Mortality benefit from screening the general population has not been established
PLCO CA Screening Trial: Screening detected a higher incidence of CA, but no difference in OS after 13 y of follow-up, suggesting overtreatment of indolent CA (J Natl Cancer Inst 2012;104:125)
ERSPC: Screening detected a higher incidence of CA, a lower prostate CA specific mortality rate, no difference in overall mortality after 11 y of follow-up (NEJM 2012;366:981)
Prevent 0-1 D from prostate CA
Diagnose 110 men w/prostate CA
Cause ˜50 serious complications from tx, including ED (29 men), incontinence (18 men), CV events (2 men), VTE (1 man), & death due to the tx (<1 man)
Histology: Gleason Score is sum of the 1° + 2° histologic grade (range of each is grade 1-5, or well- to poorly differentiated), grade 1-2 is rarely if ever classified from a needle bx so effective scale is 3 + 3 to 5 + 5 = 6-10
Gleason Score Interpretation
Gleason X
Cannot be processed
Gleason ≤6
Well differentiated, good risk
Gleason 7
Moderately differentiated, intermediate risk
Gleason 8-10
Poorly differentiated, high risk
Clinical Grade
T1: Not palpable (T1c is diagnosed on PSA screening alone)
T2: W/n the prostate (T2c is involving both lobes)
T3: Extends through the prostatic capsule (T3b invades seminal vesicle)
T4: Invades adjacent structure other then seminal vesicle, ie, bladder, levator muscles, pelvic wall
5y Prostate Ca specific (relative to aged matched controls) Survival Rates at Time of Dx:
Local (stage I-II) nearly 100%
Regional (stage III, T4, N1) nearly 100%
Distant (M1) 29%
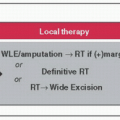
Prognosis for localized disease varies based on risk stratification w/validated nomograms to aid decision making
|
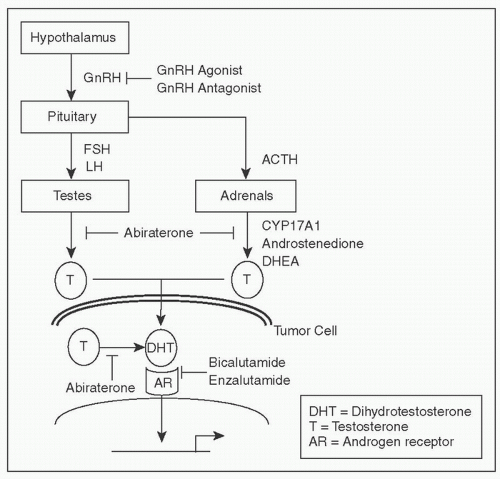
Dfn: Prostate Ca that responds to lowering testosterone to castrate levels (conventionally defined as <50 ng/dl)
Dfn Progressive disease despite castrate levels of testosterone
2nd hormone Rx: Anti-androgens as above, anti-androgen withdrawal, abiraterone, ketoconazole
Docetaxel Taxane (NEJM 2004;351:1502; JCO 2008;26:242)
Sipuleucel-T DC leukapheresed & exposed to prostatic acid phosphatase Ag fused to GM-CSF ex vivo, & re-introduced; OS benefit but no change in PSA or tumor burden, appropriate only if asx, ECOG 0-1, no visceral mets, not on: Steroids, RT, chemo, or immunotx, & life expectancy >6 mos (NEJM 2010;363:411)
Cabazitaxel Taxane derivative, only used post docetaxel (Lancet 2010;376:1147)
Abiraterone Acetate Inhibits cytochrome P450 c17 (lyase, hydroxylase) reduces testosterone/dihydrotestosterone from adrenal, testis, & tumor sources, approved for pts both pre & post docetaxel (NEJM 2010;364:1995; NEJM 2013; 368:138)
Enzalutamide Inhibits nuclear translocation, DNA binding, & coactivator recruitment of/by androgen receptor, post docetaxel (NEJM 2012;367:1187)
Notes: Above are the only 5 systemic agents that have shown increased OS in this setting.
Mitoxantrone for Pts who are not candidates for docetaxel
Castration-resistant mets before docetaxel
Further options include:
Abiraterone
Sipuleucel-T (if meets requirements above)
Docetaxel
Palliative RT
Bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals
Further options include:
Abiraterone
Enzalutamide
Cabazitaxel
Docetaxel rechallenge if previously sensitive
Mitoxantrone
Sipuleucel-T (if meets requirements above)
Special Consideration for Bone Mets
In addition to above:
Denosumab or Zoledronic acid to lower risk of SREs in castration-resistant disease
If symptomatic: Palliative RT or radionuclide (β emitters)
Most common malignancy of the urinary system, ˜74000 Pts will be diagnosed in the US in 2012, ˜15000 will die of their disease.
| ||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree