Advancing age, early menarche, late menopause, obesity, PCOS, nulliparity, involuntary infertility, older age at first birth (>35 y)
˜10% of cases are “familial”; may present earlier than sporadic cases
Conversely, a 30-60% ↓ risk of CA associated w/younger age at pregnancy & first birth (≤25 y), OCPs, and/or breast-feeding
Clear cell & endometrioid histologies assoc w/endometriosis (ARID1A)
Epithelial (EOC) (95%): Serous (most common ˜75%, majority WT1+ &/or PAX 8+), mucinous, endometrioid, clear cell, transitional cell
Germ cell (<3%, often <30 y): Dysgerminoma (like seminoma in ♂), endodermal sinus tumors, embryonal CA (like NSGCT in ♂), teratoma. Surgery + (except stage I immature teratoma/dysgerminoma) BEP × 3-4
Asx ♀ at avg risk should NOT undergo ovarian CA screening
PLCO trial: Screening w/annual transvaginal U/S (TVUS) × 4 y & CA 125 × 6 y did not ↓ ovarian CA mortality (JAMA 2011;305:2295-2303)
In high-risk ♀ (hereditary syndrome, BRCA1/2+) can consider multimodality screening (TVUS & CA125 q6mos starting at age 30-35 or 5-10 y earlier than earliest age of 1st ovarian CA in family), but rrBSO is most effective way to ↓ risk of ovarian/fallopian tube CA. rrBSO is recommended as soon as childbearing is complete or by age 35-40. In premenopausal BRCA+ ♀ can also ↓ breast CA risk
Laparotomy w/TAH/BSO w/comprehensive staging (inspection of all peritoneal surfaces, bx of suspicious areas/adhesions, omentectomy, pelvic & para-aortic LND & effort to achieve maximal cytoreduction) is the 1° procedure to establish dx, accurate disease extent & for maximal tumor cytoreduction
Mucinous tumors: + appendectomy & explore upper & lower GI tract
Optimal debulking → residual tumor <1 cm max diameter or thickness
Ideally performed by gyn oncologist & w/“no gross residual disease”
↑ CA125 in 20% early-stage & 80% of advanced-stage EOC
| ||||||||||||||||||
6-8 cycles of taxane/platinum chemo.
Stage II & stage III optimally debulked (<1 cm): IV/IP paclitaxel & IP CIS. In stage III optimally debulked pts, median PFS ↑6 mos (23.8 vs. 18), median OS ↑ 16 mos (65.6 vs. 49.7) compared w/q3wk IV Rx. ↑tox w/IP: Fatigue, pain, neuropathy, renal, IP port complications. Only ˜40% pts completed all 6 IV/IP cycles (GOG 172 NEJM 1996;354:34-43). ↑ benefit w/↑no. of IP cycles. No ↑ OS w/+ 3rd chemo drug (J Clin Oncol 2006;24:18s ASCO#5002). BEV ↑ PFS 1.7-4 mos (NEJM 2011;365:2473-2483; NEJM 2011;365:2484-2496)
Residual disease >1 cm, stage IV, not IP candidate: Dose-dense IV T/C (wkly paclitaxel) may be superior to q3wk IV T/C. In stage II-IV (opt & subop) dose-dense IV T/C vs. q3wk T/C: ↑ PFS 11 mos (28 vs. 17) & ↑ 3-y OS by 7% (72 vs. 65%) (Lancet 2009;374(9698):1331-1338)
Unresectable bulky disease or poor PS: Obtain bsy for dx. Neoadj chemo × 3-6 cycles → interval tumor debulking → adj chemo
Low malignant potential: If invasive implants, consider treating as EOC
Platinum-sensitive (recurs >6 mos): Platinum-based doublet (gem, liposomal dox, paclitaxel) ± 2° cytoreduction. 1st recurrence → + BEV ↑ PFS 4 mos (12.4 vs. 8.4) (OCEANS J Clin Oncol 2012;30(17):2039-2045); Serial relapses & remission w/chemo until platinum-resistance occurs.
Platinum-resistant (<6 mos): Single-agent lipo dox, gem, topo, tax. + BEV ↑ PFS ˜3 mos (6.7 vs. 3.4) (AURELIA J Clin Oncol 2012;30 LBA5002)
Mek inh (Selumetinib) for recurrent low grade serous (Lancet Oncol 2013;14(2):134-140)
| ||||||||
RF for poor survival: Advanced FIGO stage, nondysgerminoma or grade 2/3 immature teratoma, bulky residual disease after surgery, elevation of both HCG & AFP tumor markers preoperatively (J Clin Oncol 2006;24:4862-4866)
Sx: Abdominal pain & palpable pelvic abdominal mass (85%), abdominal distension (35%), fever (10-25%), vaginal bleeding from B-HCG/estrogen production (10%), precocious puberty 2/2 to B-HCG production (rare), NMDA receptor encephalitis (rare), hyperthyroidism (2/2 struma ovarii). Can be bilateral in benign cystic teratoma, dysgerminoma, & tumors w/components of dysgerminoma
Growing teratoma syndrome: Rare complication of immature teratomas 2/2 enlarging teratoma that becomes mature during chemo; needs prompt surgery
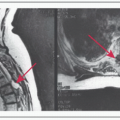
W/u: Serum tumor markers: AFP, LDH, HCG; CXR, pelvic US or CT abd/pelvis. Karyotype if dysgenetic gonads are suspected. Use tumor markers to monitor response to Rx & recurrence. R/O pregnancy if B-HCG ↑
Fertility preservation: Discuss embryo cryopreservation. If not feasible, cryopreservation of oocytes or ovarian tissue an option (experimental)
Stage I: Confined to ovaries (Stage IA: Single ovary; Stage IB: Both ovaries; Stage IC: Ovarian surface involvement or capsule rupture); Stage II: Extension into other pelvic tissues (Stage IIA: Extension/implants on uterus/tubes; Stage IIB: Extension or implants on other pelvic tissues; Stage IIC other Stage II criteria plus + washings); Stage III: Disease spread beyond pelvis or to lymph nodes but remains in abdomen/pelvis (Stage IIIA: Microscopic peritoneal mets beyond pelvis; Stage IIB: Macroscopic mets beyond pelvis (≤2 cm); Stage IIIC: Peritoneal mets beyond pelvis >2 cm or regional lymph node mets); Stage IV: Distant mets or liver parenchyma involvement
1° Surgery: Perform before chemo as pts w/completely resected disease have ↑ oncologic results, although data inconclusive. May be more critical for nondysgerminomas
Adjuvant Chemotherapy: Standard of care w/3-6 cycles of BEP (bleomycin, etoposide, CIS). Ideally give 7-10 d after surgery; give at full dose Rx even w/myelosuppression as ↑ oncologic benefit (N Engl J Med 1987;316:1435-1440; J Clin Oncol 1994;12:701-706)
Debulking Surgery after Chemotherapy: Consider if residual disease present after adjuvant chemotherapy w/negative tumor markers. Can prevent Growing Teratoma Syndrome & dedifferentiation of teratoma into active CA (Gynecol Oncol 1994;55:217-223)
RT: Previously used in dysgerminomas; currently has largely been replaced by platinum-based chemotherapy (J Clin Oncol 1991;9:1950-1955)
90% of pts that will recur, recur in first 2 y after Rx completion; if recurs after 2 y, usu slow growing & chemo resistant
Salvage Chemotherapy: If no prior chemotherapy: BEP; If prior chemotherapy: VIP (etoposide, ifosfamide, CIS), VeIP (Vinblastine, ifosfamide, CIS), TIP (paclitaxel, ifosfamide, CIS). Palliative options: Paclitaxel, GEM ± CIS, epirubicin + CIS
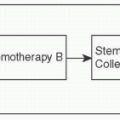
High-Dose Chemotherapy w/Stem Cell Rescue: Consider for persistent, refractory, or platinum-resistant disease (J Clin Oncol 2000;18:1173-1180)
Renal insufficiency, gonadal dysfunction, neurotoxicity, cardiovascular tox 2/2 to CIS, 2° malignancies 2/2 etoposide (solid tumors, leukemias), & pulm fibrosis 2/2 bleomycin. 80% pts preserve menstrual function after fertility sparing surgery/platinum-based chemotherapy (Obstet Gyn 2003;101(2):251)
200000 cases/y worldwide; most common gynecologic malignancy in developed countries; second most common in developing countries. Usu presents at an early stage w/abnl uterine bleeding 2° to unopposed estrogen in peri-/postmenopausal women w/avg age of 61. African-American women p/w more advanced stage disease & higher incidence of aggressive histology.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree