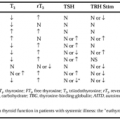
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY
Sympathetic preganglionic axons originate from cell bodies in the intermediolateral cell columns of the thoracolumbar spinal cord2 (Fig. 85-1). A central neural site projecting to the intermediolateral cell columns has been identified in the rostral ventrolateral medulla,3 and catecholaminergic neurons in this region appear to participate in regulation of blood pressure by more rostral structures and by baroreflexes; however, whether the rostral ventrolateral medulla cells that project to the sympathetic preganglionic neurons actually use catecholamines as the responsible transmitters now seems unlikely. After exiting the spinal cord, the preganglionic sympathetic axons synapse in the paravertebral chain of sympathetic ganglia and preaortic ganglia. Preganglionic fibers also pass through lower thoracic and lumbar ganglia to form the splanchnic neural innervation of the adrenal medulla. Adrenal nerve activity, therefore, at least partly reflects preganglionic outflow, whereas renal nerve sympathetic activity reflects postganglionic outflow. At the ganglionic synapse and at adrenomedullary cells, the neurotransmitter is ACh.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree