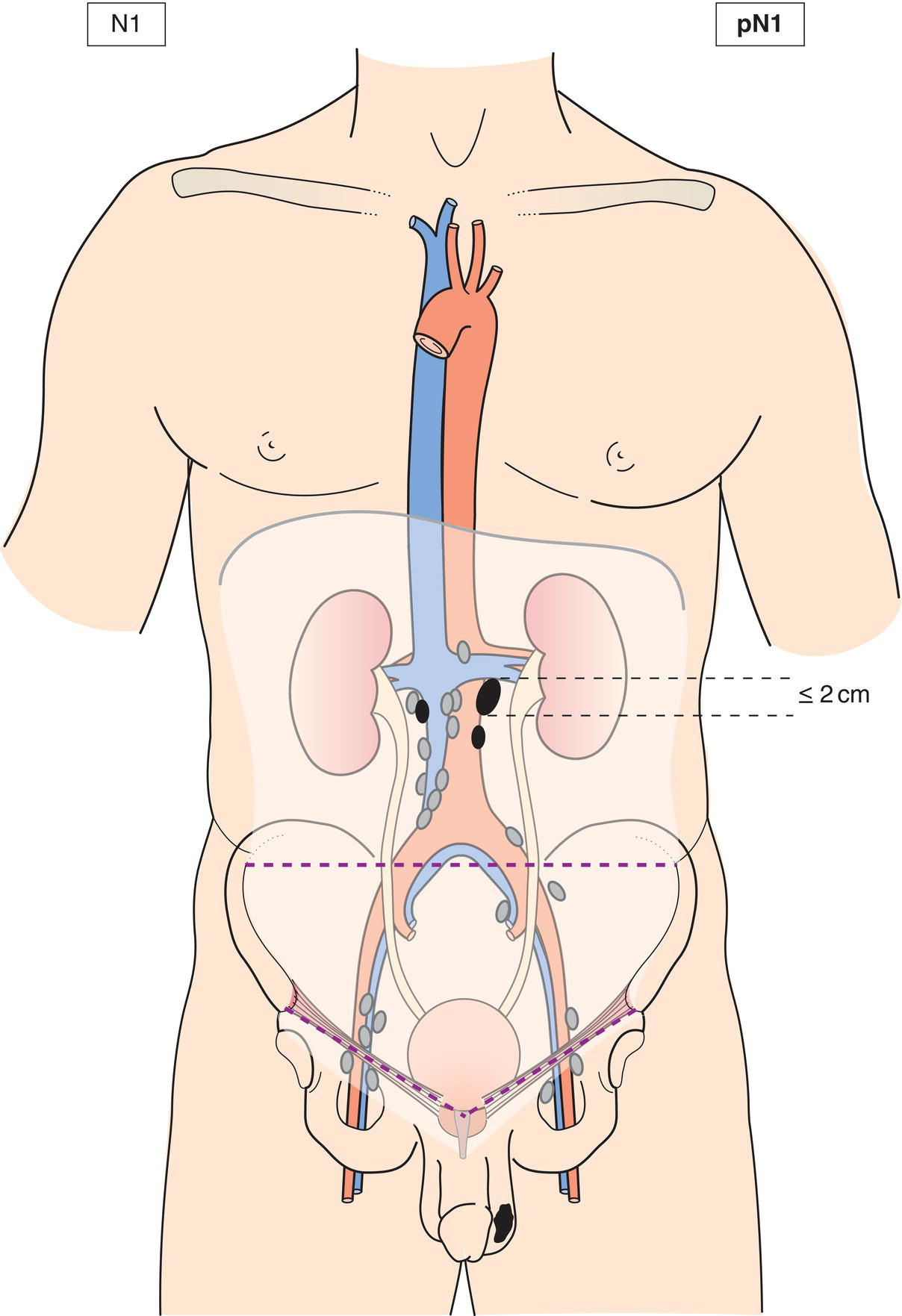
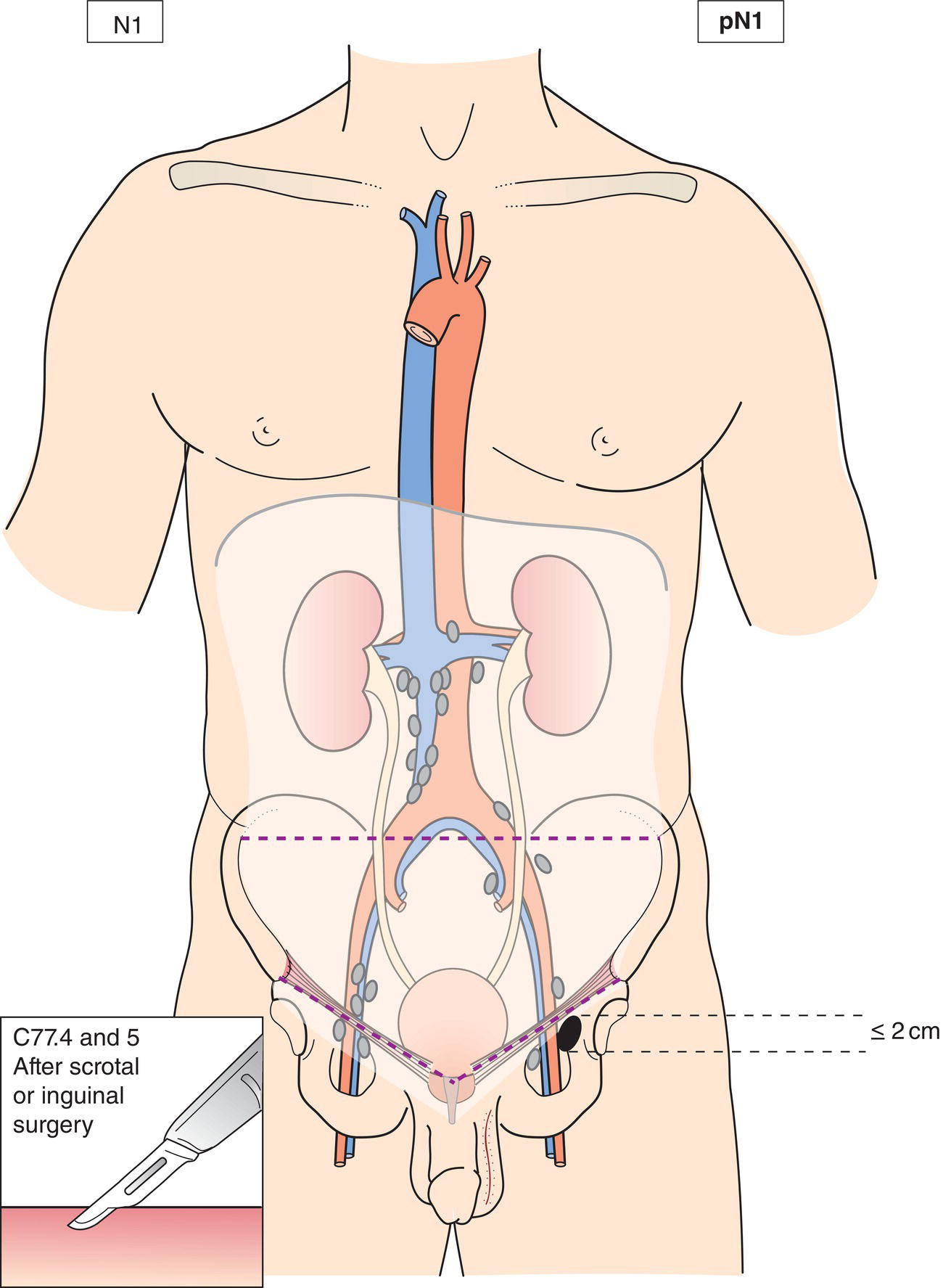
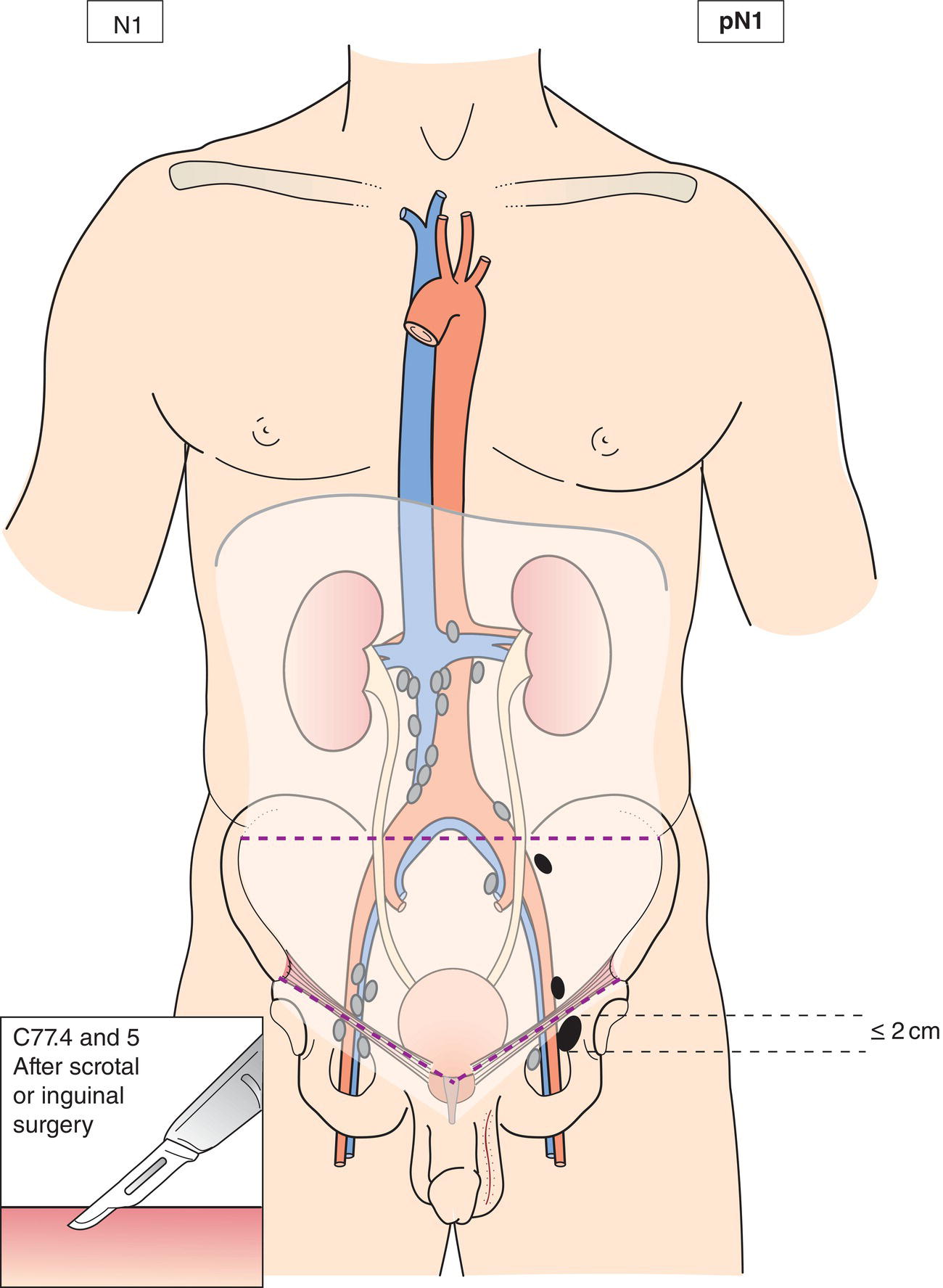
N1
Metastasis with a lymph node mass 2 cm or less in greatest dimension or multiple lymph nodes, none more than 2 cm in greatest dimension (Figs. 491, 492, 493, 494, 495)
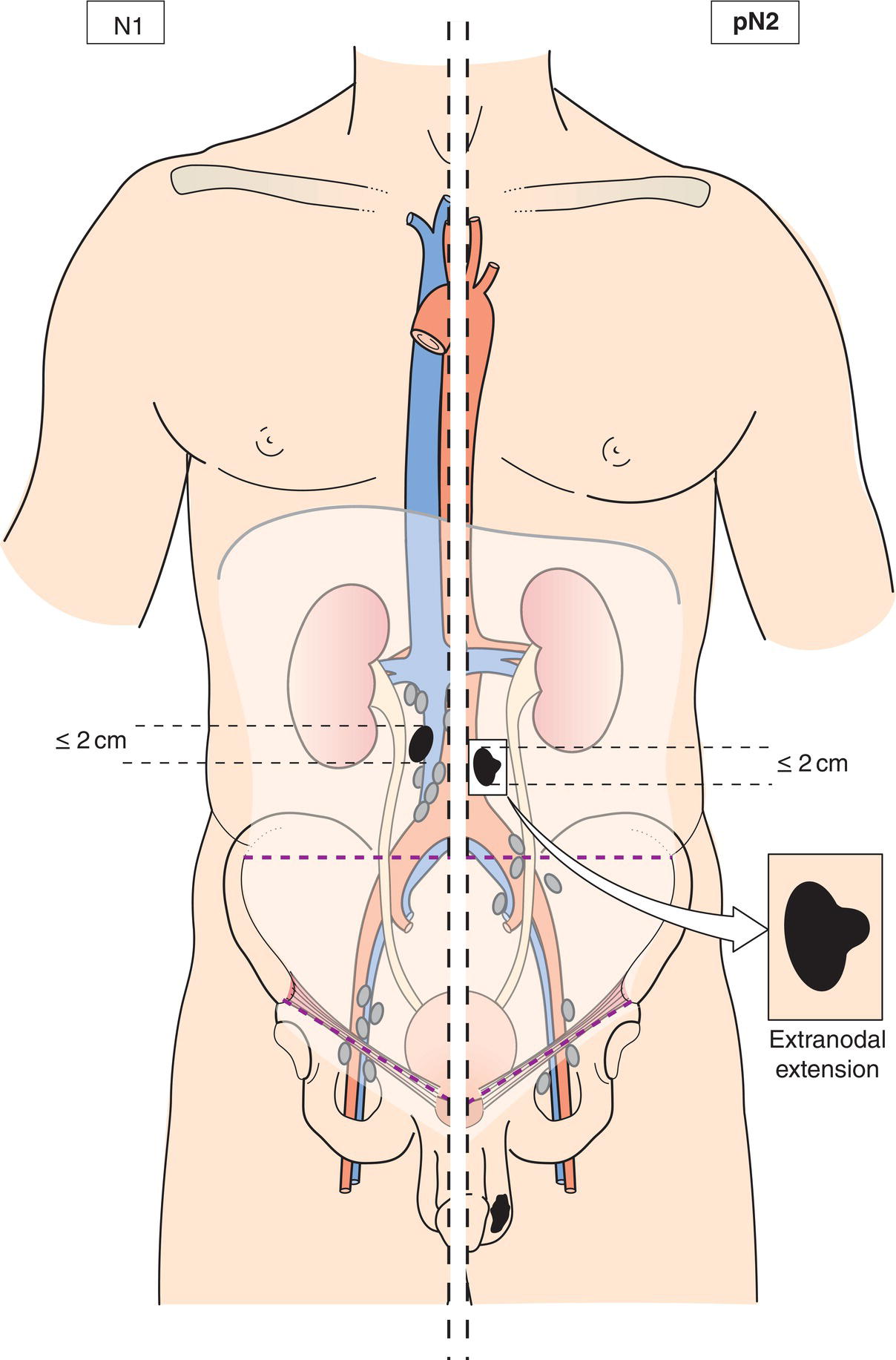
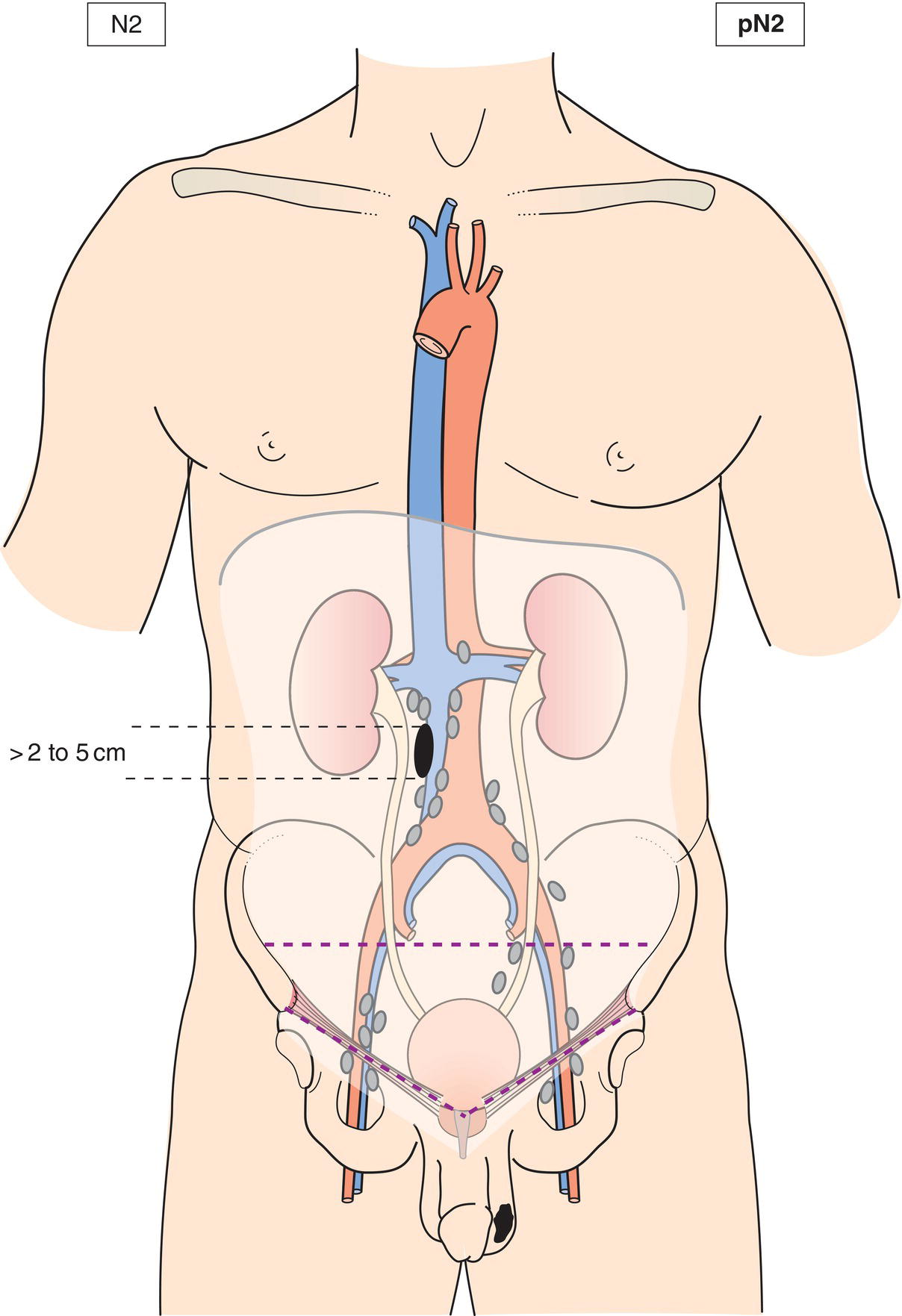
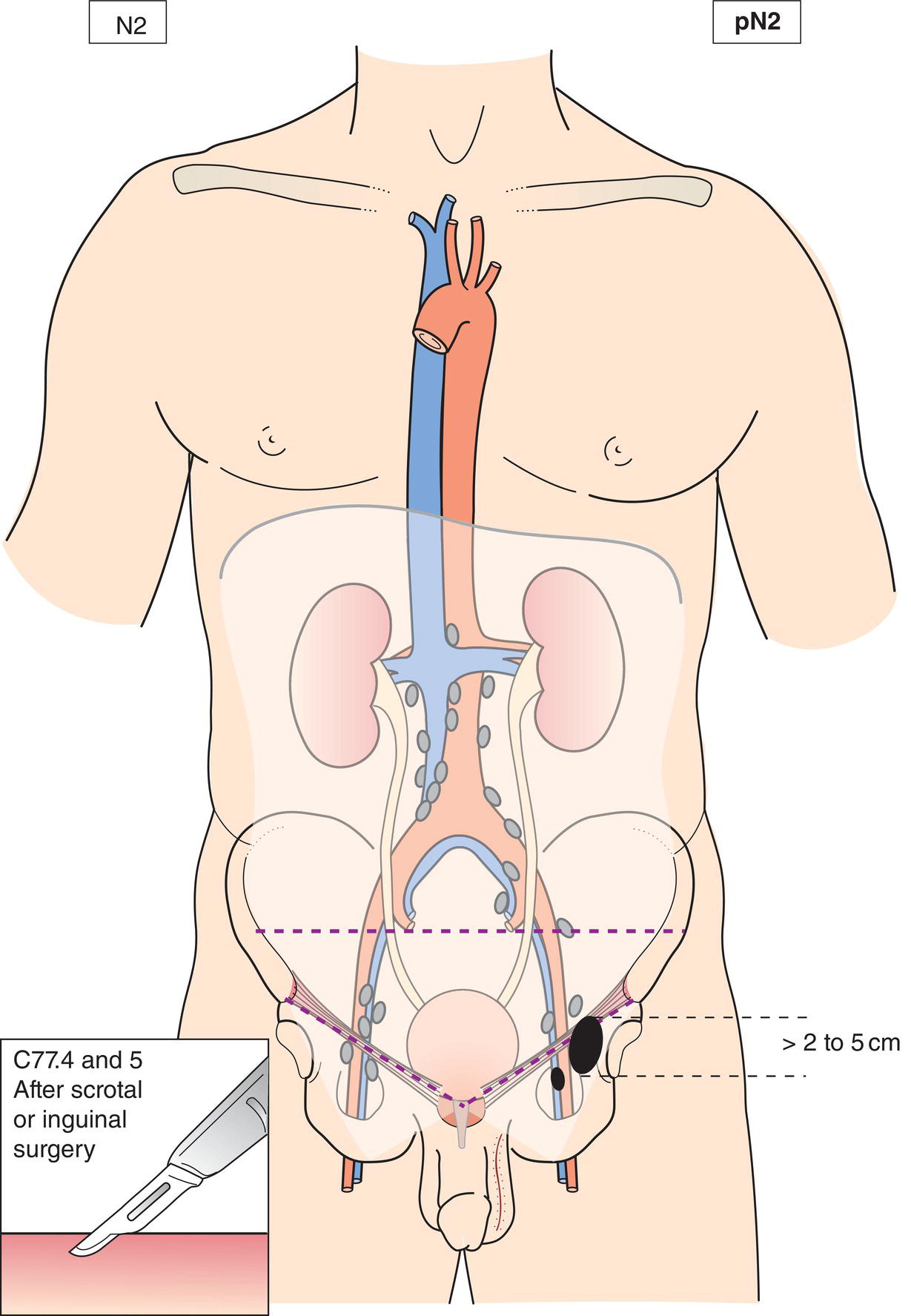
N2
Metastasis with a lymph node mass more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm in greatest dimension, or multiple lymph nodes, any one mass more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm in greatest dimension (Figs. 496, 497)
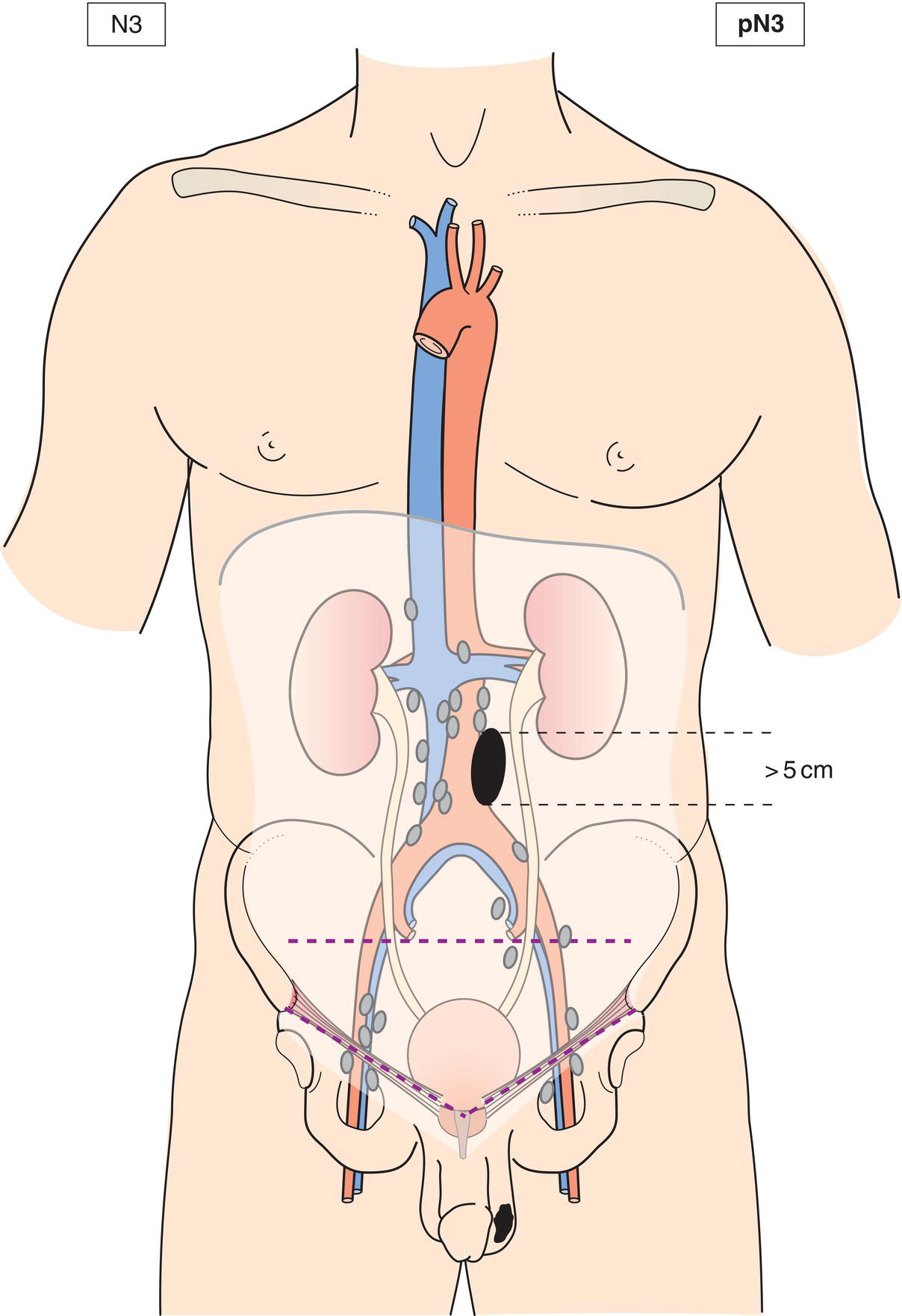
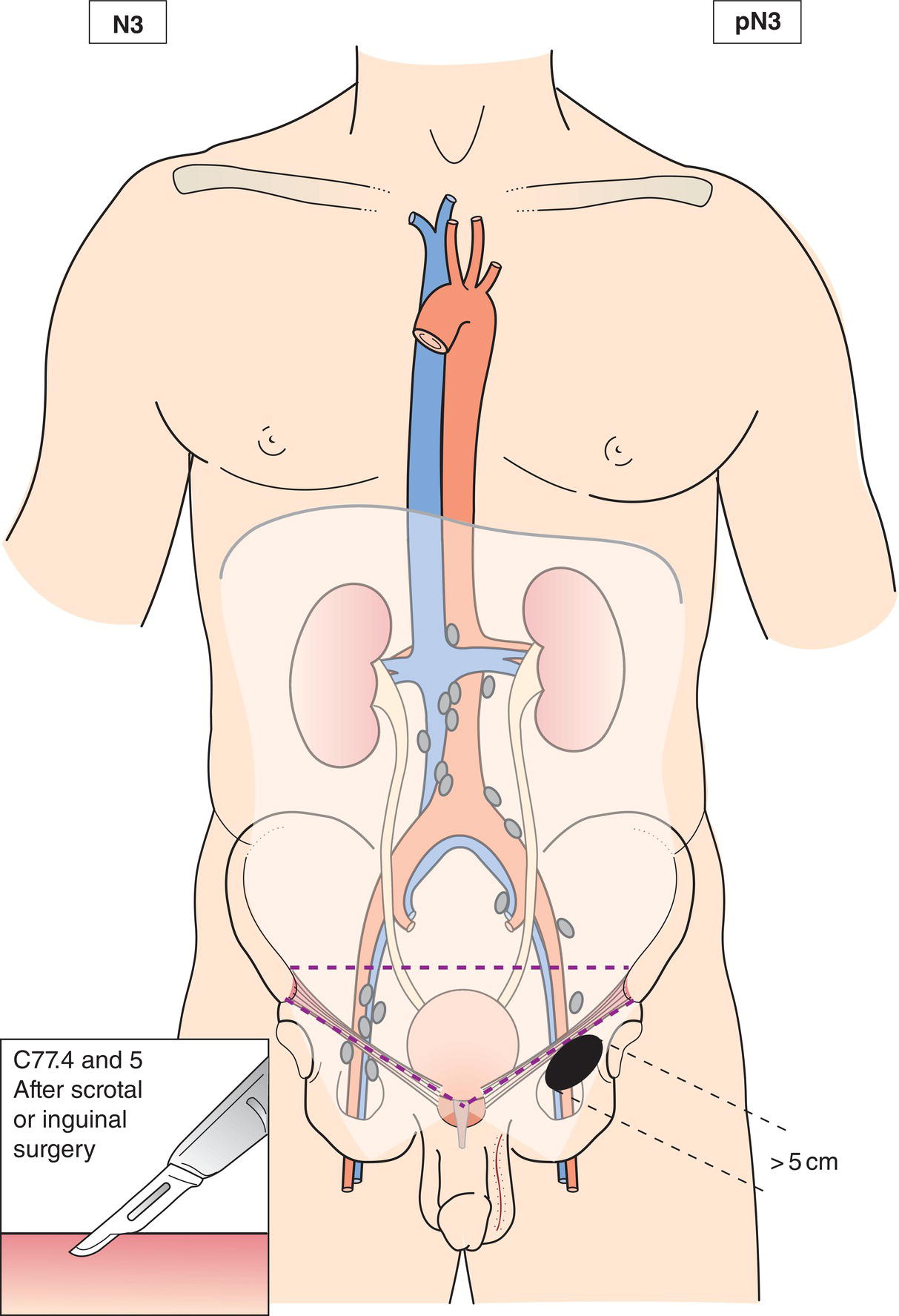
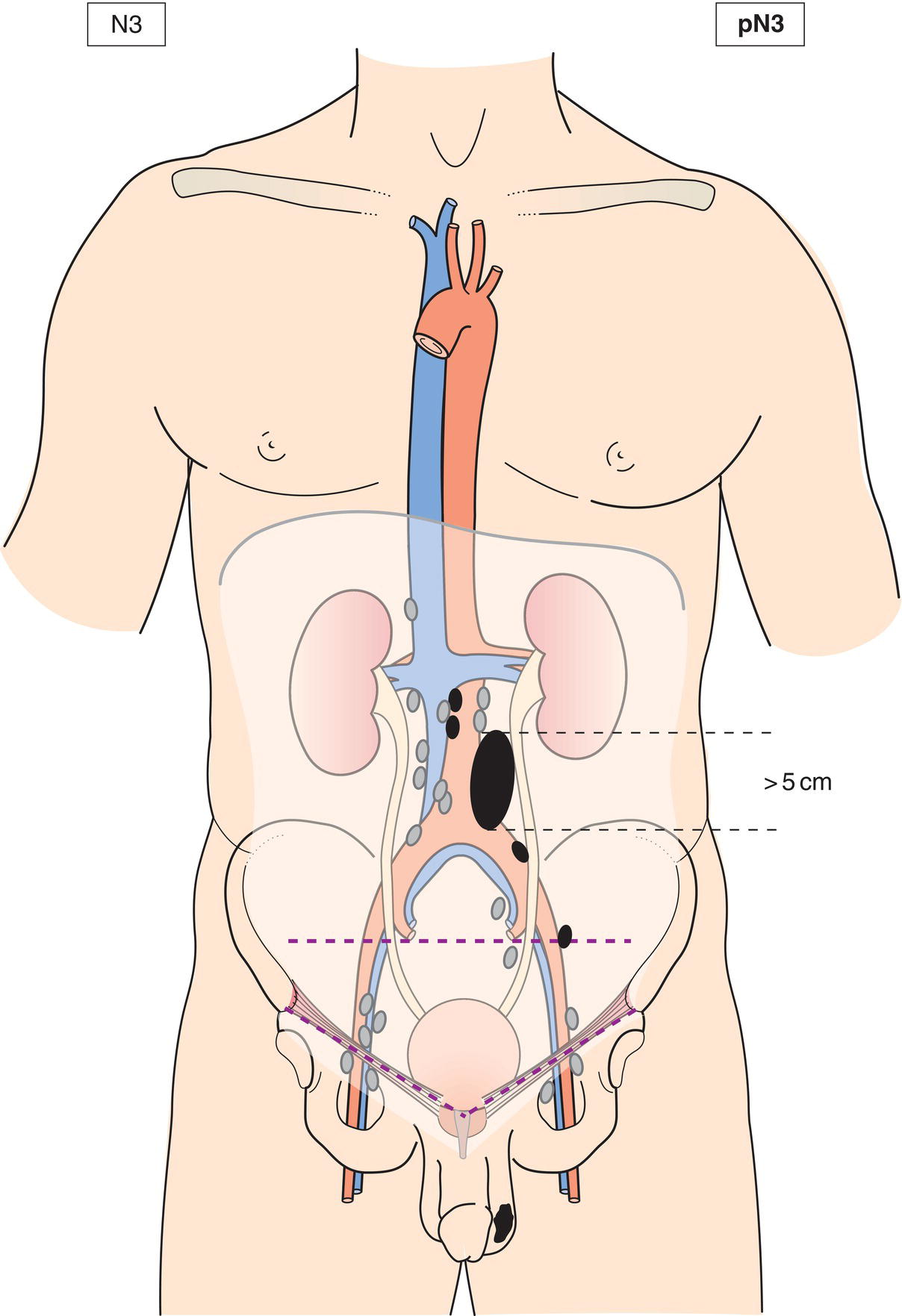
N3
Metastasis with a lymph node mass more than 5 cm in greatest dimension (Figs. 498, 499, 500, 501) 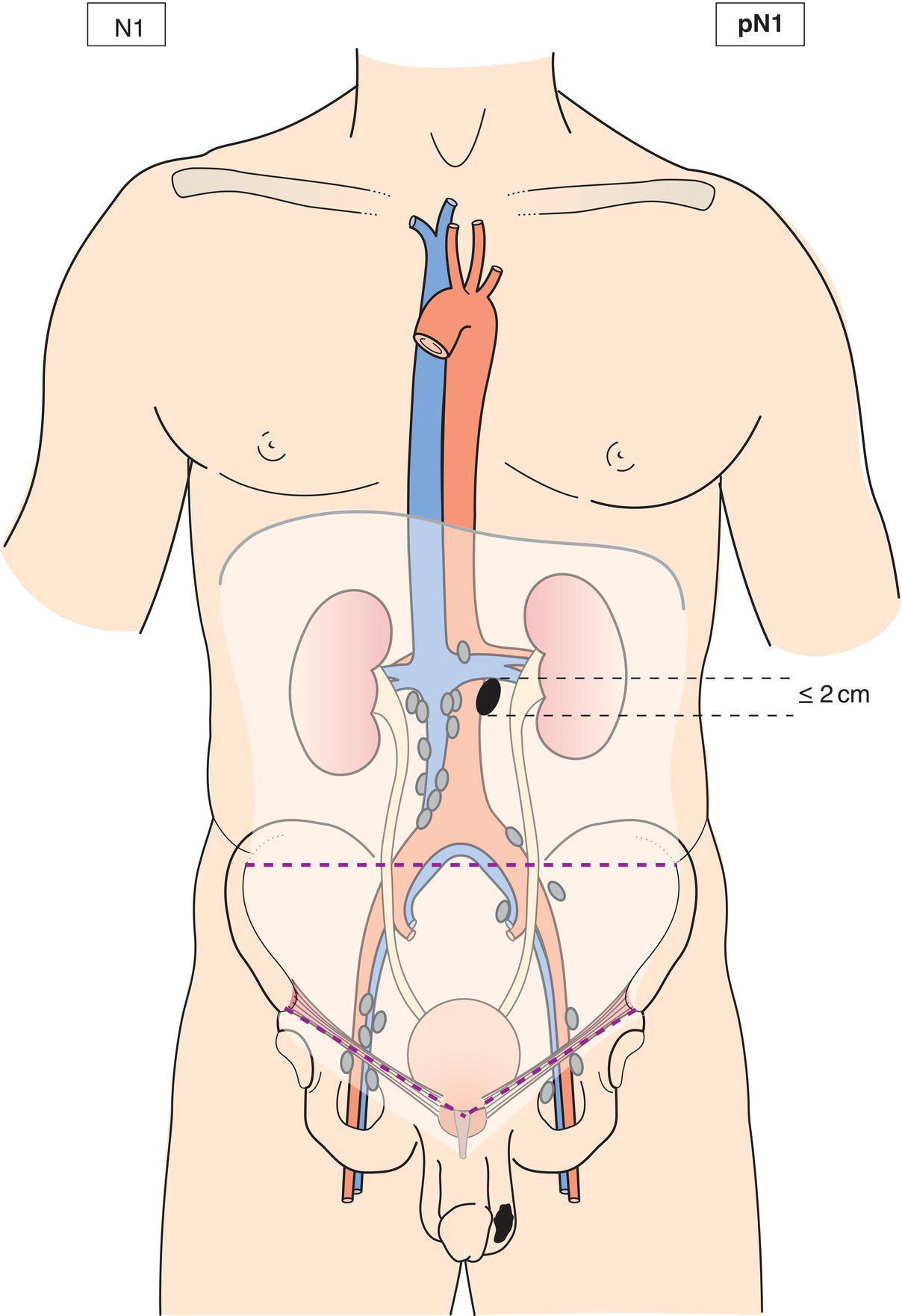
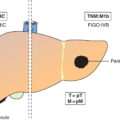
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis
M1a
Non‐regional lymph node(s) or lung metastasis
M1b
Distant metastasis other than non‐regional lymph nodes and lung
pTNM Pathological Classification
pT – Primary Tumour
pTX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed (see T – Primary Tumour, above)
pT0
No evidence of primary tumour (e.g., histologic scar in testis)
pTis
Intratubular germ cell neoplasia (carcinoma in situ)
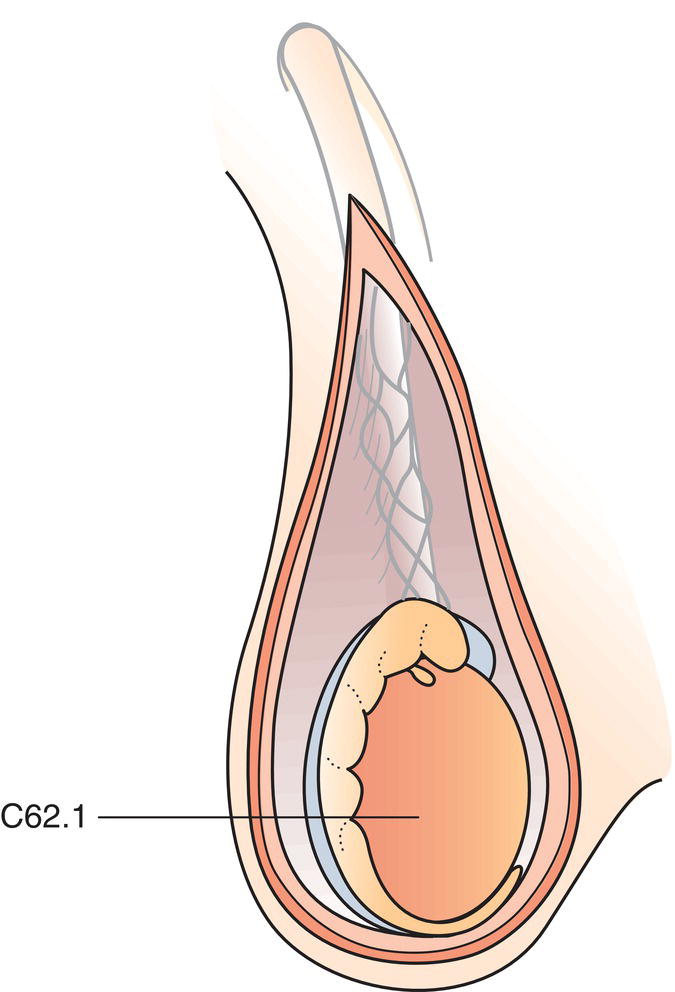
pT1
Tumour limited to testis and epididymis without vascular/lymphatic invasion; tumour may invade tunica albuginea but not tunica vaginalis (Fig. 502)
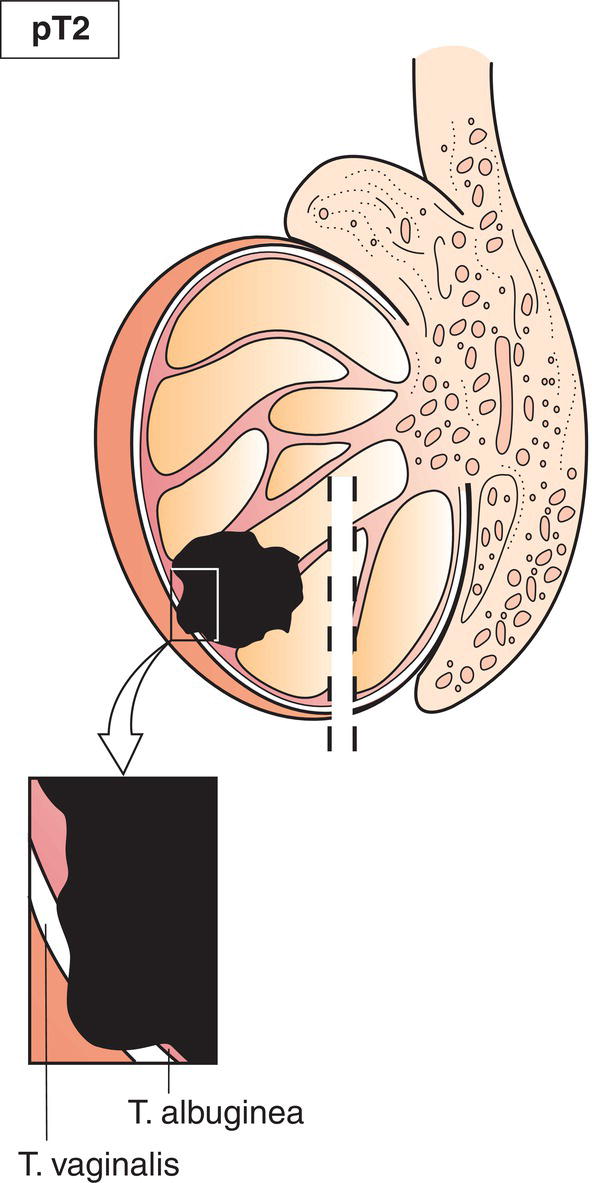
pT2
Tumour limited to testis and epididymis with vascular/lymphatic invasion (Fig. 502), or tumour extending through tunica albuginea with involvement of tunica vaginalis (Fig. 503)
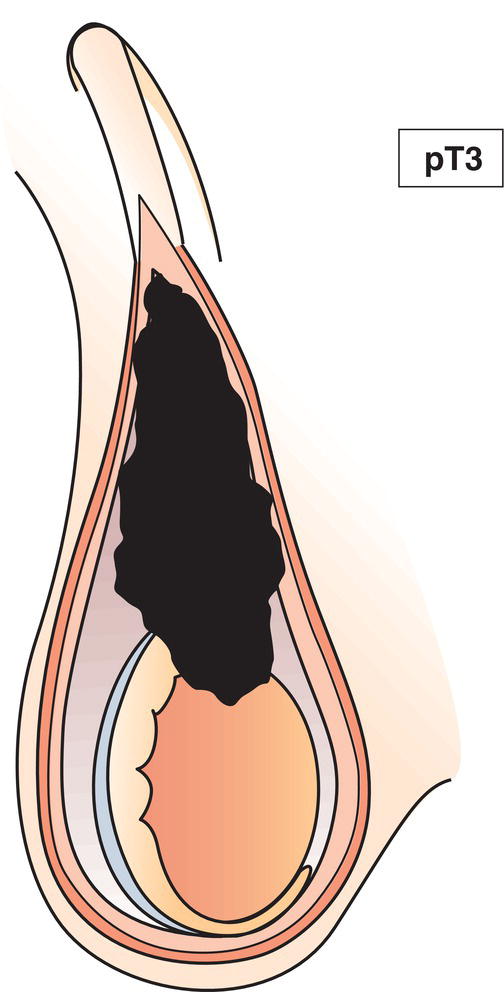
pT3
Tumour invades spermatic cord with or without vascular/lymphatic invasion (Fig. 504)
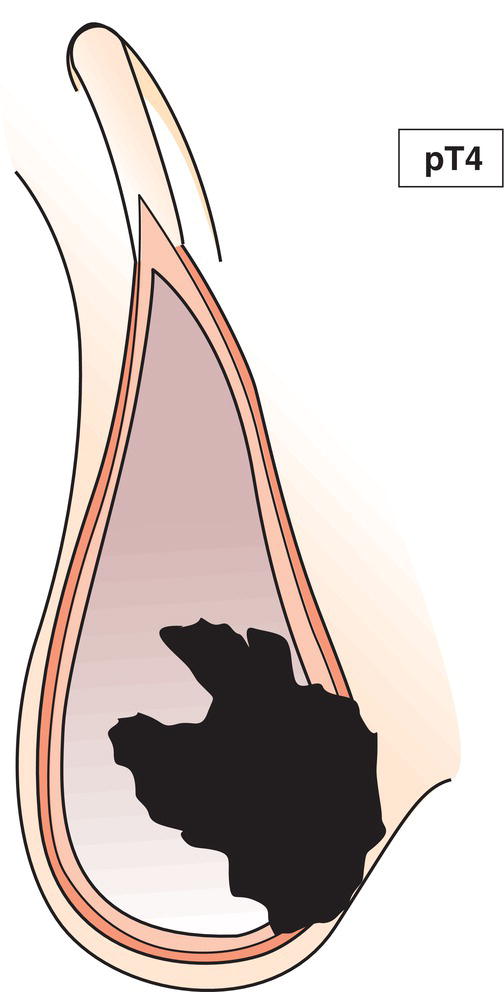
pT4
Tumour invades scrotum with or without vascular/ lymphatic invasion (Fig. 505) 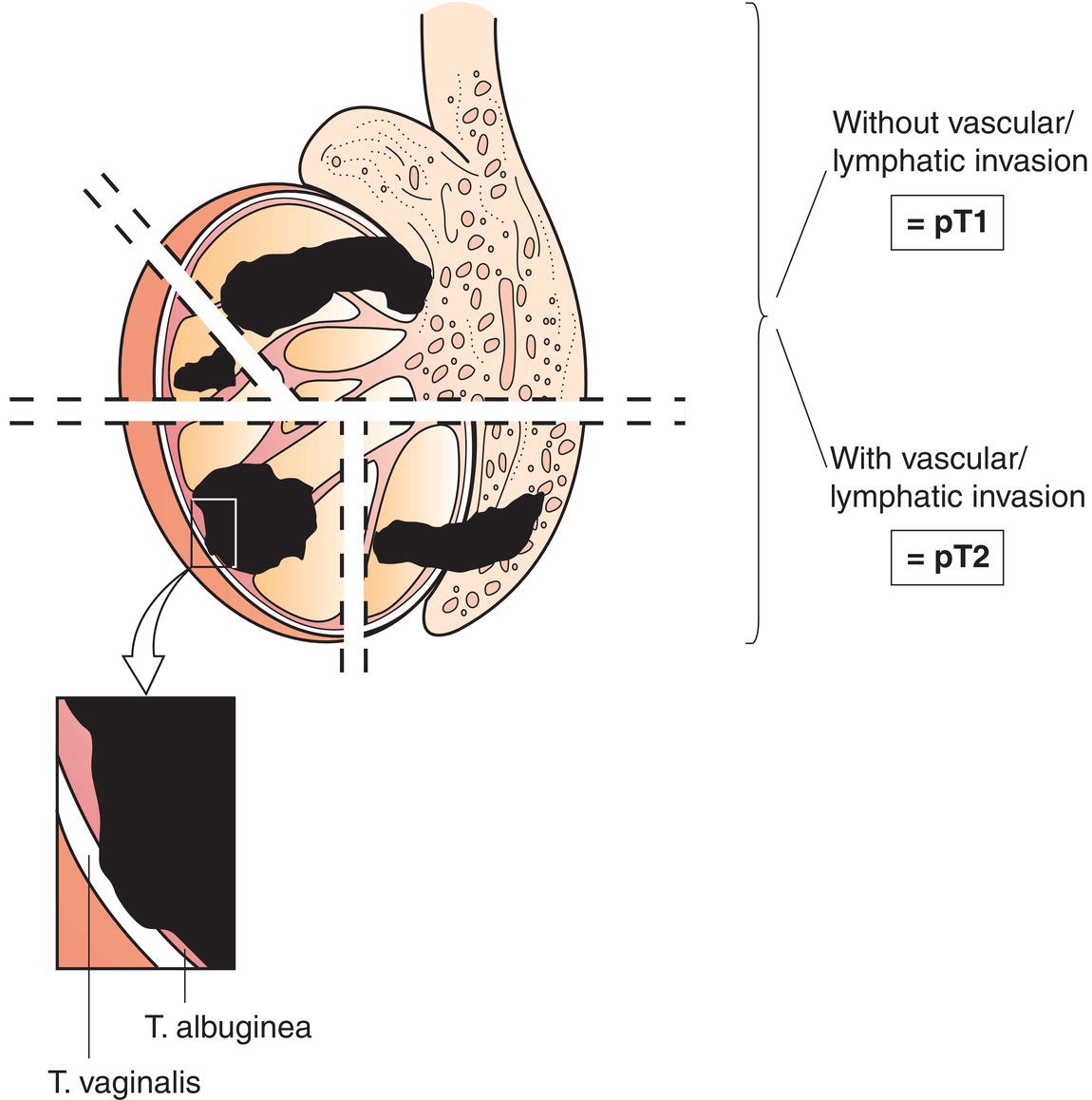
pN – Regional Lymph Nodes
pNX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
pN0
No regional lymph node metastasis
pN1
Metastasis with a lymph node mass 2 cm or less in greatest dimension and 5 or fewer positive nodes, none more than 2 cm in greatest dimension (Figs. 491, 492, 493, 494)
pN2
Metastasis with a lymph node mass (Figs. 495, 496, 497) more than 2 cm but not more than 5 cm in greatest dimension; or more than 5 nodes positive, none more than 5 cm; or evidence of extranodal extension of tumour (Fig. 495)
pN3
Metastasis with a lymph node mass more than 5 cm in greatest dimension (Figs. 498, 499, 500, 501)
pM – Distant Metastasis
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree